The Effects of N-Acetylcysteine as Adjuvant Therapy To Reduce TNF-Α Level And Increase SPO2/FIO2 Ratio In Improving Hypoxemia In COVID-19 Patients
et al., Indonesian Journal of Tropical and Infectious Disease, 9:3, Dec 2021
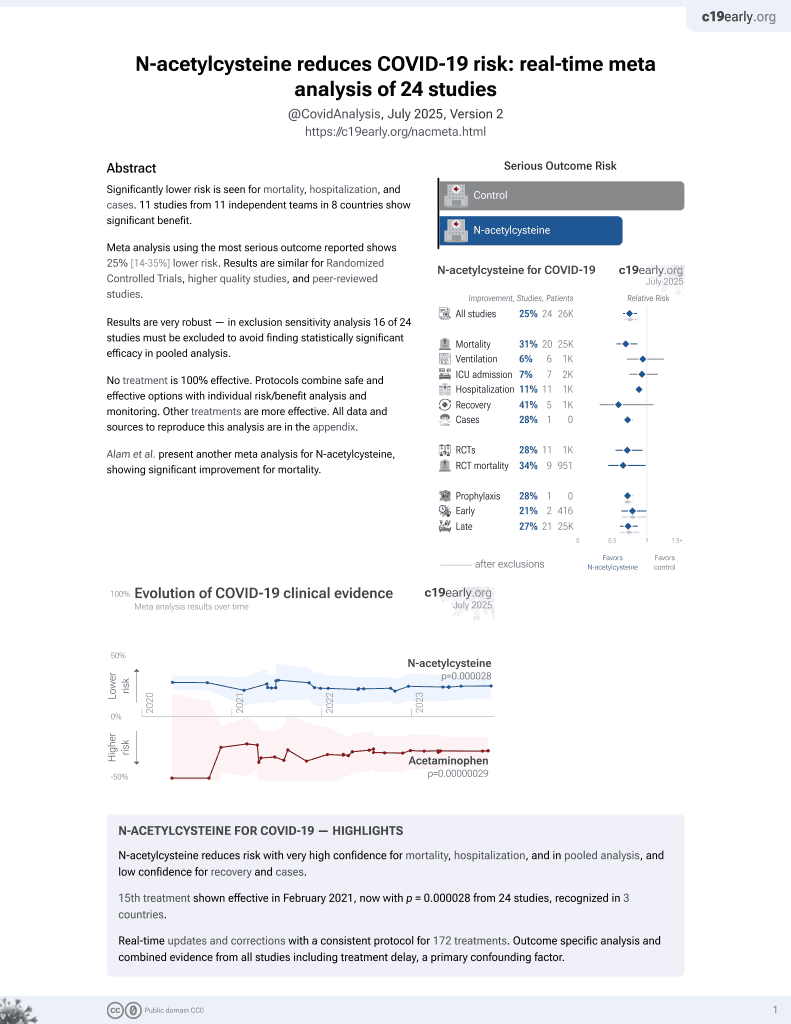
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
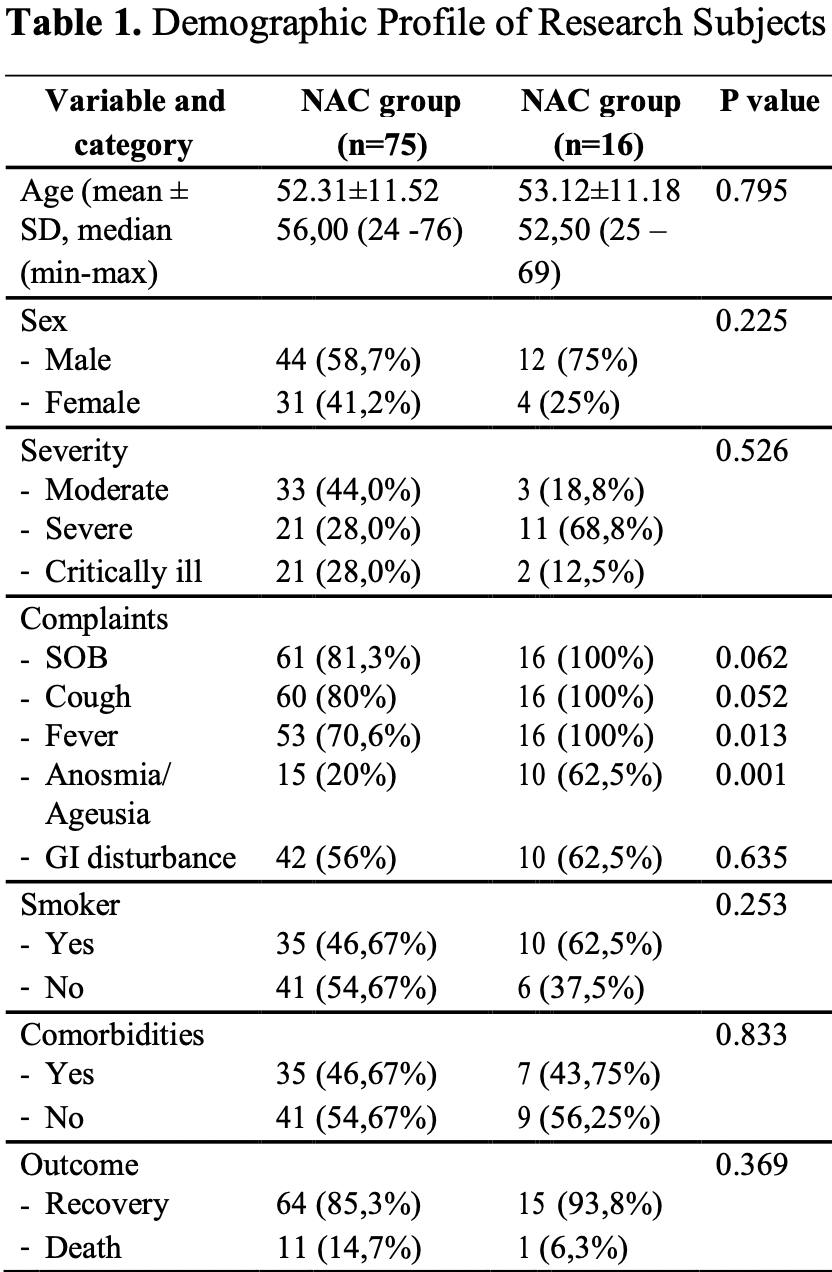
Prospective study with 75 NAC patients and 16 control patients, showing no significant difference in mortality.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of death, 134.7% higher, RR 2.35, p = 0.68, treatment 11 of 75 (14.7%), control 1 of 16 (6.2%), unadjusted.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ramadhan et al., 27 Dec 2021, prospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period June 2020 - July 2021.
