Safety and effectiveness of azithromycin in patients with COVID-19: An open-label randomised trial
et al., International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143, Oct 2020
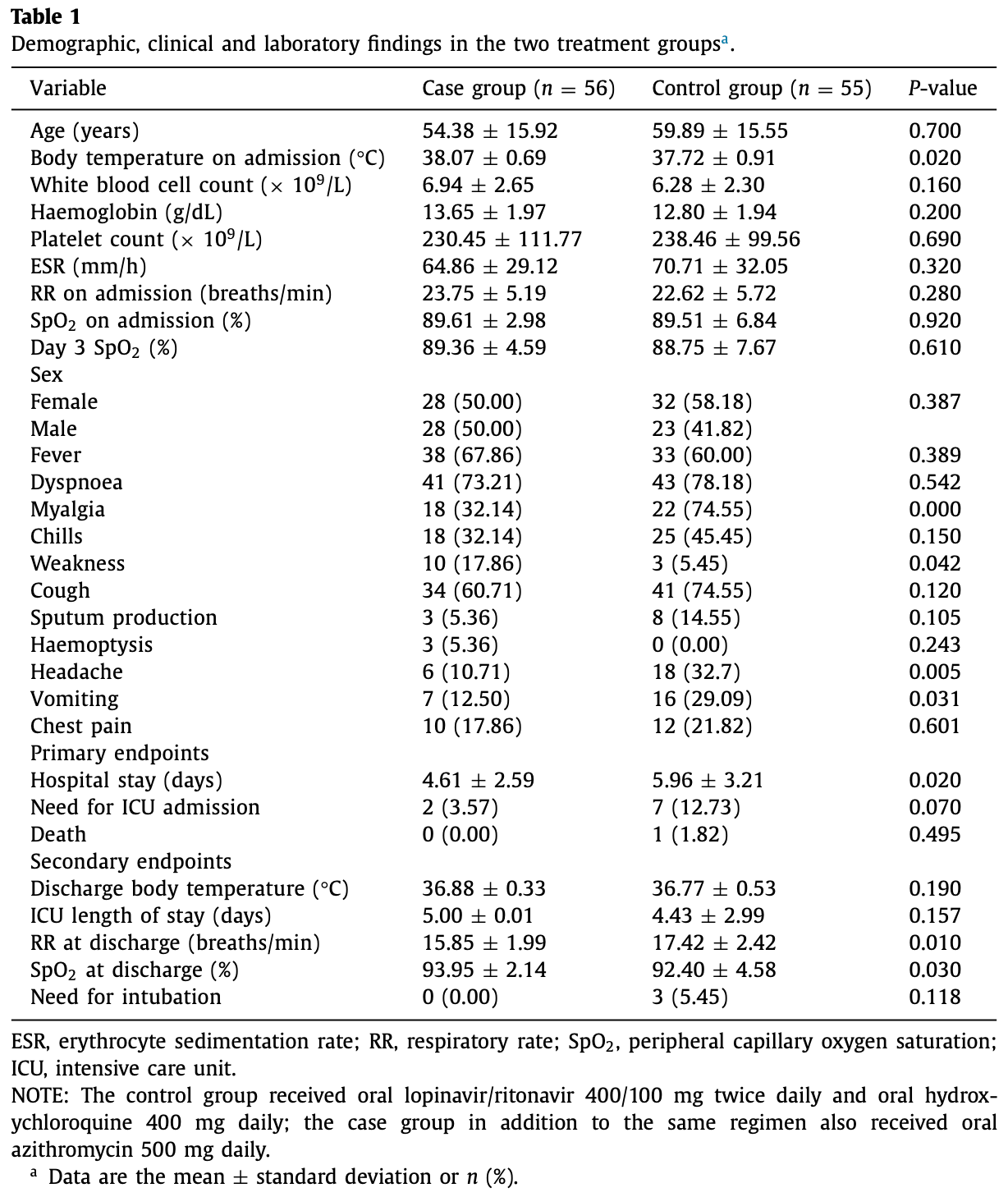
Randomized controlled trial of 111 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran showing significantly shorter hospital stay, higher oxygen saturation, and lower respiratory rate at discharge with azithromycin plus hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir compared to hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir alone. There were no significant differences in ICU admission, intubation, or mortality, although there was a trend towards lower ICU admission with azithromycin (3.6% vs. 12.7%, p = 0.07). Patients with prior cardiac disease were excluded. The study is limited by the small sample size and open-label design.
