Influence of Diet on the Bioaccessibility of Zn from Dietary Supplements: Findings from an In Vitro Digestion Model and Analytical Determinations
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu18010094, Dec 2025
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000031 from 44 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
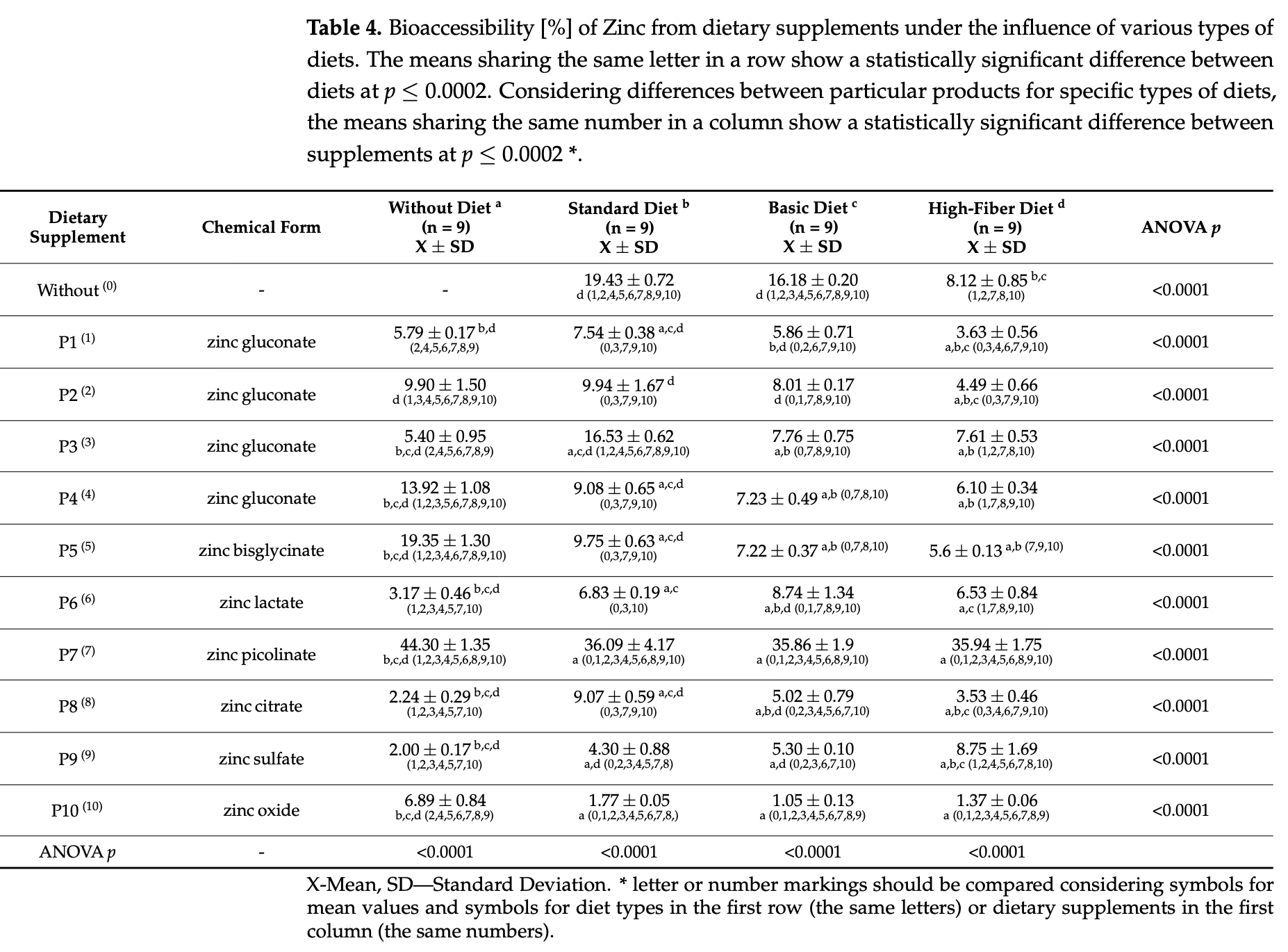
In vitro study showing that zinc supplementation bioaccessibility varies significantly based on diet type and zinc chemical form using simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Authors found that zinc picolinate demonstrated the highest bioaccessibility (35.86-44.30%) across all dietary conditions, while zinc oxide showed the lowest (1.05-6.89%). High-fiber diets significantly reduced zinc bioaccessibility from 19.43% (standard diet) to 8.12%, likely due to phytate interference. Among zinc forms tested, picolinate showed superior absorption and minimal interaction with dietary components compared to gluconate, bisglycinate, citrate, lactate, sulfate, and oxide forms.
12 preclinical studies support the efficacy of zinc for COVID-19:
1.
Agamah et al., Network-based multi-omics-disease-drug associations reveal drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19 disease phases, ScienceOpen, doi:10.58647/DRUGARXIV.PR000010.v1.
2.
Lockwood, T., Coordination chemistry suggests that independently observed benefits of metformin and Zn2+ against COVID-19 are not independent, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00590-5.
3.
El-Megharbel et al., Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of (Artemisinin/Quercetin/ Zinc) novel mixed ligand complex with assessment of its potent high antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and antioxidant capacity against toxicity induced by acrylamide in male rats, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.15638.
4.
Bess et al., Identification of oral therapeutics using an AI platform against the virus responsible for COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1297924.
5.
Pormohammad et al., Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790.
6.
Pelucelli et al., Zn2+ and Cu2+ Interaction with the Recognition Interface of ACE2 for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms24119202.
7.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
8.
Panchariya et al., Zinc2+ ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro, Chemical Communications, doi:10.1039/D1CC03563K.
