Overview of Iron and Zinc Intake in COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Students at Poltekkes Kemenkes Bandung
et al., Jurnal Inovasi Bahan Lokal dan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat, doi:10.34011/jibpm.v4i1.3399, Jul 2025
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
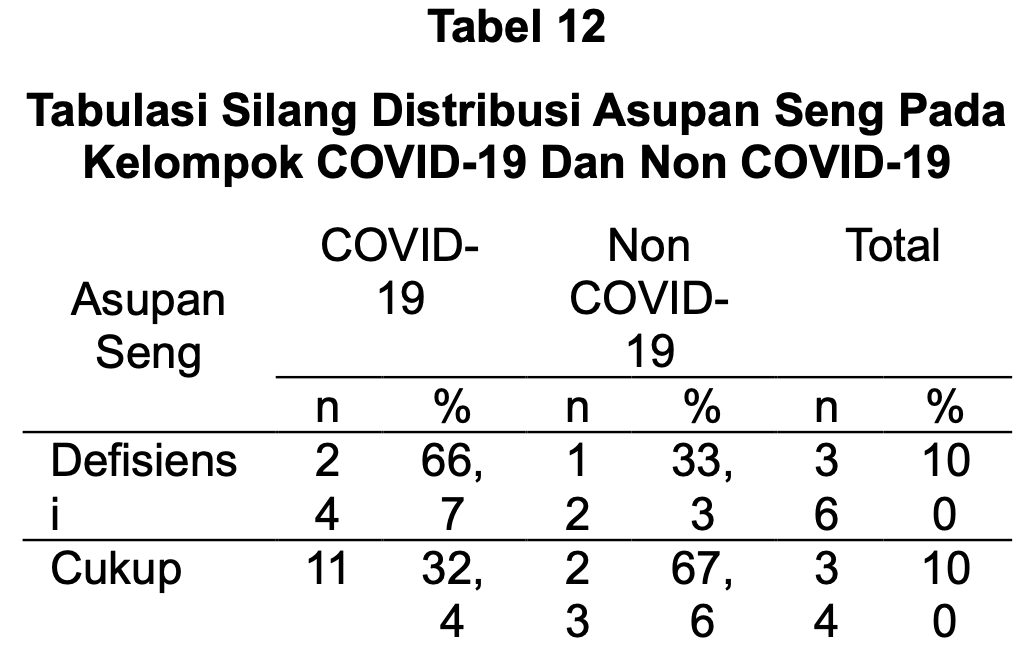
Case control study with 70 students in Indonesia. For zinc, 67% of those with deficient intake had COVID-19 compared to 32% with sufficient intake.
|
risk of case, 76.1% lower, OR 0.24, p = 0.005, high zinc levels 11 of 35 (31.4%) cases,
23 of 35 (65.7%) controls, NNT 2.9, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Nafisah et al., 29 Jul 2025, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period December 2020 - February 2021.
Contact: guridmulyo@gmail.com.
GAMBARAN ASUPAN BESI DAN SENG PADA COVID-19 DAN NON COVID-19 MAHASISWA POLTEKKES KEMENKES BANDUNG Overview of Iron and Zinc Intake in COVID-19 and Non-COVID-19 Students at Poltekkes Kemenkes Bandung
doi:10.34011/jibpm.v4i1.3399
COVID-19 is an infectious disease that causes symptoms ranging from mild to severe, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Inadequate intake of micronutrients such as iron and zinc tends to increase the risk of infection from SARS-CoV-2. This study aims to determine the overview of iron and zinc intake between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 student groups at Poltekkes Kemenkes Bandung, Cimahi area. The study design was cross-sectional with a total sample of 70 respondents. The sampling technique used was Proportional Random Sampling. Collected data included sample characteristics, COVID-19 status, iron intake, and zinc intake. The data were analyzed descriptively. The results showed that among samples with deficient iron intake, 58.7% had experienced COVID-19 and 41.3% had not (non-COVID-19), while among those with sufficient iron intake, 33.3% had experienced COVID-19 and 66.7% had not. For zinc intake, among those with deficient intake, 66.7% had experienced COVID-19 and 33.3% had not, while among those with sufficient zinc intake, 32.4% had experienced COVID-19 and 67.6% had not. To meet iron and zinc needs, students should increase their intake of these nutrients through food or supplements to boost immunity during the pandemic.
