Effect of Ammonium Chloride in addition to standard of care in outpatients and hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043, Jul 2021
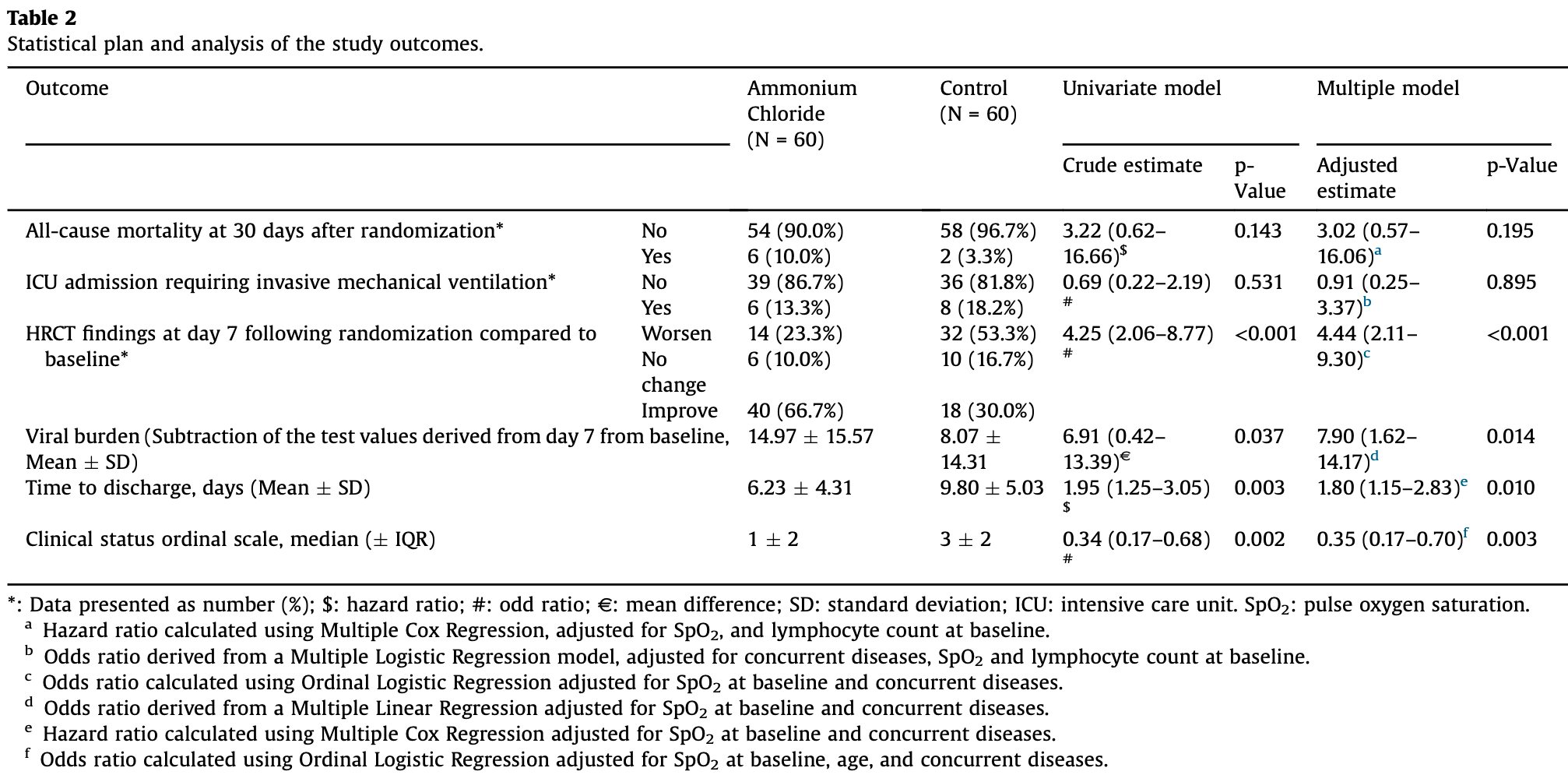
RCT 120 COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in mortality but improved recovery time and reduced viral burden with ammonium chloride treatment.
|
risk of death, 202.0% higher, HR 3.02, p = 0.20, treatment 6 of 60 (10.0%), control 2 of 60 (3.3%), Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 7.9% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.90, treatment 6 of 60 (10.0%), control 8 of 60 (13.3%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 65.0% lower, OR 0.35, p = 0.003, treatment 60, control 60, adjusted per study, clinical status, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Siami et al., 31 Jul 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period 22 August, 2020 - 22 October, 2020.