Tokarczyk et al., 27 Dec 2025, Poland, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Contact: kochw@interia.pl (corresponding author), joanna.tokarczyk@umlub.edu.pl, agnieszka.jaworowska@umlub.edu.pl, kowalczykdawid@outlook.com, monika.kasprzak@umlub.edu.pl, paweljan.jagielski@uj.edu.pl.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Influence of Diet on the Bioaccessibility of Zn from Dietary Supplements: Findings from an In Vitro Digestion Model and Analytical Determinations
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu18010094
Background: Zn is an essential mineral nutrient for human health. Its deficiency may result not only from insufficient intake but also from impaired absorption. Dietary components released from the food matrix during digestion can interact in ways that either enhance or inhibit mineral bioavailability. Objectives: The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the bioaccessibility of Zn from dietary supplements, particularly in the context of diet type, chemical form, and pharmaceutical formulation effects. Methods: The experiment was conducted using an in vitro gastrointestinal digestion model with cellulose dialysis membranes. Zn content after digestion was determined using flame atomic absorption spectrometry (F-AAS). The method employed had been previously developed and validated for use in determining the bioaccessibility of mineral nutrients. Results: The bioaccessibility of Zn from the standard, basic, and high-fiber diets was 19.43, 16.18, and 8.12%, respectively. In the presence of a standard diet, the bioaccessibility of Zn from dietary supplements was within the range 1.77-36.09%, in the presence of a basic diet, 1.05-35.86%; and in the presence of a high-fiber diet, 1.37-35.94%. The highest values were observed for zinc picolinate, whereas the lowest were determined for zinc oxide. Conclusions: A high-fiber diet significantly reduced Zn bioaccessibility. Bioaccessibility is also strongly dependent on the chemical form of zinc.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, W.K., J.T. and A.J.; methodology, W.K., J.T., A.J. and M.K.; software, W.K., J.T. and A.J.; validation, W.K. and J.T.; formal analysis, W.K. and J.T.; investigation, W.K., J.T., A.J., D.K. and M.K.; resources, W.K. and J.T.; data curation, W.K., J.T., D.K. and P.J.; writingoriginal draft preparation, W.K. and J.T.; writing-review and editing, W.K. and J.T.; visualization, J.T.; supervision, W.K.; project administration, W.K.; funding acquisition, W.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Ahmad, Shaju, Atfi, Razzaque, Zinc and Diabetes: A Connection between Micronutrient and Metabolism, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells13161359
Alnaimat, Barciela-Alonso, Herbello-Hermelo, Domínguez-González, Bermejo-Barrera, In Vitro Assessment of Major and Trace Element Bioaccessibility in Tea Samples, Talanta, doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122083
Avramescu, Rasmussen, Chénier, Gardner, Influence of pH, Particle Size and Crystal Form on Dissolution Behaviour of Engineered Nanomaterials, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res, doi:10.1007/s11356-016-7932-2
Barrie, Wright, Pizzorno, Kutter, Barron, Comparative Absorption of Zinc Picolinate, Zinc Citrate and Zinc Gluconate in Humans, Agents Actions, doi:10.1007/BF01974946
Bawiec, Jaworowska, Sawicki, Czop, Szalak et al., In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Mg from Daily Food Rations, Dietary Supplements and Medicinal Products from the Polish Market, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17050748
Bawiec, Sawicki, Łasi Ńska-Pracuta, Czop, Sowa et al., In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Cr from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements from the Polish Market, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16071022
Bawiec, Sawicki, Łasi Ńska-Pracuta, Czop, Sowa et al., In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Se from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15061511
Benarroch, What Are the Functions of Zinc in the Nervous System?, Neurology, doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000207912
Bertinato, Griffin, Huliganga, Matias, Dam et al., Calcium Exacerbates the Inhibitory Effects of Phytic Acid on Zinc Bioavailability in Rats, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126643
Beyersmann, Haase, Functions of Zinc in Signaling, Proliferation and Differentiation of Mammalian Cells, Biometals, doi:10.1023/A:1012905406548
Brnić, Wegmüller, Zeder, Senti, Hurrell, Influence of Phytase, EDTA, and Polyphenols on Zinc Absorption in Adults from Porridges Fortified with Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.113.185322
Brodkorb, Egger, Alminger, Alvito, Assunção et al., INFOGEST Static In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion, Nat. Protoc, doi:10.1038/s41596-018-0119-1
Carbonell-Capella, Buniowska, Barba, Esteve, Frígola, Analytical Methods for Determining Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Fruits and Vegetables: A Review, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf, doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12049
Cardoso, Narcy, Durosoy, Bordes, Chevalier, Dissolution Kinetics of Zinc Oxide and Its Relationship with Physicochemical Characteristics, Powder Technol, doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.049
Chasapis, Loutsidou, Spiliopoulou, Stefanidou, Zinc and Human Health: An Update, Arch. Toxicol, doi:10.1007/s00204-011-0775-1
Chen, Jiang, Wang, Chen, Tang et al., Alteration in Gut Microbiota Associated with Zinc Deficiency in School-Age Children, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14142895
Chen, Wang, Zhou, Wang, Gao et al., Association of Seminal Plasma Zinc Levels with Human Semen Quality and Its Toxic Effects on Sperm Motility, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf, doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116889
Christensen, Krüger, Hjorth, Buhl, Sørensen, Milk Osteopontin Mediates Zinc Uptake in Intestinal Cells in the Presence of Phytic Acid, Int. Dairy J, doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2024.106113
Ciborowska, Ciborowski, Dietetyka, Żywienie Zdrowego i Chorego Człowieka
Costa, Sarmento-Ribeiro, Gonçalves, Zinc, From Biological Functions to Therapeutic Potential, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24054822
Da Paixão Teixeira, Baptista, Orlando, Gigante, Pallone, Effect of Processing on the Bioaccessibility of Essential Minerals in Goat and Cow Milk and Dairy Products Assessed by Different Static In Vitro Digestion Models, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131739
De Castro Cardoso Pereira, Vicente, Meat Nutritional Composition and Nutritive Role in the Human Diet, Meat Sci, doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.09.018
De Romaña, Lönnerdal, Brown, Absorption of Zinc from Wheat Products Fortified with Iron and Either Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/78.2.279
Del Rio, Valenzano, Diguilio, Rybakovsky, Kjelstrom et al., Orally Administered Zinc Gluconate Induces Tight Junctional Remodeling and Reduces Passive Transmucosal Permeability Across Human Intestine in a Patient-Based Study, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms26178540
