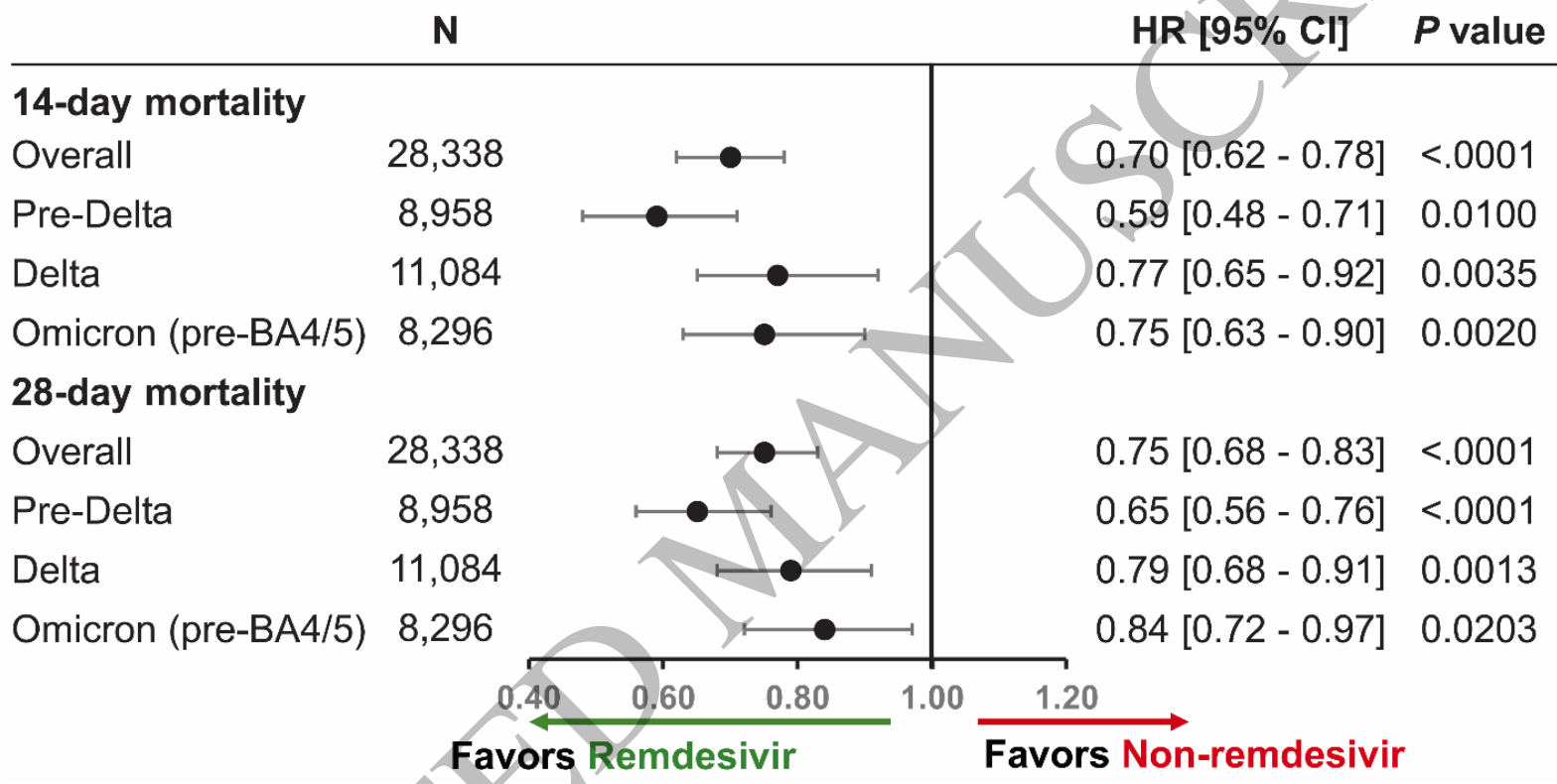
Remdesivir reduced mortality in immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 across variant waves: Findings from routine clinical practice.
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad460, Aug 2023
Retrospective 19,184 immunocompromised patients treated with remdesivir and matched controls, showing lower mortality with treatment. Several authors work at Gilead and the study was funded by Gilead.
