CytoSorb Rescue for COVID-19 Patients With Vasoplegic Shock and Multiple Organ Failure: A Prospective, Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
et al., Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005493, CytoResc, DRKS00021447, Feb 2022
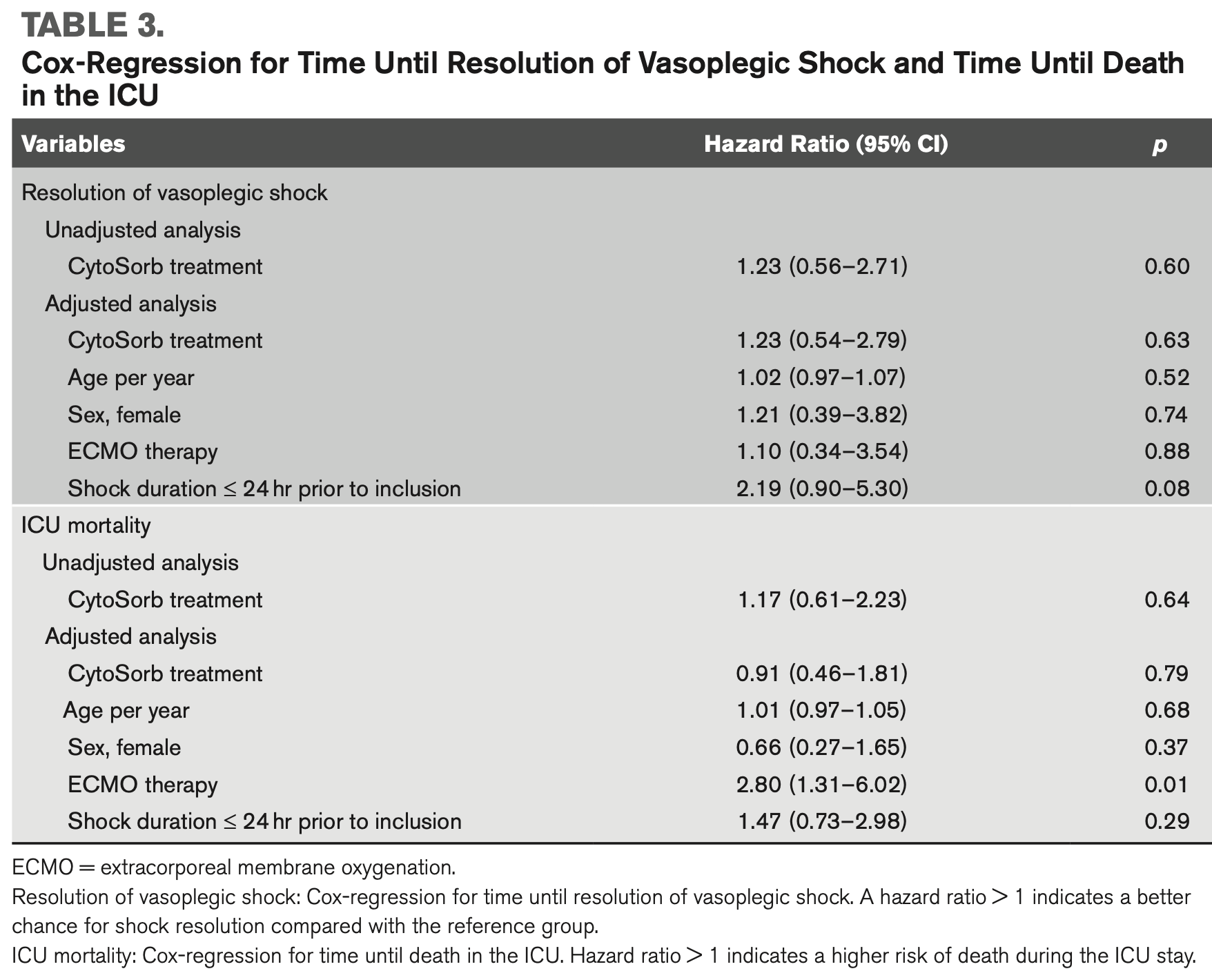
RCT 49 COVID-19 patients with vasoplegic shock and multiple organ failure showing no significant difference in shock resolution or mortality with CytoSorb extracorporeal cytokine adsorption compared to standard care.
|
risk of death, 9.0% lower, HR 0.91, p = 0.79, treatment 23, control 26, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Stockmann et al., 9 Feb 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Germany, peer-reviewed, 17 authors, study period 11 November, 2020 - 15 March, 2021, trial DRKS00021447 (CytoResc).