Devarshi, Mao, Grant, Hazels Mitmesser, Comparative Absorption and Bioavailability of Various Chemical Forms of Zinc in Humans: A Narrative Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16244269
Dima, Assadpour, Dima, Jafari, Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Food Bioactive Compounds; Overview and Assessment by In Vitro Methods, Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf, doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12623
Disilvestro, Koch, Rakes, Moderately High Dose Zinc Gluconate or Zinc Glycinate: Effects on Plasma Zinc and Erythrocyte Superoxide Dismutase Activities in Young Adult Women, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0334-3
Disilvestro, Swan, Comparison of Four Commercially Available Zinc Supplements for Performance in a Zinc Tolerance Test, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fasebj.22.1_supplement.693.3
Dong, Li, Min, Preparation, Characterization and Bioactivities of Athelia rolfsii Exopolysaccharide-Zinc Complex (AEPS-Zinc), Int. J. Biol. Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.223
Dong, Zhang, Ma, Chang, Zheng et al., Pumpkin Skin Polysaccharide-Zn(II) Complex: Preparation, Characterization, and Suppression of Inflammation in Zebrafish, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11172610
Fairweather-Tait, Sesmaisons, De, Approaches Used to Estimate Bioavailability When Deriving Dietary Reference Values for Iron and Zinc in Adults, Proc. Nutr. Soc, doi:10.1017/S0029665118000484
Forbes, Parker, Erdman, Effects of Dietary Phytate, Calcium and Magnesium Levels on Zinc Bioavailability to Rats, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/114.8.1421
Foster, Karra, Picone, Chu, Hancock et al., Dietary Fiber Intake Increases the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Healthy and Diabetic Women, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-012-9408-7
Fredlund, Isaksson, Rossander-Hulthén, Almgren, Sandberg, Absorption of Zinc and Retention of Calcium: Dose-Dependent Inhibition by Phytate, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.01.003
Gandia, Bour, Maurette, Donazzolo, Duchène et al., A Bioavailability Study Comparing Two Oral Formulations Containing Zinc (Zn Bis-Glycinate vs. Zn Gluconate) After a Single Administration to Twelve Healthy Female Volunteers, Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res, doi:10.1024/0300-9831.77.4.243
Gertig, Przysławski, Bromatologia-Zarys Nauki o Żywności i Żywieniu
Gomez, Perez-Corona, Madrid, Availability of Zinc from Infant Formula by In Vitro Methods (Solubility and Dialyzability) and Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry, J. Dairy Sci, doi:10.3168/jds.2016-11405
Grases, Costa-Bauza, Key Aspects of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate (Phytate) and Pathological Calcifications, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules24244434
Grases, Simonet, Perelló, Costa-Bauzá, Prieto, Effect of Phytate on Element Bioavailability in the Second Generation of Rats, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/S0946-672X(04)80023-3
Guillem, Alegría, Barberá, Farré, Lagarda et al., In Vitro Dialyzability of Zinc from Different Salts Used in the Supplementation of Infant Formulas, Biol. Trace Element Res, doi:10.1385/BTER:75:1-3:11
Hall, King, The Molecular Basis for Zinc Bioavailability, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24076561
Hambidge, Miller, Westcott, Sheng, Krebs, Zinc Bioavailability and Homeostasis1234, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2010.28674I
Herman, Griffin, Suwarti, Ernawati, Permaesih et al., Cofortification of Iron-Fortified Flour with Zinc Sulfate, but Not Zinc Oxide, Decreases Iron Absorption in Indonesian Children, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/76.4.813
Hotz, Dehaene, Woodhouse, Villalpando, Rivera et al., Zinc Absorption from Zinc Oxide, Zinc Sulfate, Zinc Oxide + EDTA, or Sodium-Zinc EDTA Does Not Differ When Added as Fortificants to Maize Tortillas, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/135.5.1102
Hotz, Evidence for the Usefulness of in Vitro Dialyzability, Caco-2 Cell Models, Animal Models, and Algorithms to Predict Zinc Bioavailability in Humans, Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res, doi:10.1024/0300-9831.75.6.423
Hunt, Beiseigel, Dietary Calcium Does Not Exacerbate Phytate Inhibition of Zinc Absorption by Women from Conventional Diets23, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.2008.27175
Hunt, Matthys, Johnson, Zinc, Absorption, Mineral Balance, and Blood Lipids in Women Consuming Controlled Lactoovovegetarian and Omnivorous Diets for 8 Wk, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/67.3.421
Johnson, Vishwanathan, Rasmussen, Lang, Bioavailability of AREDS1 Micronutrients from Softgel Capsules and Tablets: A Pilot Study, Mol. Vis
Johnston, Dettmar, Bishwokarma, Lively, Koufman, Activity/Stability of Human Pepsin: Implications for Reflux Attributed Laryngeal Disease, Laryngoscope, doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e31804154c3
Kiewlicz, Rybicka, Minerals and Their Bioavailability in Relation to Dietary Fiber, Phytates and Tannins from Gluten and Gluten-Free Flakes, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125452
Kim, Pai, Han, Bioactive Dietary Polyphenols on Zinc Transport across the Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Monolayers, J. Agric. Food Chem
King, Shames, Lowe, Woodhouse, Sutherland et al., Effect of Acute Zinc Depletion on Zinc Homeostasis and Plasma Zinc Kinetics in Men, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/74.1.116
Koch, Czop, Iłowiecka, Nawrocka, Wi Ącek, Dietary Intake of Toxic Heavy Metals with Major Groups of Food Products-Results of Analytical Determinations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14081626
Koch, Czop, Nawrocka, Wi Ącek, Contribution of Major Groups of Food Products to the Daily Intake of Selected Elements-Results from Analytical Determinations Supported by Chemometric Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113412
Kot, Zaręba, Wyszogrodzka-Koma, Ocena Zawartości Miedzi i Cynku w Wybranych Produktach Zbo żowych, Bromat. Chem. Toksykol
Kruger, Taylor, Du, De Moura, Lönnerdal et al., Effect of Phytate Reduction of Sorghum, through Genetic Modification, on Iron and Zinc Availability as Assessed by an in Vitro Dialysability Bioaccessibility Assay, Caco-2 Cell Uptake Assay, and Suckling Rat Pup Absorption Model, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.105
Kunachowicz, Przygodna, Nadolna, Iwanow, Tabele Składu i Wartości Odżywczej Żywności
Latunde-Dada, Kajarabille, Rose, Arafsha, Kose et al., Content and Availability of Minerals in Plant-Based Burgers Compared with a Meat Burger, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122732
Li, Lau, Yu, Microbiota-Mediated Phytate Metabolism Activates HDAC3 to Contribute Intestinal Homeostasis, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00321-5
Livingstone, Zinc, Physiology, Deficiency, and Parenteral Nutrition, Nutr. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1177/0884533615570376
Lo, Settle, Steinke, Hopkins, Effect of Phytate:Zinc Molar Ratio and Isolated Soybean Protein on Zinc Bioavailability, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/111.12.2223