The majority of patients were treated with remdesivir. A significant fraction of non-remdesivir patients may have contraindications that also increase risk. Authors provide serum creatine for 26% of the cohort, but notably provide only median and IQR, not allowing comparison of the number of patients with high values. Authors state that "renal function was not significantly different" between remdesivir and non-remdesivir patients, but this does not seem realistic given the prevalence of renal impairment and the contraindictions for remdesivir.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
Remdesivir efficacy disappears with longer
followup. Mixed-effects meta-regression of efficacy as a function of
followup duration across all remdesivir studies shows decreasing efficacy with
longer followup15. This may reflect
antiviral efficacy being offset by serious adverse effects of treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments16.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 25.0% lower, HR 0.75, p < 0.001, treatment 14,169, control 5,341, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 30.0% lower, HR 0.70, p < 0.001, treatment 14,169, control 5,341, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, Cox proportional hazards, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
13.
Mohammed et al., Bradycardia associated with remdesivir treatment in coronavirus disease 2019 patients: A propensity score-matched analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000044501.
Mozaffari et al., 9 Aug 2023, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 1 December, 2020 - 30 April, 2022.
Contact: akalil@unmc.edu, robert.gottlieb@bswhealth.org.
Remdesivir reduced mortality in immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 across variant waves: Findings from routine clinical practice.
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad460
Background: Immunocompromised patients are at high risk of severe COVID-19 and death, yet treatment strategies for immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 reflect variations in clinical practice. This comparative effectiveness study investigated the effect of remdesivir treatment on inpatient mortality among immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 across all variants of concern (VOC) periods.
References
Ao, The association between severe or death COVID-19 and solid organ transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Transplant Rev (Orlando)
Aydillo, Shedding of Viable SARS-CoV-2 after Immunosuppressive Therapy for Cancer, N Engl J Med
Baek, COVID-19-related outcomes in immunocompromised patients: A nationwide study in Korea, PLOS ONE
Beigel, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, New England Journal of Medicine
Beigel, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, The New England journal of medicine
Bhimraj, Shumaker, Baden, Cheng, Edwards et al., Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19
Cacho, Use of remdesivir in kidney transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infection, Kidney International
Chokkalingam, Association of Remdesivir Treatment With Mortality Among Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19 in the United States, JAMA Network Open
Crothers, Dexamethasone in hospitalised COVID-19 patients not on intensive respiratory support, Eur Respir J
Dougan, Bamlanivimab plus Etesevimab in Mild or Moderate Covid-19
Ferdinands, Waning of vaccine effectiveness against moderate and severe covid-19 among adults in the US from the VISION network: test negative, case-control study, BMJ
Focosi, Monoclonal antibody therapies against SARS-CoV-2, Lancet Infect Dis
Garibaldi, Comparison of Time to Clinical Improvement With vs Without Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19, JAMA Network Open
Garibaldi, Real-World Effectiveness of Remdesivir in Adults Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Retrospective, Multicenter Comparative Effectiveness Study, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Gottlieb, Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients
Group, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19
Jary, Spike Gene Evolution and Immune Escape Mutations in Patients with Mild or Moderate Forms of COVID-19 and Treated with Monoclonal Antibodies Therapies, Viruses
Jung, Steroid use in elderly critically ill COVID-19 patients, Eur Respir J
Koh, Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab and remdesivir for early treatment of high-risk hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score adjusted retrospective cohort study, Journal of Medical Virology
Lambrou, Genomic Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Predominance of the Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variants -United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Lee, Efficacy of covid-19 vaccines in immunocompromised patients: systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ
Les, Methylprednisolone Pulses in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Without Respiratory Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial, Front Med (Lausanne)
Mackenna, Risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes associated with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases and immune-modifying therapies: a nationwide cohort study in the OpenSAFELY platform, Lancet Rheumatol
Mbaeyi, The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices' Interim Recommendations for Additional Primary and Booster Doses of COVID-19 Vaccines -United States, 2021, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Mozaffari, Remdesivir treatment in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a comparative analysis of in-hospital all-cause mortality in a large multi-center observational cohort, Clin Infect Dis
Pasin, Corticosteroids for Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) With Different Disease Severity: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth
Paul, Genomic Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 Variants Circulating in the United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Piccicacco, Real-world effectiveness of early remdesivir and sotrovimab in the highestrisk COVID-19 outpatients during the Omicron surge, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Planas, Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature
Rajme-López, Early Outpatient Treatment With Remdesivir in Patients at High Risk for Severe COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study, Open Forum Infectious Diseases