Contact: kargarapgv@gmail.com, hamidrezamozhgani@gmail.com.
Effect of Ammonium Chloride in addition to standard of care in outpatients and hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043
Objective: The COVID-19 pandemic has called an urgent need for drug repurposing to improve the outcome of the disease. Quaternary ammonium compounds have been demonstrated to have antiviral effects and may be of use against SARS-CoV-2 infections. Design: In this double-blind, single-center study, we enrolled patients with positive PCR test and/or CT findings for COVID-19. The participants of each group were randomly assigned to Diphenhydramine Compound (Diphenhydramine + Ammonium Chloride) plus standard of care or to Diphenhydramine alone and standard of care groups. The primary outcome was all-cause mortality within 30 days of randomization. Secondary outcomes include viral burden, clinical status, assessed by a 5-point ordinal scale, and length of stay in hospitalized patients. Results: A total of 120 patients were included in the trial, 60 of which were assigned to the Ammonium Chloride group. The primary endpoint was not statistically different between the two groups (HR: 3.02 (95% CI, 0.57-16.06; p = 0.195)). Recovery time and viral burden were significantly lower in the Ammonium Chloride group, corresponding to an odds ratios of 1.8 (95% CI, 1.15-2.83; p = 0.01) and 7.90 (95% CI, 1.62-14.17; p = 0.014), respectively.
Conclusion: The findings of this study advocate the careful addition of Ammonium Chloride to standard of care for COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval The trial was approved by ethics committee at Alborz University of Medical Sciences .
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary material related to this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043 .
References
Baker, Williams, Tropsha, Ekins, Repurposing quaternary ammonium compounds as potential treatments for COVID-19, Pharm Res
Helmy, Fawzy, Elaswad, Sobieh, Kenney et al., The COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive review of taxonomy, genetics, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control, J Clin Med
Kheirabad, Nourozi, Ammonium chloride as a potential candidate for the treatment and controlling of Covid-19, Iran J Virol
Self, Semler, Leither, Casey, Angus et al., Effect of hydroxychloroquine on clinical status at 14 days in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Siami, Aghajanian, Mansouri, None, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Who, WHO COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971221003544"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of Ammonium Chloride in addition to standard of care in outpatients and hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siami",
"given": "Zeinab",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghajanian",
"given": "Sepehr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansouri",
"given": "Somayeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mokhames",
"given": "Zakiye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pakzad",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kabir",
"given": "Kourosh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Norouzi",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soleimani",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hedayat Yaghoobi",
"given": "Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shadabi",
"given": "Shahrzad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tajbakhsh",
"given": "Ramin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kargar Kheirabad",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mozhgani",
"given": "Sayed-Hamidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"ijidonline.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-19T05:14:45Z",
"timestamp": 1618809285000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-13T23:08:49Z",
"timestamp": 1649891329000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012411",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100012411",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Alborz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T11:49:51Z",
"timestamp": 1740138591921,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618185600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971221003544?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971221003544?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "306-308",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-020-02842-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing quaternary ammonium compounds as potential treatments for COVID-19",
"author": "Baker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pharm Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043_bib0005",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9041225",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive review of taxonomy, genetics, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control",
"author": "Helmy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1225",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043_bib0010",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Ammonium chloride as a potential candidate for the treatment and controlling of Covid-19",
"author": "Kargar Kheirabad",
"first-page": "42",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Iran J Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043_bib0015",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22240",
"article-title": "Effect of hydroxychloroquine on clinical status at 14 days in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Self",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2165",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043_bib0020",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.043_bib0025",
"unstructured": "WHO. WHO COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, 17 November 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 5,
"references-count": 5,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971221003544"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of Ammonium Chloride in addition to standard of care in outpatients and hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "108"
}