Maares, Haase, A Guide to Human Zinc Absorption: General Overview and Recent Advances of In Vitro Intestinal Models, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12030762
Maret, Zinc in Cellular Regulation: The Nature and Significance of "Zinc Signals, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms18112285
Marze, Bioavailability of Nutrients and Micronutrients: Advances in Modeling and In Vitro Approaches, Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol, doi:10.1146/annurev-food-030216-030055
Mathers, Dietary Fibre and Health: The Story so Far, Proc. Nutr. Soc
Mayer Labba, Steinhausen, Almius, Bach Knudsen, Sandberg, Nutritional Composition and Estimated Iron and Zinc Bioavailability of Meat Substitutes Available on the Swedish Market, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14193903
Menezes, Oliveira, França, Souza, Nogueira, Bioaccessibility of Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Zn, and Crude Protein in Beef, Pork and Chicken after Thermal Processing, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.090
Miller, Krebs, Hambidge, Mathematical Model of Zinc Absorption: Effects of Dietary Calcium, Protein and Iron on Zinc Absorption, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S000711451200195X
Miller, Schricker, Rasmussen, Van Campen, An In Vitro Method for Estimation of Iron Availability from Meals, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/34.10.2248
Minekus, Alminger, Alvito, Ballance, Bohn et al., A Standardised Static In Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food-An International Consensus, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/C3FO60702J
Moreda-Piñeiro, Herbello-Hermelo, Domínguez-González, Bermejo-Barrera, Moreda-Piñeiro, Bioavailability Assessment of Essential and Toxic Metals in Edible Nuts and Seeds, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.006
Moreda-Piñeiro, Moreda-Piñeiro, Bermejo-Barrera, In Vivo and In Vitro Testing for Selenium and Selenium Compounds Bioavailability Assessment in Foodstuff, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2014.934437
Moskwa, Naliwajko, Puścion-Jakubik, Soroczy Ńska, Socha et al., In Vitro Assessment of the Bioaccessibility of Zn, Ca, Mg, and Se from Various Types of Nuts, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods12244453
Nadolna, Kunachowicz, Iwanow, Dishes, Composition and Nutritional Value
Narayan, Sharma, Yadav, Biji, Khatun et al., Picolinic Acid Is a Inhibitor of Enveloped Virus Entry That Restricts SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza a Virus In Vivo, Cell Rep. Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101127
Ollig, Kloubert, Weßels, Haase, Rink, Parameters Influencing Zinc in Experimental Systems In Vivo and In Vitro, Metals, doi:10.3390/met6030071
Ośko, Pierlejewska, Grembecka, Comparison of the Potential Relative Bioaccessibility of Zinc Supplements-In Vitro Studies, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122813
Puścion-Jakubik, Bielecka, Grabia, Mielech, Markiewicz-Żukowska et al., Consumption of Food Supplements during the Three COVID-19 Waves in Poland-Focus on Zinc and Vitamin, D. Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13103361
Ran, Hu, He, Li, Li et al., Phytic Acid Improves Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice by Modulating the Gut-Liver Axis, J. Agric. Food Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04406
Rosado, Díaz, Muñoz, Westcott, González et al., Bioavailability of Zinc Oxide Added to Corn Tortilla Is Similar to That of Zinc Sulfate and Is Not Affected by Simultaneous Addition of Iron, Food Nutr. Bull, doi:10.1177/156482651203300406
Sajkowska, Moskwa, Socha, Leśniewska, Evaluation of the Bioaccessibility of Essential and Toxic Trace Elements in Basil, Peppermint, and Rosemary Using an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model, J. Agric. Food Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10940
Sanna, Firinu, Zavattari, Valera, Zinc Status and Autoimmunity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10010068
Sapota, Daragó, Skrzypi Ńska-Gawrysiak, Nasiadek, Klimczak et al., The Bioavailability of Different Zinc Compounds Used as Human Dietary Supplements in Rat Prostate: A Comparative Study, Biometals, doi:10.1007/s10534-014-9724-9
Sauer, Pfaender, Hagmeyer, Tarana, Mattes et al., Characterization of Zinc Amino Acid Complexes for Zinc Delivery In Vitro Using Caco-2 Cells and Enterocytes from hiPSC, BioMetals, doi:10.1007/s10534-017-0033-y
Schlegel, Windisch, Bioavailability of Zinc Glycinate in Comparison with Zinc Sulphate in the Presence of Dietary Phytate in an Animal Model with Zn Labelled Rats, J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr, doi:10.1111/j.1439-0396.2005.00583.x
Schoofs, Schmit, Rink, Zinc Toxicity: Understanding the Limits, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules29133130
Shkembi, Huppertz, Influence of Dairy Products on Bioavailability of Zinc from Other Food Products: A Review of Complementarity at a Meal Level, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13124253
Sreenivasulu, Raghu, Nair, Polyphenol-Rich Beverages Enhance Zinc Uptake and Metallothionein Expression in Caco-2 Cells, J. Food Sci, doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01582.x
Suliburska, Krejpcio, Evaluation of the Content and Bioaccessibility of Iron, Zinc, Calcium and Magnesium from Groats, Rice, Leguminous Grains and Nuts, J. Food Sci. Technol, doi:10.1007/s13197-011-0535-5
Tokarczyk, Koch, Dietary Zn-Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules30132742
Vucenik, Anticancer Properties of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol: An Overview, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol, doi:10.3177/jnsv.65.S18
Wang, Fang, Chen, Zinc and Central Nervous System Disorders, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092140
Wegmüller, Tay, Zeder, Brnić, Hurrell, Zinc Absorption by Young Adults from Supplemental Zinc Citrate Is Comparable with That from Zinc Gluconate and Higher than from Zinc Oxide, J. Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.113.181487
Wolfe, Gibson, Gadowsky, O'connor, Zinc Status of a Group of Pregnant Adolescents at 36 Weeks Gestation Living in Southern Ontario, J. Am. Coll. Nutr, doi:10.1080/07315724.1994.10718389
Yin, Cai, Chen, Du, Xu et al., Investigation of Bioaccessibility of Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn in Market Vegetables in the Colon Using PBET Combined with SHIME, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-17901-1
Youn, Choi, Food Additive Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Dissolution, Interaction, Fate, Cytotoxicity, and Oral Toxicity, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23116074
Zagórska, Pietrzak, Kukula-Koch, Czop, Laszuk et al., Influence of Diet on the Bioavailability of Active Components from Zingiber Officinale Using an In Vitro Digestion Model, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods12213897
Zhang, Li, Xu, Zang, Li et al., Effects of Dietary Supplements on the Bioaccessibility of Se, Zn and Cd in Rice: Preliminary Observations from In Vitro Gastrointestinal Simulation Tests, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17144978