CytoSorb Rescue for COVID-19 Patients With Vasoplegic Shock and Multiple Organ Failure: A Prospective, Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Pilot Study*
Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1097/ccm.0000000000005493
To investigate the effect of extracorporeal cytokine reduction by CytoSorb (CytoSorbents, Monmouth Junction, NJ) on COVID-19-associated vasoplegic shock.
DESIGN: Prospective, randomized controlled pilot study. SETTING: Eight ICUs at three sites of the tertiary-care university hospital Charité-
References
Alharthy, Faqihi, Memish, Continuous renal replacement therapy with the addition of CytoSorb cartridge in critically ill patients with COVID-19 plus acute kidney injury: A case-series, Artif Organs
Ankawi, Xie, Yang, What have we learned about the use of Cytosorb adsorption columns?, Blood Purif
Arulkumaran, Thomas, Brealey, Plasma exchange for COVID-19 thrombo-inflammatory disease, EJHaem
Aziz, Fatima, Assaly, Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis, J Med Virol
Brouwer, Duran, Kuijper, Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb shows a decreased observed versus expected 28-day all-cause mortality in ICU patients with septic shock: A propensity-score-weighted retrospective study, Crit Care
Dimski, Brandenburger, Mackenzie, Elimination of glycopeptide antibiotics by cytokine hemoadsorption in patients with septic shock: A study of three cases, Int J Artif Organs
Dr, Enghard received honoraria from GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca and filed two patents for novel urinary biomarkers outside the submitted work
Drs, Enghard and Lehner contributed equally
Fajgenbaum, June, Cytokine storm, N Engl J Med
Friesecke, Stecher, Gross, Extracorporeal cytokine elimination as rescue therapy in refractory septic shock: A prospective single-center study, J Artif Organs
Friesecke, Träger, Schittek, International registry on the use of the CytoSorb® adsorber in ICU patients: Study protocol and preliminary results, Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, COVID-19 Lombardy ICU Network: Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med
Griffiths, Mcauley, Perkins, Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome, BMJ Open Respir Res
Gupta, Coca, Chan, STOP-COVID Investigators: AKI treated with renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19, J Am Soc Nephrol
Harm, Schildböck, Hartmann, Cytokine removal in extracorporeal blood purification: An in vitro Study, Blood Purif
Hawchar, László, Öveges, Extracorporeal cytokine adsorption in septic shock: A proof of concept randomized, controlled pilot study, J Crit Care
Karagiannidis, Mostert, Hentschker, Case characteristics, resource use, and outcomes of 10 021 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 920 German hospitals: An observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Kielstein, Borchina, Fühner, Hemofiltration with the Seraph® 100 Microbind® Affinity filter decreases SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Crit Care
Lambden, Laterre, Levy, The SOFA scoredevelopment, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials, Crit Care
Lat, Coopersmith, Backer, Research Committee of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign: The surviving sepsis campaign: Fluid resuscitation and vasopressor therapy research priorities in adult patients, Intensive Care Med Exp
Moore, June, Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19, Science
Olson, Oliver, Treatment for severe cronavirus disease 2019 with the Seraph-100 microbind affinity blood filter, Crit Care Explor
Perreau, Suffiotti, Vidal, The cytokines HGF and CXCL13 predict the severity and the mortality in COVID-19 patients, Nat Commun
Poli, Alberio, Bauer-Doerries, Cytokine clearance with CytoSorb® during cardiac surgery: A pilot randomized controlled trial, Crit Care
Poli, Rimmelé, Schneider, Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb®, Intensive Care Med
Rieder, Wengenmayer, Staudacher, Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, Crit Care
Scharf, Schroeder, Paal, Can the cytokine adsorber CytoSorb® help to mitigate cytokine storm and reduce mortality in critically ill patients? A propensity score matching analysis, Ann Intensive Care
Schädler, Pausch, Heise, The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial, PLoS One
Sinha, Calfee, Cherian, Prevalence of phenotypes of acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A prospective observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Sinha, Matthay, Calfee, Is a "Cytokine Storm" relevant to COVID-19?, JAMA Intern Med
Stockmann, Keller, Büttner, CytoResc Trial Investigators: CytoResc -"CytoSorb" rescue for critically ill patients undergoing the COVID-19 cytokine storm: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Supady, Weber, Rieder, Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (CYCOV): A single centre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Thakkar, Chand, Aboodi, Characteristics, outcomes and 60-day hospital mortality of ICU patients with COVID-19 and acute kidney injury, Kidney
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/ccm.0000000000005493",
"ISSN": [
"0090-3493"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000005493",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>OBJECTIVES:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To investigate the effect of extracorporeal cytokine reduction by CytoSorb (CytoSorbents, Monmouth Junction, NJ) on COVID-19–associated vasoplegic shock.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>DESIGN:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Prospective, randomized controlled pilot study.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>SETTING:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Eight ICUs at three sites of the tertiary-care university hospital Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>PATIENTS:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>COVID-19 patients with vasoplegic shock requiring norepinephrine greater than 0.2 µg/kg/min, C-reactive protein greater than 100 mg/L, and indication for hemodialysis.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>INTERVENTIONS:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Randomization of 1:1 to receive CytoSorb for 3–7 days or standard therapy. To account for inadvertent removal of antibiotics, patients in the treatment group received an additional dose at each adsorber change.