The Effects of N-Acetylcysteine as Adjuvant Therapy To Reduce TNF-Α Level And Increase SPO2/FIO2 Ratio In Improving Hypoxemia In COVID-19 Patients
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a crucial role in COVID-19 disease
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This research received grant from COVID Research and Innovation Consortium by LPDP-RistekBrin.
CONFLIC OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
REFERENCE 1. Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang D, Xu Z, Ji J, Wen C. this study prove that there is the involvement of TNF-α in the mechanism of action of NAC. NAC interferes with the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway by suppressing the expression of NLRP3 and caspase-1 activation mRNA. NAC decreased IL1β, IL18, IL6 and TNF-ɑ in vitro. NAC inhibits downstream activity post-TNF-α receptor activation, and under oxidative stress, NAC inhibits
World Health
CONCLUSION This finding is by the previous studies, in which Changes in TNF-α levels and alterations in SpO2/FiO2 ratio of COVID-19 patients in the group without adjuvant NAC therapy showed a positive correlation. On the other hand, in the group that did not receive adjuvant NAC therapy, the correlation coe cient was negative and not significant. it was found that the administration of NAC can increase the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. The conclusions of TNF-α and IL-6 gene expression. 9. De Flora S, Balansky R, La Maestra S. Rationale for using changes in TNF-ɑlevels and diferences in the SpO2/FiO2 ratio in COVID-19 patients who did not receive adjuvant NAC therapy. There was a significant decrease in TNF-ɑ levels a fter NA C a dministration a s a djuvants. I n addition, there was also a substantial increase in the SpO2FiO2 ratio after administration of adjuvant..
References
Alamdari, Moghaddam, Amini, Keramati, Zarmehri et al., Application of methylene blue-vitamin C-N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial, European journal of pharmacology
Avdeev, Gaynitdinova, Merzhoeva, Berikkhanov, N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of COVID-19 among hospitalized patients, The Journal of Infection
De Alencar, Moreira, Müller, Chaves, Fukuhara et al., A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with N-acetylcysteine to treat severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clinical Infectious Diseases
Dinicola, De Grazia, Carlomagno, Pintucci, Wu et al., N-acetylcysteine as a potent molecule to destroy bacterial biofilms. A systematic review, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Furman, Campisi, Verdin, Carrera-Bastos, Targ et al., Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span, Nature medicine
Gallo Marin, Aghagoli, Lavine, Yang, Si et al., Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review, Reviews in medical virology
Griendling, Sorescu, Ushio-Fukai, NAD (P) H oxidase: role in cardiovascular biology and disease, Circulation research
Hasan, N-acetylcysteine in Severe COVID-19: The Possible Mechanism, Int J Infect
Ibrahim, Smith, Lewis, Kon, Goldenberg et al., Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous N-acetylcysteine, Clinical Immunology
Ijtid, None
Li G Fan, Coronavirus infections and immune responses, Journal of Medical Virology
Niles, Gogesch, Kronhart, Iannazzo, Kochs et al., Macrophages and Dendritic Cells Are Not the Major Source of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Upon SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Frontiers in Immunology
Poe, Corn, N-Acetylcysteine: A potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Medical hypotheses
Shah, Formal, Alam, Ganguly, Chattopadhyay, Overview of the immune response during SARS-CoV-2 infection: lessons from the past, Frontiers in immunology
Shi, Yang, Zhou, Xi, Sun et al., Activated carbon N-acetylcysteine microcapsule protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in young rats via activating telomerase and inhibiting apoptosis, PLoS One
Silva, Therapeutic approaches for tumor necrosis factor inhibition, Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Wong, Lee, Kua, N-Acetylcysteine as Adjuvant Therapy for COVID-19-A Perspective on the Current State of the Evidence, Journal of inflammation research
Zhang, Ju, Ma, Wang, N-acetylcysteine improves oxidative stress, and inflammatory response in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial, Medicine
Šalamon, Kramar, Pirc Marolt, Poljšak, Milisav, Medical and Dietary Uses of N-Acetylcysteine, Antioxidants