COVID-19 mortality among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor users - Results from a nationwide cohort
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028, May 2023
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
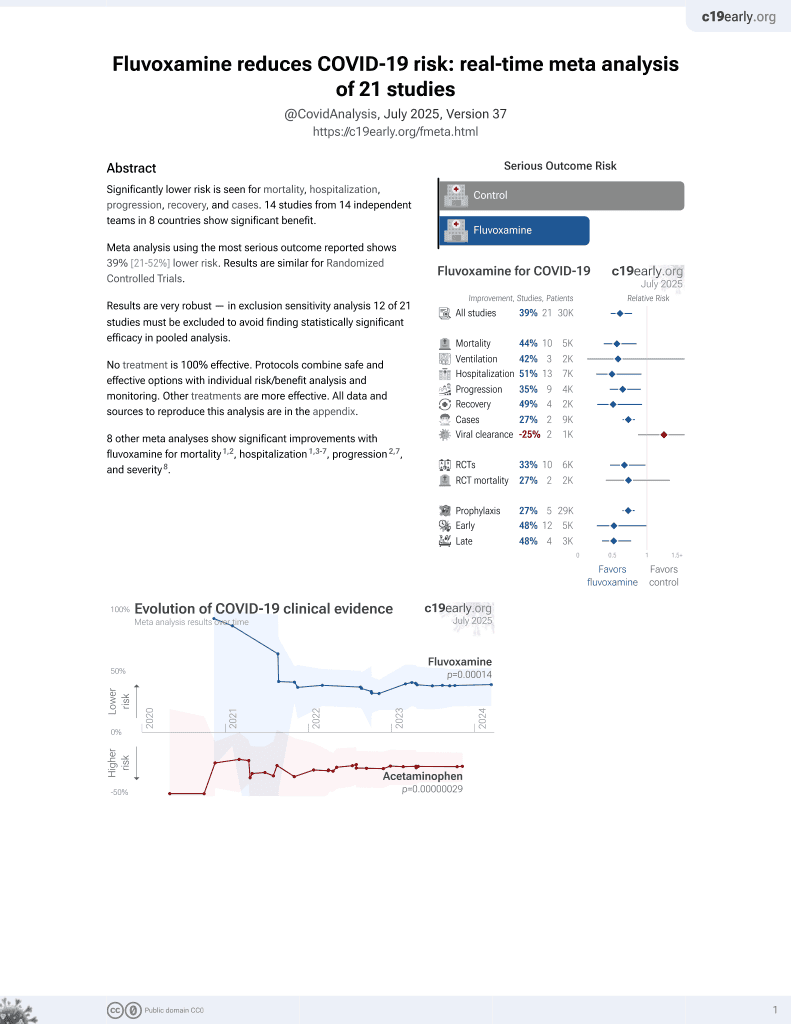
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
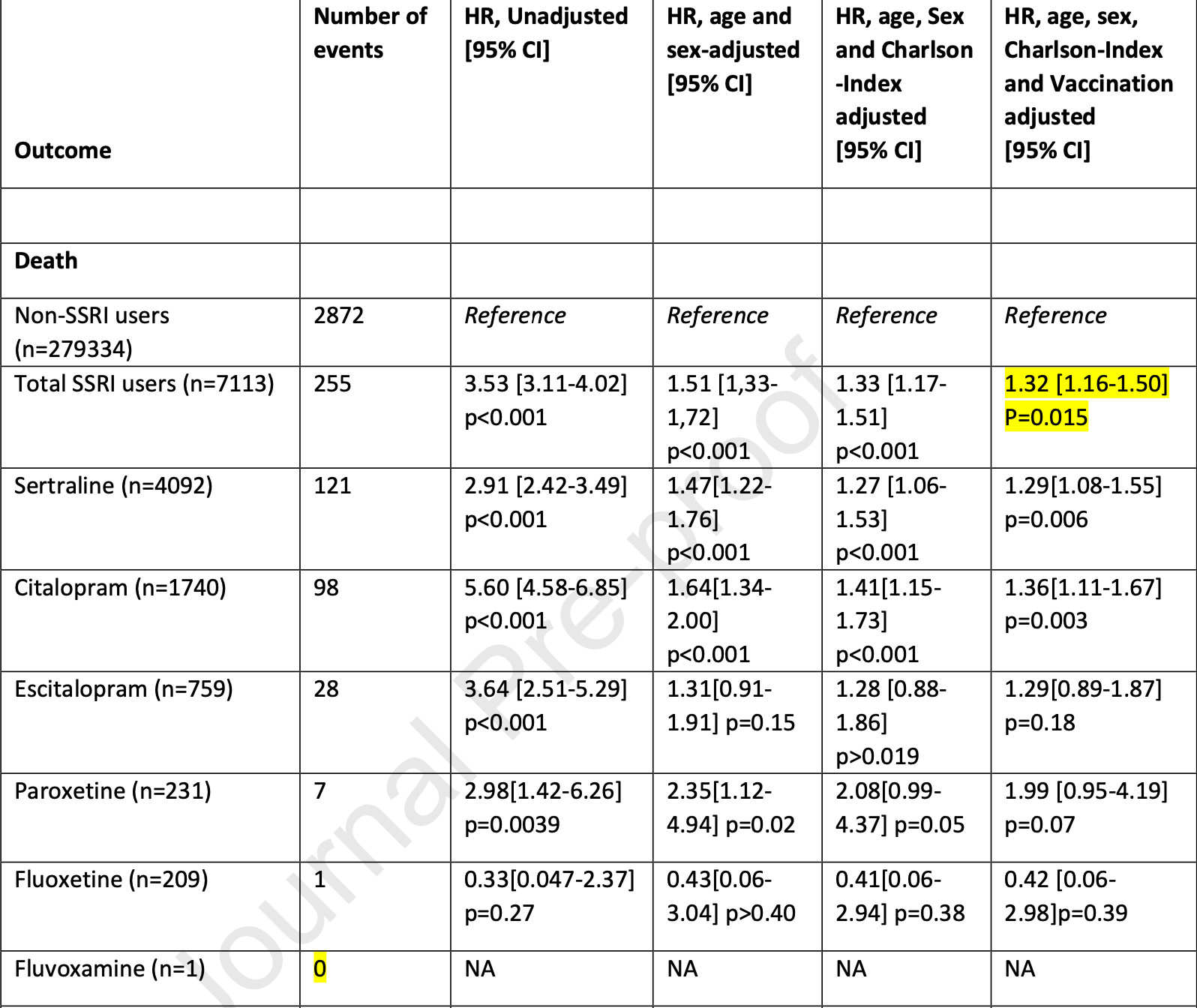
Retrospective 7,113 COVID+ SSRI users and 279,334 COVID+ non-SSRI users in Denmark, showing lower mortality with fluoxetine, without statistical significance, but higher mortality for other SSRIs.
|
risk of death, 57.7% lower, HR 0.42, p = 0.39, NNT 182, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, fluoxetine, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 44.5% lower, HR 0.55, p = 0.30, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, fluoxetine, severe acute respiratory syndrome or death, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 10.8% lower, HR 0.89, p = 0.84, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, fluoxetine, severe acute respiratory syndrome, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 31.6% higher, HR 1.32, p = 0.01, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, all SSRIs, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 22.5% higher, HR 1.22, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, all SSRIs, severe acute respiratory syndrome or death, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of progression, 6.9% higher, HR 1.07, p = 0.40, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, all SSRIs, severe acute respiratory syndrome, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Stauning et al., 5 May 2023, retrospective, Denmark, peer-reviewed, mean age 50.4, 4 authors, study period 26 February, 2020 - 5 October, 2021.
Contact: marius.ahm.stauning@regionh.dk.