Zhang, Ye, Pentapeptide-Zinc Chelate from Sweet Almond Expeller Amandin Hydrolysates: Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics, Stability and Zinc Transport Ability In Vitro, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27227936
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu18010094",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu18010094",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Zn is an essential mineral nutrient for human health. Its deficiency may result not only from insufficient intake but also from impaired absorption. Dietary components released from the food matrix during digestion can interact in ways that either enhance or inhibit mineral bioavailability. Objectives: The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the bioaccessibility of Zn from dietary supplements, particularly in the context of diet type, chemical form, and pharmaceutical formulation effects. Methods: The experiment was conducted using an in vitro gastrointestinal digestion model with cellulose dialysis membranes. Zn content after digestion was determined using flame atomic absorption spectrometry (F-AAS). The method employed had been previously developed and validated for use in determining the bioaccessibility of mineral nutrients. Results: The bioaccessibility of Zn from the standard, basic, and high-fiber diets was 19.43, 16.18, and 8.12%, respectively. In the presence of a standard diet, the bioaccessibility of Zn from dietary supplements was within the range 1.77–36.09%, in the presence of a basic diet, 1.05–35.86%; and in the presence of a high-fiber diet, 1.37–35.94%. The highest values were observed for zinc picolinate, whereas the lowest were determined for zinc oxide. Conclusions: A high-fiber diet significantly reduced Zn bioaccessibility. Bioaccessibility is also strongly dependent on the chemical form of zinc.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu18010094"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0002-3330-1224",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Medical University of Lublin, 4a Chodźki Str., 20-093 Lublin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tokarczyk",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0009-3247-1011",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Medical University of Lublin, 4a Chodźki Str., 20-093 Lublin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jaworowska",
"given": "Agnieszka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Medical University of Lublin, 4a Chodźki Str., 20-093 Lublin, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Kowalczyk",
"given": "Dawid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6022-5880",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Medical University of Lublin, 4a Chodźki Str., 20-093 Lublin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kasprzak",
"given": "Monika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7583-8965",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nutrition and Drug Research, Institute of Public Health, Faculty of Health Sciences, Jagiellonian University Medical College, 31-066 Kraków, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jagielski",
"given": "Paweł",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8749-9657",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food and Nutrition, Medical University of Lublin, 4a Chodźki Str., 20-093 Lublin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Koch",
"given": "Wojciech",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-29T08:47:27Z",
"timestamp": 1766998047000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-30T05:15:50Z",
"timestamp": 1767071750000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-30T05:20:47Z",
"timestamp": 1767072047530,
"version": "3.48.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1766793600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/18/1/94/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "94",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10010068",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Sanna, A., Firinu, D., Zavattari, P., and Valera, P. (2018). Zinc Status and Autoimmunity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24054822",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "Costa, M.I., Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B., and Gonçalves, A.C. (2023). Zinc: From Biological Functions to Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18112285",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_3",
"unstructured": "Maret, W. (2017). Zinc in Cellular Regulation: The Nature and Significance of “Zinc Signals”. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00204-011-0775-1",
"article-title": "Zinc and Human Health: An Update",
"author": "Chasapis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "521",
"journal-title": "Arch. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1012905406548",
"article-title": "Functions of Zinc in Signaling, Proliferation and Differentiation of Mammalian Cells",
"author": "Beyersmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "331",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells13161359",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Ahmad, R., Shaju, R., Atfi, A., and Razzaque, M.S. (2024). Zinc and Diabetes: A Connection between Micronutrient and Metabolism. Cells, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116889",
"article-title": "Association of Seminal Plasma Zinc Levels with Human Semen Quality and Its Toxic Effects on Sperm Motility",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116889",
"journal-title": "Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0000000000207912",
"article-title": "What Are the Functions of Zinc in the Nervous System?",
"author": "Benarroch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "714",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15092140",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Wang, B., Fang, T., and Chen, H. (2023). Zinc and Central Nervous System Disorders. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Kunachowicz, H., Przygodna, B., Nadolna, I., and Iwanow, K. (2017). Tabele Składu i Wartości Odżywczej Żywności, PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie. [2nd ed.]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.09.018",
"article-title": "Meat Nutritional Composition and Nutritive Role in the Human Diet",
"author": "Vicente",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "586",
"journal-title": "Meat Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131739",
"article-title": "Effect of Processing on the Bioaccessibility of Essential Minerals in Goat and Cow Milk and Dairy Products Assessed by Different Static In Vitro Digestion Models",
"author": "Baptista",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "131739",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13197-011-0535-5",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the Content and Bioaccessibility of Iron, Zinc, Calcium and Magnesium from Groats, Rice, Leguminous Grains and Nuts",
"author": "Suliburska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "589",
"journal-title": "J. Food Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Ocena Zawartości Miedzi i Cynku w Wybranych Produktach Zbożowych",