|
risk of death, 66.9% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.50, treatment 0 of 56 (0.0%), control 1 of 55 (1.8%), NNT 55, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 85.8% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.12, treatment 0 of 56 (0.0%), control 3 of 55 (5.5%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 71.9% lower, RR 0.28, p = 0.09, treatment 2 of 56 (3.6%), control 7 of 55 (12.7%), NNT 11.
|
|
hospitalization time, 22.7% lower, relative time 0.77, p = 0.02, treatment 56, control 55.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sekhavati et al., 31 Oct 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 18 authors, study period 24 April, 2020 - 8 May, 2020.
Contact: fatemejafari72@gmail.com, ghiasvand_62@yahoo.com.
Safety and effectiveness of azithromycin in patients with COVID-19: An open-label randomised trial
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143
As no specific pharmacological treatment has been validated for use in coronavirus disease 2019 , we aimed to assess the effectiveness of azithromycin (AZM) in these patients at a referral centre in Iran. An open-label, randomised controlled trial was conducted on patients with laboratoryconfirmed COVID-19. A total of 55 patients in the control group receiving hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) were compared with 56 patients in the case group who in addition to the same regimen also received AZM. Patients with prior cardiac disease were excluded from the study. Furthermore, patients from the case group were assessed for cardiac arrythmia risk based on the American College of Cardiology (ACC) risk assessment for use of AZM and HCQ. The main outcome measures were vital signs, SpO 2 levels, duration of hospitalisation, need for and length of intensive care unit admission, mortality rate and results of 30-day follow-up after discharge. Initially, there was no significant difference between the general conditions and vital signs of the two groups. The SpO 2 levels at discharge were significantly higher, the respiratory rate was lower and the duration of admission was shorter in the case group. There was no significant difference in the mortality rate between the two groups. Patients who received AZM in addition to HCQ and LPV/r had a better general condition. HCQ + AZM combination may be beneficial for individuals who are known to have a very low underlying risk for cardiac arrhythmia based on the ACC criteria.
References
Arabi, Alothman, Balkhy, Al-Dawood, Aljohani et al., Treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome with a combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Arshad, Kilgore, Chaudhry, Jacobsen, Wang et al., Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and combination in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.099
Bacharier, Guilbert, Mauger, Boehmer, Beigelman et al., Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Behzad, Aghaghazvini, Radmard, Gholamrezanezhad, Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: radiologic and clinical overview, Clin Imaging
Bosseboeuf, Aubry, Nhan, Pina, Rolain et al., Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus, J Antivir Antiretrovir
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Azevedo, Veiga et al., Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2019014
Chen, Chan, Jiang, Kao, Lu et al., In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds, J Clin Virol
Chorin, Dai, Shulman, Wadhwani, Bar-Cohen et al., The QT interval in patients with COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0888-2
Choudhary, Sharma, Potential use of hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin and azithromycin drugs in fighting COVID-19: trends, scope and relevance, New Microbes New Infect
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Wong, Chan et al., Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax
Colson, Rolain, Raoult, Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Cortegiani, Ingoglia, Ippolito, Giarratano, Einav, A systematic review on the efficacy and safety of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19, J Crit Care, doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.03.005
Dahly, Gates, Morris, Statistical review of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label nonrandomized clinical trial, Preprint posted online, doi:10.5281/zenodo.3724167
Fanin, Calegari, Beverina, Tiraboschi, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19, Intern Emerg Med, doi:10.1007/s11739-020-02388-y
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Meddeb, Mailhe et al., Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Hu, Sun, Dai, Deng, Li et al., Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Virol
Hulme, Wagenmakers, Damkier, Madelung, Siebner et al., A Bayesian reanalysis of the effects of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on viral carriage in patients with COVID-19, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.31.20048777
Jean, Lee, Hsueh, Treatment options for COVID-19: the reality and challenges, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.034
Juurlink, Safety considerations with chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the management of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Can Med Assoc J, doi:10.1503/cmaj.200528
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Lane, Weaver, Kostka, Duarte-Salles, Abrahao et al., Safety of hydroxychloroquine, alone and in combination with azithromycin, in light of rapid wide-spread use for COVID-19: a multinational, network cohort and self-controlled case series study, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.08.20054551
Marmor, Carr, Easterbrook, Farjo, Mieler, Recommendations on screening for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology, Ophthalmology
Million, Lagier, Gautret, Colson, Fournier et al., Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille, France, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101738
Mitra, Greenstein, Epstein, An algorithm for managing QT prolongation in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients treated with either chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with azithromycin: possible benefits of intravenous lidocaine, HeartRhythm Case Rep, doi:10.1016/j.hrcr.2020.03.016
Molina, Delaugerre, Goff, Lima, Ponscarme et al., No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical benefit with the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection, Med Mal Infect, doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.006
Monteil, Kwon, Prado, Hagelkrüys, Wimmer et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2, Cell
Morgan, Patel, Dvorkina, Suspected hydroxychloroquine-associated QT-interval prolongation in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus, J Clin Rheumatol
Negida, Bahbah, Comments on the hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin study and lessons for future clinical trials of COVID-19 treatments, doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.24669.36325
Okubo, Isono, Asano, Sato, Lopinavir-ritonavir combination induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and kills urological cancer cells, Anticancer Res