References
Almatsier, PRINSIP DASAR ILMU GIZI
Ambarwati, Peran Zinc terhadap Peningkatan Sistem Imunitas, Jurnal Keperawatan
Biswas, Rahaman, Bizwas, Haque, Ibrahim, Association of Sex, Age, and Comorbidities with Mortality in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Intervirology
Dhok, Butola, Anjankar, Shinde, Kute et al., Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Improving Immunity during Covid-19 Pandemic -A Review, Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences, doi:10.14260/jemds/2020/497
Gunard, Pemeriksaan Diagnosis Laboratorium COVID-19 : Keterbatasan dan Tantangannya Saat Ini Laboratory Diagnostic Tests for COVID-19, Current Limitations and Challenges
Han, Yang, The transmission and diagnosis of 2019 novel coronavirus infection disease (COVID-19): A Chinese perspective, Journal of Medical Virology
Handarini, Wulandari, Pembelajaran Daring Sebagai Upaya Study From Home (SFH), Jurnal Pendidikan Administrasi Perkantoran (JPAP)
Handayani, Penyakit Virus Corona 2019, Jurnal Respirologi Indonesia
Jin, Yang, Ji, Wu, Chen et al., Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of covid-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12040372
Kemenkes, Pedoman Pencegahan dan Pengendalian Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
Kemenkes, Peta Sebaran
Kemenkes, TABEL KOMPOSISI PANGAN INDONESIA 2017
Kesehatan, PMK RI NO 28 TAHUN 2019 TENTANG ANGKA KECUKUPAN GIZI YANG DIANJURKAN UNTUK MASYARAKAT INDONESI
Khoirul, Penerapan metode probabilitas dalam analisis defisiensi asupan kalsium, besi, seng dan vitamin d pada anak dan remaja indonesia khoirul anwar
Kumar, Kumar, Kumar, Bedi, Gupta et al., Role of vitamins and minerals as immunity boosters in COVID-19, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00826-7
Liu, Cong, Wang, Mei, Peng et al., Risk of Malnutrition Is Common in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: A Cross-sectional Study, Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1093/jn/nxab009
Lubis, Ramadhani, Rasyid, Stres Akademik Mahasiswa dalam Melaksanakan Kuliah Daring Selama Masa Pandemi Covid 19, Psikostudia : Jurnal Psikologi, doi:10.30872/psikostudia.v10i1.5454
Lv, Chen, Liang, Liu, Gao et al., Association between iron status and the risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19, Clinical Nutrition
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Nur, Permatasari, Mawaddah, REVIEW ARTIKEL: FAKTOR RISIKO PASIEN TERINFEKSI COVID-19 DAN METODE PENCEGAHANNYA, Farmaka
Nurbaiti, GIZI MIKRO KEDOKTERAN JILID II
Par'i, Penilaian Status Gizi : Dilengkapi Proses Asuha Gizi Terstandar
Purwati, Karsari, Dinaryanti, Hendrianto, Syaiful Ihsan et al., The Potency of Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) and Natural Killer (NK) Cells as A Therapeutic of SARS-CoV-2 Indonesia Isolates Infection by Viral Inactivation (In Vitro Study), Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy
Putri, Hubungan Usia, Jenis Kelamin Dan Gejala Dengan COVID-19 di Sumatera barat, Artikel Penelitian
Ransun, Maureen, Punuh, Gambaran Kecukupan Mineral Mikro Pada Mahasiswa Semester 2 Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat Universitas Sam Ratulangi Manado Selama Masa Pandemi Covid-19, Kesmas
Richardson, Lovegrove, Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: A UK perspective, British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S000711452000330X
Royani, Irwan, Arifin, Pengaruh Mengkonsumsi Teh Setelah Makan terhadap Anemia Defisiensi Besi pada Remaja Putri, UMI Medical Journal, doi:10.33096/umj.v2i2.22
Sediaoetama, achmad djaeni, Ilmu Gizi
Shakoor, Feehan, Al, Ali, Platat et al., Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: Could they help against COVID-19?
Sirajuddin, Astuti, SURVEY KONSUMSI PANGAN
Siswanto, Fitrah, PERAN BEBERAPA ZAT GIZI MIKRO DALAM SISTEM IMUNITAS, GIZI INDONESIA, doi:10.36457/gizindo.v36i1.116
Suega, Interrelasi Besi Dengan Sitokin Dan Vice Versa, Journal of Internal Medicine
Sumarmi, Kerja Harmoni Zat Gizi dalam Meningkatkan Imunitas Tubuh Terhadap Covid-19: Mini Review, Amerta Nutrition
Susilo, Rumende, Pitoyo, Santoso, Yulianti et al., Coronavirus Disease 2019: Tinjauan Literatur Terkini, Jurnal Penyakit Dalam Indonesia, doi:10.7454/jpdi.v7i1.415
Velthuis, Shakoor, Feehan, Al, Ali et al., Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Weßels, Rolles, John Slusarenko, Rink, Zinc deficiency as a possible risk factor for increased susceptibility and severe progression of COVID-19, British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000738
Who, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
Who, WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard
Winaktu, Peran Zinc pada Respons Imun, Jurnal Kedokteran Meditek
Wolff, Nee, Hickey, Marschollek, Risk factors for Covid-19 severity and fatality: a structured literature review, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-020-01509-1
Zhang, Penninger, Li, Zhong, Slutsky, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target, Intensive Care Medicine, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05985-9