"author": "Kot",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Bromat. Chem. Toksykol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules30132742",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Tokarczyk, J., and Koch, W. (2025). Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Molecules, 30."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16071022",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Bawiec, P., Sawicki, J., Łasińska-Pracuta, P., Czop, M., Sowa, I., Helon, P., Pietrzak, K., and Koch, W. (2024). In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Cr from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements from the Polish Market. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0946-672X(04)80023-3",
"article-title": "Effect of Phytate on Element Bioavailability in the Second Generation of Rats",
"author": "Grases",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules24244434",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Grases, F., and Costa-Bauza, A. (2019). Key Aspects of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate (Phytate) and Pathological Calcifications. Molecules, 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665123002215",
"article-title": "Dietary Fibre and Health: The Story so Far",
"author": "Mathers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3177/jnsv.65.S18",
"article-title": "Anticancer Properties of Inositol Hexaphosphate and Inositol: An Overview",
"author": "Vucenik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S18",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125452",
"article-title": "Minerals and Their Bioavailability in Relation to Dietary Fiber, Phytates and Tannins from Gluten and Gluten-Free Flakes",
"author": "Kiewlicz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125452",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "305",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122083",
"article-title": "In Vitro Assessment of Major and Trace Element Bioaccessibility in Tea Samples",
"author": "Alnaimat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "122083",
"journal-title": "Talanta",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "225",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2014.934437",
"article-title": "In Vivo and In Vitro Testing for Selenium and Selenium Compounds Bioavailability Assessment in Foodstuff",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665118000484",
"article-title": "de Approaches Used to Estimate Bioavailability When Deriving Dietary Reference Values for Iron and Zinc in Adults",
"author": "Sesmaisons",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24076561",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Hall, A.G., and King, J.C. (2023). The Molecular Basis for Zinc Bioavailability. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1541-4337.12623",
"article-title": "Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Food Bioactive Compounds; Overview and Assessment by In Vitro Methods",
"author": "Dima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2862",
"journal-title": "Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15122813",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Ośko, J., Pierlejewska, W., and Grembecka, M. (2023). Comparison of the Potential Relative Bioaccessibility of Zinc Supplements—In Vitro Studies. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41596-018-0119-1",
"article-title": "INFOGEST Static In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion",
"author": "Brodkorb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "991",
"journal-title": "Nat. Protoc.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1541-4337.12049",
"article-title": "Analytical Methods for Determining Bioavailability and Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Fruits and Vegetables: A Review",
"author": "Buniowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10940",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the Bioaccessibility of Essential and Toxic Trace Elements in Basil, Peppermint, and Rosemary Using an In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Model",
"author": "Sajkowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6189",
"journal-title": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods12244453",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Moskwa, J., Naliwajko, S.K., Puścion-Jakubik, A., Soroczyńska, J., Socha, K., Koch, W., and Markiewicz-Żukowska, R. (2023). In Vitro Assessment of the Bioaccessibility of Zn, Ca, Mg, and Se from Various Types of Nuts. Foods, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.090",
"article-title": "Bioaccessibility of Ca, Cu, Fe, Mg, Zn, and Crude Protein in Beef, Pork and Chicken after Thermal Processing",
"author": "Menezes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "240",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.006",
"article-title": "Bioavailability Assessment of Essential and Toxic Metals in Edible Nuts and Seeds",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "146",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "205",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2016-11405",
"article-title": "Availability of Zinc from Infant Formula by In Vitro Methods (Solubility and Dialyzability) and Size-Exclusion Chromatography Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry",
"author": "Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9405",
"journal-title": "J. Dairy Sci.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15061511",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Bawiec, P., Sawicki, J., Łasińska-Pracuta, P., Czop, M., Sowa, I., Iłowiecka, K., and Koch, W. (2023). In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Se from Daily Food Rations and Dietary Supplements. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu17050748",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Bawiec, P., Jaworowska, A., Sawicki, J., Czop, M., Szalak, R., and Koch, W. (2025). In Vitro Evaluation of Bioavailability of Mg from Daily Food Rations, Dietary Supplements and Medicinal Products from the Polish Market. Nutrients, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831.75.6.423",
"article-title": "Evidence for the Usefulness of in Vitro Dialyzability, Caco-2 Cell Models, Animal Models, and Algorithms to Predict Zinc Bioavailability in Humans",
"author": "Hotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2010.28674I",
"article-title": "Zinc Bioavailability and Homeostasis1234",
"author": "Hambidge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1478S",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13103361",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "Puścion-Jakubik, A., Bielecka, J., Grabia, M., Mielech, A., Markiewicz-Żukowska, R., Mielcarek, K., Moskwa, J., Naliwajko, S.K., Soroczyńska, J., and Gromkowska-Kępka, K.J. (2021). Consumption of Food Supplements during the Three COVID-19 Waves in Poland—Focus on Zinc and Vitamin, D. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.53270/2021.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Ciborowska, H., and Ciborowski, A. (2022). Dietetyka. Żywienie Zdrowego i Chorego Człowieka, PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie. [5th ed.]."