Rabkin, Nomenclature, categorization and usage of formulae to adjust QT interval for heart rate, World J Cardiol, doi:10.4330/wjc.v7.i6.315
Rosenberg, Dufort, Udo, Wilberschied, Kumar et al., Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8630
Sadr, Seyedalinaghi, Ghiasvand, Nezhad, Javadian et al., Isolated severe thrombocytopenia in a patient with COVID-19: a case report, IDCases, doi:10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00820
Sandeep, Mcgregor, Energetics based modeling of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin binding to the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein-ACE2 complex, ChemRxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12015792
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019
Savarino, Trani, Donatelli, Cauda, Cassone, New insights into the antiviral effects of chloroquine, Lancet Infect Dis
Sermo, Sermo's COVID-19 real time barometer study
Simpson, Ventricular arrhythmia risk due to hydroxychloroquineazithromycin treatment for COVID-19, Cardiology Magazine
Wang, Wang, Ye, Liu, Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Wu, Ma, Kuo, Juan, Cheng, Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Yao, Ye, Zhang, Cui, Huang et al., In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143",
"ISSN": [
"0924-8579"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143",
"alternative-id": [
"S0924857920303411"
],
"article-number": "106143",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Safety and effectiveness of azithromycin in patients with COVID-19: An open-label randomised trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Ltd and International Society of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sekhavati",
"given": "Ehsan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafari",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SeyedAlinaghi",
"given": "SeyedAhmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamalimoghadamsiahkali",
"given": "Saeidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadr",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tabarestani",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pirhayati",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zendehdel",
"given": "Abolfazl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4610-402X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Manafi",
"given": "Navid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajiabdolbaghi",
"given": "Mahboubeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmadinejad",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kouchak",
"given": "Hamid Emadi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafari",
"given": "Sirous",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalili",
"given": "Hosein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salehi",
"given": "Mohamadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seifi",
"given": "Arash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Golestan",
"given": "Fereshteh Shahmari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghiasvand",
"given": "Fereshteh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-25T01:25:25Z",
"timestamp": 1598318725000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-14T23:44:02Z",
"timestamp": 1610667842000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004484",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-16T08:26:53Z",
"timestamp": 1713256013853
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 68,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857920303411?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0924857920303411?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "106143",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0001",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105948",
"article-title": "Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0002",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00820",
"article-title": "Isolated severe thrombocytopenia in a patient with COVID-19: a case report",
"author": "Sadr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00820",
"journal-title": "IDCases",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0003",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.05.013",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19: radiologic and clinical overview",
"author": "Behzad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Clin Imaging",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0004",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104371",
"article-title": "Prevalence and severity of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0005",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.03.005",
"article-title": "A systematic review on the efficacy and safety of chloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Cortegiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0006",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105923",
"article-title": "Chloroquine for the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Colson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0007",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70361-9",
"article-title": "New insights into the antiviral effects of chloroquine",
"author": "Savarino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0008",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0161-6420(02)01168-5",
"article-title": "Recommendations on screening for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology",
"author": "Marmor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Ophthalmology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0009",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "732",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0010",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21873/anticanres.13793",
"article-title": "Lopinavir–ritonavir combination induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and kills urological cancer cells",
"author": "Okubo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5891",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0011",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-017-2427-0",
"article-title": "Treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome with a combination of lopinavir–ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Arabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0012",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.003",
"article-title": "In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0013",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"article-title": "Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0014",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0403596101",
"article-title": "Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10012",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0015",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13896",