COVID-19 mortality among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor users—results from a nationwide cohort
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of interest CTP has previously received research grants from Novo Nordisk and Bayer AG not related to the current study. Remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
Writing
References
Albayrak, Hashimoto, Sigma-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Clinical Implications in Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_11
Baadsgaard, Quitzau, Danish registers on personal income and transfer payments, Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, doi:10.1177/1403494811405098
Calusic, Marcec, Luksa, Jurkovic, Kovac et al., Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls, British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, doi:10.1111/bcp.15126
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Version 3.4.1 "Single Candle" Copyright (C), The R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Fico, Isayeva, Prisco, Oliva, Solè et al., Psychotropic drug repurposing for COVID-19: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, European Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.10.004
Firouzabadi, Kheshti, Abdollahifard, Taherifard, Kheshti, The effect of selective J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors on clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.892
Fosbøl, Gislason, Jacobsen, Abildstrom, Hansen et al., The pattern of use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from 1997 to 2005: A nationwide study on 4.6 million people, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.1592
Frank, Epidemiology, When an entire country is a cohort, Science, doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.287.5462.2398
Hamer, Kivimäki, Gale, Batty, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: A community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK, Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, doi:10.1016/J.BBI.2020.05.059
Hannestad, Dellagioia, Bloch, The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis, Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1038/NPP.2011.132
Hashimoto, Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, doi:10.1007/S00406-020-01231-X
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Kornhuber, Gulbins, Reiersen et al., Antidepressant Use and Its Association with 28-Day Mortality in Inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: Support for the FIASMA Model against COVID-19, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11195882
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Beeker, Jannot et al., Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Molecular Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4
Jensen, Rasmussen, Danish education registers, Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, doi:10.1177/1403494810394715
Kildemoes, Sørensen, Hallas, The Danish National Prescription Registry, Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, doi:10.1177/1403494810394717
Kuswardhani, Henrina, Pranata, Lim, Lawrensia et al., Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome, doi:10.1016/J.DSX.2020.10.022
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients with Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA -Journal of the American Medical Association, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Nyirenda, Sofroniou, Toews, Mikolajewska, Lehane et al., Fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD015391
Oskotsky, Marić, Tang, Oskotsky, Wong et al., Mortality Risk among Patients with COVID-19 Prescribed Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090
Pedersen, The Danish Civil Registration System, Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, doi:10.1177/1403494810387965
Quan, Sundararajan, Halfon, Fong, Burnand et al., Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data, Medical Care, doi:10.1097/01.MLR.0000182534.19832.83
Rauchman, Mendelson, Rauchman, Kasselman, Pinkhasov et al., Ongoing use of SSRIs does not alter outcome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis, Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11010070
Reis, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, The Lancet Global Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4
Schmidt, Schmidt, Adelborg, Sundbøll, Laugesen et al., The Danish health care system and epidemiological research: from health care contacts to database records, Clinical Epidemiology, doi:10.2147/CLEP.S179083
Schmidt, Schmidt, Sandegaard, Ehrenstein, Pedersen et al., The Danish National Patient Registry: a review of content, data quality, and research potential, Clinical Epidemiology, doi:10.2147/CLEP.S91125
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Vai, Mazza, Marisa, Beezhold, Kärkkäinen et al., Joint European policy on the COVID-19 risks for people with mental disorders: An umbrella review and evidence-and consensus-based recommendations for mental and public health, European Psychiatry, doi:10.1192/J.EURPSY.2022.2307
Voldstedlund, Haarh, Mølbak, The danish microbiology database (MIBA), Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES2014.19.1.20667/CITE/PLAINTEXT
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028",
"ISSN": [
"1198-743X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028",
"alternative-id": [
"S1198743X23002033"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "COVID-19 mortality among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor users - Results from a nationwide cohort"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stauning",
"given": "Marius Ahm",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gür",
"given": "Dogukan Jesper",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torp-Pedersen",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tingleff",
"given": "Jens",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalmicrobiologyandinfection.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-06T01:43:56Z",
"timestamp": 1683337436000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-06T01:44:15Z",
"timestamp": 1683337455000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-06T04:26:34Z",
"timestamp": 1683347194391
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1682899200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 3,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683158400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X23002033?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X23002033?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.10.004",
"article-title": "Psychotropic drug repurposing for COVID-19: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Fico",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "European Neuropsychopharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib1",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-020-01231-x",
"article-title": "Repurposing of CNS drugs to treat COVID-19 infection: targeting the sigma-1 receptor",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib2",
"volume": "271",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.892",
"article-title": "The effect of selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors on clinical outcome of COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Firouzabadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Health Science Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib3",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Ongoing use of SSRIs does not alter outcome in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis",