},
{
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Gertig, H., and Przysławski, J. (2015). Bromatologia—Zarys Nauki o Żywności i Żywieniu, PZWL Wydawnictwo Lekarskie. [1st ed.]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113412",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Koch, W., Czop, M., Nawrocka, A., and Wiącek, D. (2020). Contribution of Major Groups of Food Products to the Daily Intake of Selected Elements-Results from Analytical Determinations Supported by Chemometric Analysis. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14081626",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Koch, W., Czop, M., Iłowiecka, K., Nawrocka, A., and Wiącek, D. (2022). Dietary Intake of Toxic Heavy Metals with Major Groups of Food Products—Results of Analytical Determinations. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Nadolna, I., Kunachowicz, H., and Iwanow, K. (1994). Dishes, Composition and Nutritional Value, National Food and Nutrition Institute."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C3FO60702J",
"article-title": "A Standardised Static In Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus",
"author": "Minekus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1113",
"journal-title": "Food Funct.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/34.10.2248",
"article-title": "An In Vitro Method for Estimation of Iron Availability from Meals",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2248",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "34",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods12213897",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Zagórska, J., Pietrzak, K., Kukula-Koch, W., Czop, M., Laszuk, J., and Koch, W. (2023). Influence of Diet on the Bioavailability of Active Components from Zingiber Officinale Using an In Vitro Digestion Model. Foods, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0884533615570376",
"article-title": "Zinc: Physiology, Deficiency, and Parenteral Nutrition",
"author": "Livingstone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "371",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/74.1.116",
"article-title": "Effect of Acute Zinc Depletion on Zinc Homeostasis and Plasma Zinc Kinetics in Men",
"author": "King",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-food-030216-030055",
"article-title": "Bioavailability of Nutrients and Micronutrients: Advances in Modeling and In Vitro Approaches",
"author": "Marze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12030762",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_51",
"unstructured": "Maares, M., and Haase, H. (2020). A Guide to Human Zinc Absorption: General Overview and Recent Advances of In Vitro Intestinal Models. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/met6030071",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Ollig, J., Kloubert, V., Weßels, I., Haase, H., and Rink, L. (2016). Parameters Influencing Zinc in Experimental Systems In Vivo and In Vitro. Metals, 6."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/67.3.421",
"article-title": "Zinc Absorption, Mineral Balance, and Blood Lipids in Women Consuming Controlled Lactoovovegetarian and Omnivorous Diets for 8 Wk",
"author": "Hunt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "421",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "67",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-012-9408-7",
"article-title": "Dietary Fiber Intake Increases the Risk of Zinc Deficiency in Healthy and Diabetic Women",
"author": "Foster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15122732",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Latunde-Dada, G.O., Kajarabille, N., Rose, S., Arafsha, S.M., Kose, T., Aslam, M.F., Hall, W.L., and Sharp, P.A. (2023). Content and Availability of Minerals in Plant-Based Burgers Compared with a Meat Burger. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14193903",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Mayer Labba, I.-C., Steinhausen, H., Almius, L., Bach Knudsen, K.E., and Sandberg, A.-S. (2022). Nutritional Composition and Estimated Iron and Zinc Bioavailability of Meat Substitutes Available on the Swedish Market. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.01.003",
"article-title": "Absorption of Zinc and Retention of Calcium: Dose-Dependent Inhibition by Phytate",
"author": "Fredlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "49",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2004). Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition, World Health Organization. [2nd ed.]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3844",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_59",
"unstructured": "European Food Safety Authority (2014). EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Zinc. EFSA J., 12, 3844."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00321-5",
"article-title": "Microbiota-Mediated Phytate Metabolism Activates HDAC3 to Contribute Intestinal Homeostasis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14142895",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_61",
"unstructured": "Chen, X., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Tang, S., Wang, S., Su, L., Huang, X., Long, D., and Wang, L. (2022). Alteration in Gut Microbiota Associated with Zinc Deficiency in School-Age Children. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04406",
"article-title": "Phytic Acid Improves Hepatic Steatosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Fed Mice by Modulating the Gut–Liver Axis",
"author": "Ran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11401",
"journal-title": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-17901-1",
"article-title": "Investigation of Bioaccessibility of Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn in Market Vegetables in the Colon Using PBET Combined with SHIME",
"author": "Yin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17578",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126643",
"article-title": "Calcium Exacerbates the Inhibitory Effects of Phytic Acid on Zinc Bioavailability in Rats",
"author": "Bertinato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126643",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/114.8.1421",
"article-title": "Effects of Dietary Phytate, Calcium and Magnesium Levels on Zinc Bioavailability to Rats",
"author": "Forbes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1421",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "114",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711451200195X",
"article-title": "Mathematical Model of Zinc Absorption: Effects of Dietary Calcium, Protein and Iron on Zinc Absorption",
"author": "Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "695",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2008.27175",
"article-title": "Dietary Calcium Does Not Exacerbate Phytate Inhibition of Zinc Absorption by Women from Conventional Diets23",
"author": "Hunt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "839",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/111.12.2223",
"article-title": "Effect of Phytate:Zinc Molar Ratio and Isolated Soybean Protein on Zinc Bioavailability",
"author": "Lo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2223",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "111",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01582.x",
"article-title": "Polyphenol-Rich Beverages Enhance Zinc Uptake and Metallothionein Expression in Caco-2 Cells",
"author": "Sreenivasulu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H123",
"journal-title": "J. Food Sci.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.113.185322",
"article-title": "Influence of Phytase, EDTA, and Polyphenols on Zinc Absorption in Adults from Porridges Fortified with Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide",
"author": "Zeder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1467",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf104260j",
"article-title": "Bioactive Dietary Polyphenols on Zinc Transport across the Intestinal Caco-2 Cell Monolayers",
"author": "KIM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3606",
"journal-title": "J. Agric. Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-017-0033-y",
"article-title": "Characterization of Zinc Amino Acid Complexes for Zinc Delivery In Vitro Using Caco-2 Cells and Enterocytes from hiPSC",
"author": "Sauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "643",
"journal-title": "BioMetals",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17144978",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_73",