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The primary endpoint was time until resolution of vasoplegic shock, estimated by Cox-regression. Secondary endpoints included mortality, interleukin-6 concentrations, and catecholamine requirements. The study was registered in the German Registry of Clinical Trials (DRKS00021447). From November 2020 to March 2021, 50 patients were enrolled. Twenty-three patients were randomized to receive CytoSorb and 26 patients to receive standard of care. One patient randomized to cytokine adsorption was excluded due to withdrawal of informed consent. Resolution of vasoplegic shock was observed in 13 of 23 patients (56.5%) in the CytoSorb and 12 of 26 patients (46.2%) in the control group after a median of 5 days (interquartile range [IQR], 4–5 d) and 4 days (IQR, 3–5 d). The hazard ratio (HR) for the primary endpoint, adjusted for the predefined variables age, gender, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation-therapy, or time from shock onset to study inclusion was HR, 1.23 (95% CI, 0.54–2.79); <jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">p</jats:italic> = 0.63. The mortality rate was 78% in the CytoSorb and 73% in the control group (unadjusted HR, 1.17 [95% CI, 0.61–2.23]; <jats:italic toggle=\"yes\">p</jats:italic> = 0.64). The effects on inflammatory markers, catecholamine requirements, and the type and rates of adverse events were similar between the groups.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>CONCLUSIONS:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In severely ill COVID-19 patients, CytoSorb did not improve resolution of vasoplegic shock or predefined secondary endpoints.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Stockmann",
"given": "Helena",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Thelen",
"given": "Philipp",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Stroben",
"given": "Fabian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biometry and Clinical Epidemiology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Pigorsch",
"given": "Mareen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biometry and Clinical Epidemiology, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Keller",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Study Center, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Krannich",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology and Postoperative Intensive Care, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Campus Charité Mitte and Campus Virchow Klinikum, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Spies",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Treskatsch",
"given": "Sascha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiac Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine, Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Ocken",
"given": "Michele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Kunz",
"given": "Julius Valentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Krüger",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Khadzhynov",
"given": "Dmytro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Kron",
"given": "Susanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Budde",
"given": "Klemens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Eckardt",
"given": "Kai-Uwe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Enghard",
"given": "Philipp",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Medical Intensive Care, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin, corporate member of Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, and Berlin Institute of Health, Berlin, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Lehner",
"given": "Lukas Johannes",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Critical Care Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"lww.com",
"ovid.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-09T08:41:12Z",
"timestamp": 1644396072000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-02T17:15:09Z",
"timestamp": 1746206109000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-06T10:11:33Z",
"timestamp": 1746526293575,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 58,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/CCM.0000000000005493",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "964-976",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30316-7",
"article-title": "Case characteristics, resource use, and outcomes of 10",
"author": "Karagiannidis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "853",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "R1-20250502",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25948",
"article-title": "Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis.",
"author": "Aziz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2283",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "R2-20250502",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R3-20250502",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R4-20250502",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11330",
"article-title": "Association between administration of IL-6 antagonists and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A meta-analysis.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "499",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R5-20250502",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03597-3",
"article-title": "Hemofiltration with the Seraph® 100 Microbind® Affinity filter decreases SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in critically ill COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Kielstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R6-20250502",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000180",
"article-title": "Treatment for severe cronavirus disease 2019 with the Seraph-100 microbind affinity blood filter.",
"author": "Olson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0180",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Explor",
"key": "R7-20250502",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Plasma exchange for COVID-19 thrombo-inflammatory disease.",
"author": "Arulkumaran",
"journal-title": "EJHaem",
"key": "R8-20250502",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-018-5464-6",
"article-title": "Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb®.",
"author": "Poli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "R9-20250502",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00063-017-0342-5",
"article-title": "International registry on the use of the CytoSorb® adsorber in ICU patients: Study protocol and preliminary results.",
"author": "Friesecke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "Med Klin Intensivmed Notfmed",
"key": "R10-20250502",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0187015",
"article-title": "The effect of a novel extracorporeal cytokine hemoadsorption device on IL-6 elimination in septic patients: A randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Schädler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0187015",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "R11-20250502",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2399-4",