"author": "Rauchman",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib4",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4",
"article-title": "Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study",
"author": "Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5199",
"journal-title": "Molecular Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib5",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090",
"article-title": "Mortality Risk among Patients with COVID-19 Prescribed Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants",
"author": "Oskotsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e42",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Global Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib7",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs Placebo and Clinical Deterioration in Outpatients with Symptomatic COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2292",
"journal-title": "JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib8",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15126",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls",
"author": "Calusic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2065",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib9",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"article-title": "Prospective Cohort of Fluvoxamine for Early Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 19",
"author": "Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Nyirenda",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib11",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11195882",
"article-title": "Antidepressant Use and Its Association with 28-Day Mortality in Inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: Support for the FIASMA Model against COVID-19",
"author": "Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib12",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES2014.19.1.20667",
"article-title": "The danish microbiology database (MIBA) 2010 to 2013",
"author": "Voldstedlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eurosurveillance",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib13",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1403494810394717",
"article-title": "The Danish National Prescription Registry",
"author": "Wallach Kildemoes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Scandinavian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib14",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CLEP.S91125",
"article-title": "The Danish National Patient Registry: a review of content, data quality, and research potential",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Clinical Epidemiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib15",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1403494811405098",
"article-title": "Danish registers on personal income and transfer payments",
"author": "Baadsgaard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Scandinavian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib16",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1403494810394715",
"article-title": "Danish education registers",
"author": "Jensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Scandinavian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib17",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1403494810387965",
"article-title": "The Danish Civil Registration System",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Scandinavian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib18",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.1592",
"article-title": "The pattern of use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from 1997 to 2005: A nationwide study on 4.6 million people",
"author": "Fosbøl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "822",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib19",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83",
"article-title": "Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data",
"author": "Quan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1130",
"journal-title": "Medical Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib20",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib21",
"unstructured": "R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Version 3.4.1 “Single Candle” Copyright (C) 2017 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing 2017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"article-title": "Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: A community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK",
"author": "Hamer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Brain, Behavior, and Immunity",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib22",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1192/j.eurpsy.2022.2307",
"article-title": "Joint European policy on the COVID-19 risks for people with mental disorders: An umbrella review and evidence- and consensus-based recommendations for mental and public health",
"author": "Vai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "European Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib23",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CLEP.S179083",
"article-title": "The Danish health care system and epidemiological research: from health care contacts to database records",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Clinical Epidemiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.287.5462.2398",
"article-title": "Epidemiology. When an entire country is a cohort",
"author": "Frank",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2398",
"journal-title": "Science (New York, NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib25",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.022",
"article-title": "Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tuty Kuswardhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2103",
"journal-title": "Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib26",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review",
"author": "Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1898",
"journal-title": "Molecular Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib27",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/npp.2011.132",
"article-title": "The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Hannestad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2452",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychopharmacology : Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib28",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_11",
"article-title": "Sigma-1 Receptor Agonists and Their Clinical Implications in Neuropsychiatric Disorders",
"author": "Albayrak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib29",
"volume": "964",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.04.028_bib30",
"unstructured": "National Instituets of Health - U.S. Government., Update Dec 16 2021. Fluvoxamine | COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines n.d. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/immunomodulators/fluvoxamine/ (accessed November 11, 2022)."
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1198743X23002033"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 mortality among selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor users - Results from a nationwide cohort",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}