Kovid-19 - Huvemek® Phase 2 clinical trial
, Press Release, 3/25, EudraCT2020-002091-12, Mar 2021
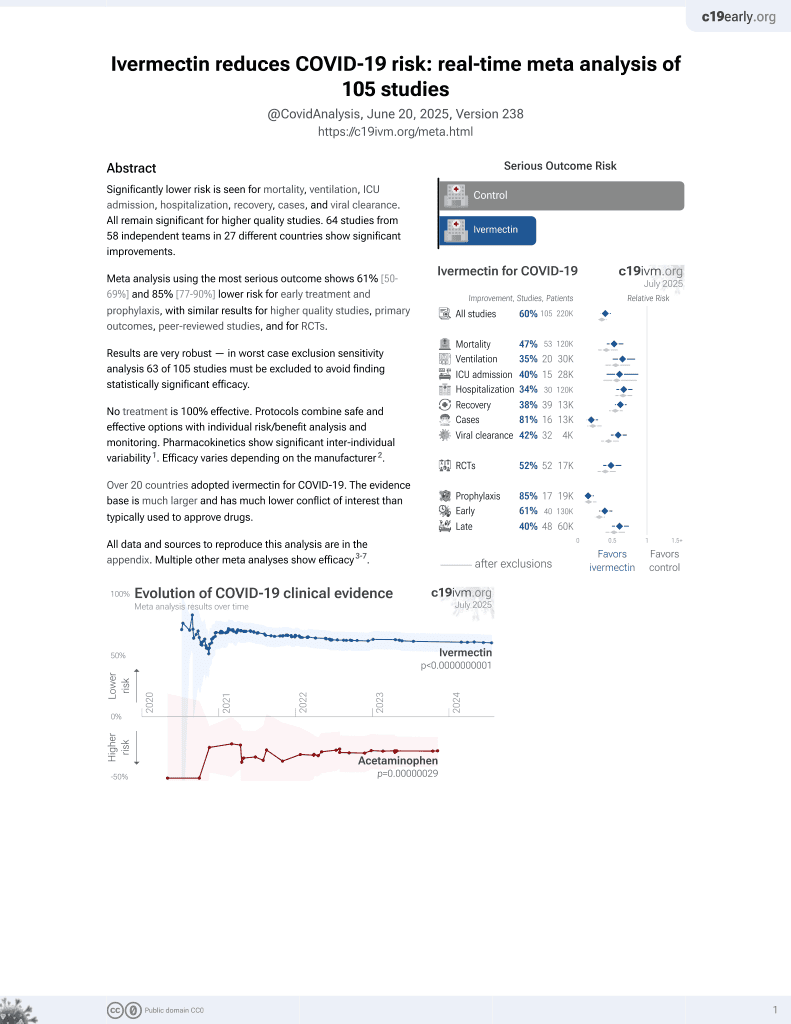
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Multicenter double-blind RCT with 100 hospitalized patients in Bulgaria showing faster viral clearance, greater clinical improvement, and improved biomarkers with treatment. Limited data has been reported currently. No serious adverse events were observed.
Authors administered ivermectin on an empty stomach. Ivermectin is
a lipophilic drug with low aqueous solubility and is better absorbed when
given with food, especially high-fat meals. Administration with a high-fat
meal can significantly increase plasma and tissue concentrations (~2.5x plasma
concentration in Guzzo) and reduce time to onset of action.
Standard practice for systemic use of ivermectin is administration with food
(for intestinal parasitic infections, systemic distribution may not be
required). Specifying fasted administration may avoid or delay the attainment
of therapeutic concentrations and raises concerns about possible investigator
bias.
This is the 21st of 53 COVID-19 RCTs for ivermectin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000087.
This is the 44th of 106 COVID-19 controlled studies for ivermectin, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of no improvement, 31.6% lower, RR 0.68, p = 0.28, treatment 13 of 50 (26.0%), control 19 of 50 (38.0%), NNT 8.3, patients with improvement on WHO scale, day 7.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 31.8% lower, RR 0.68, p = 0.21, treatment 15 of 50 (30.0%), control 22 of 50 (44.0%), NNT 7.1, patients with improvement on WHO scale, day 6.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 36.0% lower, RR 0.64, p = 0.10, treatment 16 of 50 (32.0%), control 25 of 50 (50.0%), NNT 5.6, patients with improvement on WHO scale, day 5.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 34.5% lower, RR 0.66, p = 0.07, treatment 19 of 50 (38.0%), control 29 of 50 (58.0%), NNT 5.0, patients with improvement on WHO scale, day 4.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Huvemek et al., 25 Mar 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Bulgaria, preprint, 1 author, average treatment delay 7.0 days, dosage 400μg/kg days 1-3, trial EudraCT2020-002091-12.