Efficacy of Various Treatment Modalities on Patient-related Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients – A Retrospective Study
et al., Indian Journal of Clinical Practice, 32:9, Feb 2022
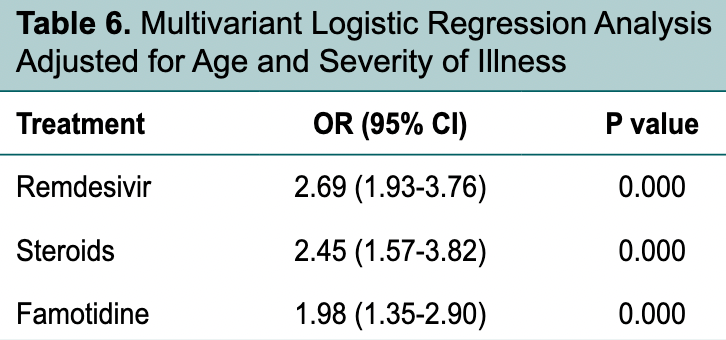
Retrospective 1,000 COVID+ hospitalized patients in India, showing lower mortality with famotidine and remdesivir in multivariable logistic regression.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Remdesivir efficacy disappears with longer
followup. Mixed-effects meta-regression of efficacy as a function of
followup duration across all remdesivir studies shows decreasing efficacy with
longer followup15. This may reflect
antiviral efficacy being offset by serious adverse effects of treatment.
Study covers remdesivir and famotidine.
|
risk of death, 52.9% lower, RR 0.47, p < 0.001, treatment 108 of 413 (26.2%), control 197 of 587 (33.6%), adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Siraj et al., 28 Feb 2022, retrospective, India, peer-reviewed, median age 56.0, 13 authors, study period March 2020 - December 2020.
Medicine ^Assistant Professor ¶ Additional Professor ⇑ Professor Dept. of Rheumatology ψ Professor φ Professor and Head
Background: The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) began in China, in December 2019, and was declared a pandemic by WHO on March 11, 2020. The treatment is evolving and is mostly supportive in nature. Material and methods: This was a single-center retrospective study that included confirmed COVID-19 cases treated at our institute (a tertiary care hospital in Jammu and Kashmir, India), between March 2020 and December 2020. Patients with age more than 18 years were included in the study. Results: On evaluating the effect of various drug therapies used in management of COVID-19 patients of all severity, use of remdesivir and famotidine was associated with significantly higher odds of survival. In subgroup of patients with severe disease, use of systemic steroids was associated with significantly higher odds of survival in addition to remdesivir and famotidine. In patients with severe COVID-19 illness, likelihood of survival was significantly higher in those who received combination of systemic steroids plus remdesivir compared to steroids and remdesivir alone. Conclusion: Steroids were effective in severe COVID-19 illness and the combination of steroids and remdesivir was more effective in severe illness. There is a need to undertake more large scale prospective randomized trials to determine the most effective drug therapies to treat the sick patients and prevent worsening of mild cases.
References
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., ACTT-1 Study Group Members. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19 -Final report, N Engl J Med
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Azevedo, Veiga et al., Coalition Covid-19 Brazil I Investigators. Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Tracey, Callahan et al., Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Garibaldi, Wang, Robinson, Zeger, Bandeen-Roche et al., Comparison of time to clinical improvement with vs without remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hermine, Tharaux, Resche-Rigon, Porcher, Ravaud et al., Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med
Horby, Pessoa-Amorim, Peto, Brightling, Sarkar et al., Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19, RECOVERY
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Janowitz, Gablenz, Pattinson, Wang, Conigliaro et al., Famotidine use and quantitative symptom tracking for COVID-19 in non-hospitalised patients: a case series, Gut
Lee, Chan, Hui, Ng, Wu et al., Effects of early corticosteroid treatment on plasma SARS-associated coronavirus RNA concentrations in adult patients, J Clin Virol
Lee, Mcdonald, Butler-Laporte, Harrison, Cheng et al., Remdesivir and systemic corticosteroids for the treatment of COVID-19: a Bayesian re-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Mather, Seip, Mckay, Impact of famotidine use on clinical outcomes of hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Am J Gastroenterol
Misra, Nath, Hadda, Vibha, Efficacy of various treatment modalities for nCOV-2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Clin Invest
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Preziosi, Sathiyamoorthy et al., Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19--Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results, N Engl J Med
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham et al., Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Recovery Collaborative Group, Horby, Mafham, Linsell, Bell et al., Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Rubin, Longo, Baden, Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in Covid-19 -Cooling the inflammatory soup, N Engl J Med
Ruiz-Irastorza, Pijoan, Bereciartua, Dunder, Dominguez et al., Second week methyl-prednisolone pulses improve prognosis in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia: an observational comparative study using routine care data, PLoS One
Salama, Han, Yau, Reiss, Kramer et al., Tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Soin, Kumar, Choudhary, Sharma, Mehta et al., Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, López, Cattelan et al., Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Tang, Feng, Ni, Zhang, Liu et al., Early use of corticosteroid may prolong SARS-CoV-2 shedding in non-intensive care unit patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: a multicenter, single-blind, randomized control trial, Respiration
Van Paassen, Vos, Hoekstra, Neumann, Boot et al., Corticosteroid use in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis on clinical outcomes, Crit Care
Villar, Ferrando, Martínez, Ambrós, Muñoz et al., Dexamethasone in ARDS Network. Dexamethasone treatment for the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Wu, Liu, Yang, Zhang, Zhong et al., Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods, Acta Pharm Sin B
siraj