"unstructured": "Zhang, R., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Zang, Z., Li, H., and Wang, L. (2020). Effects of Dietary Supplements on the Bioaccessibility of Se, Zn and Cd in Rice: Preliminary Observations from In Vitro Gastrointestinal Simulation Tests. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01974946",
"article-title": "Comparative Absorption of Zinc Picolinate, Zinc Citrate and Zinc Gluconate in Humans",
"author": "Barrie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Agents Actions",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fasebj.22.1_supplement.693.3",
"article-title": "Comparison of Four Commercially Available Zinc Supplements for Performance in a Zinc Tolerance Test",
"author": "DiSilvestro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693.3",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101127",
"article-title": "Picolinic Acid Is a Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Enveloped Virus Entry That Restricts SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza a Virus In Vivo",
"author": "Narayan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101127",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules29133130",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "Schoofs, H., Schmit, J., and Rink, L. (2024). Zinc Toxicity: Understanding the Limits. Molecules, 29."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16244269",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_78",
"unstructured": "Devarshi, P.P., Mao, Q., Grant, R.W., and Hazels Mitmesser, S. (2024). Comparative Absorption and Bioavailability of Various Chemical Forms of Zinc in Humans: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23116074",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_79",
"unstructured": "Youn, S.-M., and Choi, S.-J. (2022). Food Additive Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Dissolution, Interaction, Fate, Cytotoxicity, and Oral Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-016-7932-2",
"article-title": "Influence of pH, Particle Size and Crystal Form on Dissolution Behaviour of Engineered Nanomaterials",
"author": "Avramescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1553",
"journal-title": "Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.049",
"article-title": "Dissolution Kinetics of Zinc Oxide and Its Relationship with Physicochemical Characteristics",
"author": "Cardoso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "746",
"journal-title": "Powder Technol.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1385/BTER:75:1-3:11",
"article-title": "In Vitro Dialyzability of Zinc from Different Salts Used in the Supplementation of Infant Formulas",
"author": "Guillem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Element Res.",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.1994.10718389",
"article-title": "Zinc Status of a Group of Pregnant Adolescents at 36 Weeks Gestation Living in Southern Ontario",
"author": "Wolfe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Coll. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/156482651203300406",
"article-title": "Bioavailability of Zinc Oxide Added to Corn Tortilla Is Similar to That of Zinc Sulfate and Is Not Affected by Simultaneous Addition of Iron",
"author": "Rosado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Food Nutr. Bull.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/135.5.1102",
"article-title": "Zinc Absorption from Zinc Oxide, Zinc Sulfate, Zinc Oxide + EDTA, or Sodium-Zinc EDTA Does Not Differ When Added as Fortificants to Maize Tortillas",
"author": "Hotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1102",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/76.4.813",
"article-title": "Cofortification of Iron-Fortified Flour with Zinc Sulfate, but Not Zinc Oxide, Decreases Iron Absorption in Indonesian Children",
"author": "Herman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_86",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/78.2.279",
"article-title": "Absorption of Zinc from Wheat Products Fortified with Iron and Either Zinc Sulfate or Zinc Oxide",
"author": "Brown",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1439-0396.2005.00583.x",
"article-title": "Bioavailability of Zinc Glycinate in Comparison with Zinc Sulphate in the Presence of Dietary Phytate in an Animal Model with Zn Labelled Rats",
"author": "Schlegel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10534-014-9724-9",
"article-title": "The Bioavailability of Different Zinc Compounds Used as Human Dietary Supplements in Rat Prostate: A Comparative Study",
"author": "Sapota",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "495",
"journal-title": "Biometals",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202505.0528.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_90",
"unstructured": "Del Rio, E.A., Valenzano, M.C., DiGuilio, K.M., Rybakovsky, E., Kjelstrom, S., Montone, G., Mercogliano, G., Newman, G., Wong, P., and Albert, N. (2025). Orally Administered Zinc Gluconate Induces Tight Junctional Remodeling and Reduces Passive Transmucosal Permeability Across Human Intestine in a Patient-Based Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 26."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-015-0334-3",
"article-title": "Moderately High Dose Zinc Gluconate or Zinc Glycinate: Effects on Plasma Zinc and Erythrocyte Superoxide Dismutase Activities in Young Adult Women",
"author": "DiSilvestro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831.77.4.243",
"article-title": "A Bioavailability Study Comparing Two Oral Formulations Containing Zinc (Zn Bis-Glycinate vs. Zn Gluconate) After a Single Administration to Twelve Healthy Female Volunteers",
"author": "Gandia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.113.181487",
"article-title": "Zinc Absorption by Young Adults from Supplemental Zinc Citrate Is Comparable with That from Zinc Gluconate and Higher than from Zinc Oxide",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "132",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Bioavailability of AREDS1 Micronutrients from Softgel Capsules and Tablets: A Pilot Study",
"author": "Johnson",
"first-page": "1228",
"journal-title": "Mol. Vis.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13124253",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_95",
"unstructured": "Shkembi, B., and Huppertz, T. (2021). Influence of Dairy Products on Bioavailability of Zinc from Other Food Products: A Review of Complementarity at a Meal Level. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.105",
"article-title": "Effect of Phytate Reduction of Sorghum, through Genetic Modification, on Iron and Zinc Availability as Assessed by an in Vitro Dialysability Bioaccessibility Assay, Caco-2 Cell Uptake Assay, and Suckling Rat Pup Absorption Model",
"author": "Kruger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1019",
"journal-title": "Food Chem.",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MLG.0b013e31804154c3",
"article-title": "Activity/Stability of Human Pepsin: Implications for Reflux Attributed Laryngeal Disease",
"author": "Johnston",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1036",
"journal-title": "Laryngoscope",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27227936",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_98",
"unstructured": "Zhang, J., and Ye, Z. (2022). Pentapeptide-Zinc Chelate from Sweet Almond Expeller Amandin Hydrolysates: Structural and Physicochemical Characteristics, Stability and Zinc Transport Ability In Vitro. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.idairyj.2024.106113",
"article-title": "Milk Osteopontin Mediates Zinc Uptake in Intestinal Cells in the Presence of Phytic Acid",
"author": "Christensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106113",
"journal-title": "Int. Dairy J.",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods11172610",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_100",
"unstructured": "Dong, S., Zhang, B., Ma, Y., Chang, H., Zheng, Z., and Zhao, X. (2022). Pumpkin Skin Polysaccharide–Zn(II) Complex: Preparation, Characterization, and Suppression of Inflammation in Zebrafish. Foods, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.223",
"article-title": "Preparation, Characterization and Bioactivities of Athelia rolfsii Exopolysaccharide-Zinc Complex (AEPS-Zinc)",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Biol. Macromol.",
"key": "ref_101",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 101,
"references-count": 101,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/18/1/94"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Influence of Diet on the Bioaccessibility of Zn from Dietary Supplements: Findings from an In Vitro Digestion Model and Analytical Determinations",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3390/mdpi_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "18"
}