Shoham, Vaccines and therapeutics for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19. eClinicalMedicine
Singson, Factors Associated with Severe Outcomes Among Immunocompromised Adults Hospitalized for COVID-19 -COVID-NET, 10 States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Song, Risk and Outcome of Breakthrough COVID-19 Infections in Vaccinated Patients With Cancer: Real-World Evidence From the National COVID Cohort Collaborative, J Clin Oncol
Spinner, Effect of Remdesivir vs Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients With Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA
Sun, Association Between Immune Dysfunction and COVID-19 Breakthrough Infection After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in the US, JAMA Internal Medicine
Tartof, Analysis of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake Among Immunocompromised Individuals in a Large US Health System, JAMA Network Open
Trøseid, Immunocompromised patients have been neglected in COVID-19 trials: a call for action, Clinical Microbiology and Infection
Turtle, Outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalised immunocompromised patients: An analysis of the WHO ISARIC CCP-UK prospective cohort study, PLOS Medicine
Van Doesum, Impact of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and monoclonal antibodies on outcome post-CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy: an EPICOVIDEHA survey, Blood Adv
Vijenthira, Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3377 patients, Blood
Wilhelm, Limited neutralisation of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.2 by convalescent and vaccine serum and monoclonal antibodies. eBioMedicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad460",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad460",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Immunocompromised patients are at high risk of severe COVID-19 and death, yet treatment strategies for immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 reflect variations in clinical practice. This comparative effectiveness study investigated the effect of remdesivir treatment on inpatient mortality among immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 across all variants of concern (VOC) periods.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Data for immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 between December 2020 and April 2022 were extracted from the US PINC AI Healthcare Database. Patients initiating remdesivir within two days of hospitalization were matched 1:1 using propensity score matching with replacement to patients who did not receive remdesivir during their hospitalization for COVID-19. Additional matching criteria included admission month, age group, and hospital. Cox Proportional Hazards models were used to examine the effect of remdesivir on risk of 14- and 28-day mortality during VOC periods.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 19,184 remdesivir patients were matched to 11,213 non-remdesivir patients. Overall, 11.1% and 17.7% of remdesivir patients died within 14 and 28 days, respectively, compared with 15.4% and 22.4% of non-remdesivir patients. Remdesivir was associated with a reduction in mortality at 14 days (hazard ratio [95% confidence interval]: 0.70 [0.62–0.78]) and 28 days (0.75 [0.68–0.83]). Survival benefit remained significant during the Pre-Delta, Delta, and Omicron time-periods.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Prompt initiation of remdesivir in immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 is associated with significant survival benefit across all variant waves. These findings provide much-needed evidence relating to the effectiveness of a foundational treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients among a high-risk population.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Foster City , California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mozaffari",
"given": "Essy",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara, New York , New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chandak",
"given": "Aastha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Baylor University Medical Center , Dallas, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott & White Heart and Vascular Hospital , Dallas, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott & White The Heart Hospital , Plano, Texas , USA"
},
{
"name": "Baylor Scott & White Research Institute , Dallas, Texas , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gottlieb",
"given": "Robert L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UCLA Health , Torrance, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chima-Melton",
"given": "Chidinma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara , London , United Kingdom"
}
],
"family": "Read",
"given": "Stephanie H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Certara , Paris , France"
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Heng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Foster City , California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Chiang",
"given": "Mel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Foster City , California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "EunYoung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Foster City , California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Rikisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences, Foster City , California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6489-6294",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Nebraska Medical Center , Omaha, Nebraska , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kalil",
"given": "Andre C",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-08T04:31:21Z",
"timestamp": 1691469081000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-09T18:52:17Z",
"timestamp": 1691607137000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-10T04:31:13Z",
"timestamp": 1691641873145
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691539200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad460/51077887/ciad460.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad460/51077887/ciad460.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad460/7240094"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Remdesivir reduced mortality in immunocompromised patients hospitalized for COVID-19 across variant waves: Findings from routine clinical practice.",
"type": "journal-article"
}