"article-title": "Cytokine clearance with CytoSorb® during cardiac surgery: A pilot randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Poli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R12-20250502",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000500013",
"article-title": "What have we learned about the use of Cytosorb adsorption columns?",
"author": "Ankawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"journal-title": "Blood Purif",
"key": "R13-20250502",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10047-017-0967-4",
"article-title": "Extracorporeal cytokine elimination as rescue therapy in refractory septic shock: A prospective single-center study.",
"author": "Friesecke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "J Artif Organs",
"key": "R14-20250502",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03130-y",
"article-title": "Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.",
"author": "Rieder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R16-20250502",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aor.13864",
"article-title": "Continuous renal replacement therapy with the addition of CytoSorb cartridge in critically ill patients with COVID-19 plus acute kidney injury: A case-series.",
"author": "Alharthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E101",
"journal-title": "Artif Organs",
"key": "R17-20250502",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00177-6",
"article-title": "Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (CYCOV): A single centre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial.",
"author": "Supady",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "755",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "R18-20250502",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04501-0",
"article-title": "CytoResc - “CytoSorb” rescue for critically ill patients undergoing the COVID-19 cytokine storm: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Stockmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "R19-20250502",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2019-000420",
"article-title": "Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Griffiths",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e000420",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Respir Res",
"key": "R20-20250502",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40635-021-00369-9",
"article-title": "The surviving sepsis campaign: Fluid resuscitation and vasopressor therapy research priorities in adult patients.",
"author": "Lat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med Exp",
"key": "R21-20250502",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0391398820917151",
"article-title": "Elimination of glycopeptide antibiotics by cytokine hemoadsorption in patients with septic shock: A study of three cases.",
"author": "Dimski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Int J Artif Organs",
"key": "R22-20250502",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2663-7",
"article-title": "The SOFA score-development, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials.",
"author": "Lambden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "374",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R23-20250502",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2588-1",
"article-title": "Hemoadsorption with CytoSorb shows a decreased observed versus expected 28-day all-cause mortality in ICU patients with septic shock: A propensity-score-weighted retrospective study.",
"author": "Brouwer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R24-20250502",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb8925",
"article-title": "Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19.",
"author": "Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "R25-20250502",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra2026131",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm.",
"author": "Fajgenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2255",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R26-20250502",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30366-0",
"article-title": "Prevalence of phenotypes of acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A prospective observational study.",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1209",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "R27-20250502",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3313",
"article-title": "Is a “Cytokine Storm” relevant to COVID-19?",
"author": "Sinha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1152",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "R28-20250502",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy.",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1345",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "R29-20250502",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34067/KID.0004282020",
"article-title": "Characteristics, outcomes and 60-day hospital mortality of ICU patients with COVID-19 and acute kidney injury.",
"author": "Thakkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1339",
"journal-title": "Kidney360",
"key": "R30-20250502",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2020060897",
"article-title": "AKI treated with renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "R31-20250502",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.11.003",
"article-title": "Extracorporeal cytokine adsorption in septic shock: A proof of concept randomized, controlled pilot study.",
"author": "Hawchar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "R32-20250502",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-021-00905-6",
"article-title": "Can the cytokine adsorber CytoSorb® help to mitigate cytokine storm and reduce mortality in critically ill patients? A propensity score matching analysis.",
"author": "Scharf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "R33-20250502",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000502680",
"article-title": "Cytokine removal in extracorporeal blood purification: An in vitro Study.",
"author": "Harm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Blood Purif",
"key": "R34-20250502",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25191-5",
"article-title": "The cytokines HGF and CXCL13 predict the severity and the mortality in COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Perreau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4888",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "R35-20250502",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/CCM.0000000000005493"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "CytoSorb Rescue for COVID-19 Patients With Vasoplegic Shock and Multiple Organ Failure: A Prospective, Open-Label, Randomized Controlled Pilot Study*",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1097/lww.0000000000001000",
"volume": "50"
}