"article-title": "Early administration of azithromycin and prevention of severe lower respiratory tract illnesses in preschool children with a history of such illnesses: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Bacharier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2034",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0016",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4172/1948-5964.1000173",
"article-title": "Azithromycin inhibits the replication of Zika virus",
"author": "Bosseboeuf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "J Antivir Antiretrovir",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0017",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Energetics based modeling of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin binding to the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein–ACE2 complex",
"author": "Sandeep",
"journal-title": "ChemRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0018",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2",
"author": "Monteil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0019",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0020",
"series-title": "Sermo's COVID-19 real time barometer study",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0888-2",
"article-title": "The QT interval in patients with COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin",
"author": "Chorin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "808",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0021",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/RHU.0b013e31829d5e50",
"article-title": "Suspected hydroxychloroquine-associated QT-interval prolongation in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus",
"author": "Morgan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "286",
"journal-title": "J Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0022",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Ventricular arrhythmia risk due to hydroxychloroquine–azithromycin treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Simpson",
"journal-title": "Cardiology Magazine",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0023",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4330/wjc.v7.i6.315",
"article-title": "Nomenclature, categorization and usage of formulae to adjust QT interval for heart rate",
"author": "Rabkin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"journal-title": "World J Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0024",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review",
"author": "Sanders",
"first-page": "1824",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0025",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100684",
"article-title": "Potential use of hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin and azithromycin drugs in fighting COVID-19: trends, scope and relevance",
"author": "Choudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "New Microbes New Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0026",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gautret",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0027",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.034",
"article-title": "Treatment options for COVID-19: the reality and challenges",
"author": "Jean",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "436",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0028",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Fanin",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0029",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A Bayesian reanalysis of the effects of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on viral carriage in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Hulme",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0030",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Negida",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0031",
"series-title": "Comments on the hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin study and lessons for future clinical trials of COVID-19 treatments",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Statistical review of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label nonrandomized clinical trial",
"author": "Dahly",
"journal-title": "Preprint posted online",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0032",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medmal.2020.03.006",
"article-title": "No evidence of rapid antiviral clearance or clinical benefit with the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Molina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Med Mal Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0033",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101738",
"article-title": "Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille, France",
"author": "Million",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Travel Med Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0034",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Cavalcanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0035",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8630",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with hydroxychloroquine or azithromycin with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York State",
"author": "Rosenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2493",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0036",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.099",
"article-title": "Treatment with hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, and combination in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Arshad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "396",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0037",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hrcr.2020.03.016",
"article-title": "An algorithm for managing QT prolongation in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients treated with either chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine in conjunction with azithromycin: possible benefits of intravenous lidocaine",
"author": "Mitra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "244",
"journal-title": "HeartRhythm Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0038",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.200528",
"article-title": "Safety considerations with chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in the management of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Juurlink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E450",
"journal-title": "Can Med Assoc J",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0039",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Safety of hydroxychloroquine, alone and in combination with azithromycin, in light of rapid wide-spread use for COVID-19: a multinational, network cohort and self-controlled case series study",
"author": "Lane",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106143_bib0040",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0924857920303411"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and effectiveness of azithromycin in patients with COVID-19: An open-label randomised trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "56"
}