Clinical outcomes of using remdesivir in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A prospective randomised study
et al., Indian Journal of Anasthesia, doi:10.4103/ija.IJA_149_21, Mar 2021
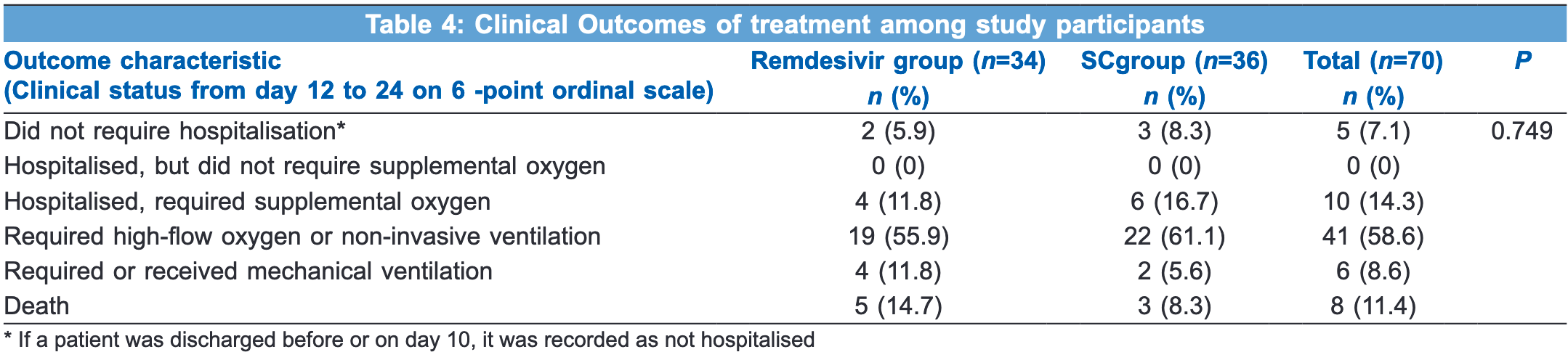
Small RCT with 34 remdesivir patients and 36 controls finding no significant difference in clinical outcomes.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 76.5% higher, RR 1.76, p = 0.47, treatment 5 of 34 (14.7%), control 3 of 36 (8.3%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 111.8% higher, RR 2.12, p = 0.42, treatment 4 of 34 (11.8%), control 2 of 36 (5.6%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Mahajan et al., 20 Mar 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period June 2020 - December 2020, average treatment delay 6.84 days.
Clinical outcomes of using remdesivir in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A prospective randomised study
Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, doi:10.4103/ija.ija_149_21
Background and Aims: When the world was frantically searching for a drug effective against the coronavirus disease (COVID)-19, remdesivir, a broad-spectrum anti-viral medication, became a part of the COVID treatment. We planned a study to evaluate improvement in clinical outcomes with remdesivir treatment for five days. Methods: Participants more than 40-years old and with moderate to severe COVID-19 but not on mechanical ventilation were randomly assigned into two groups-remdesivir group (34 cases) to receive the study drug intravenous (IV) remdesivir for five days plus the standard care (SC) and non-remdesivir group (36 cases) to receive the SC but not to receive the study drug. Follow-up was continued for 12 days after the beginning of treatment or until discharge/death. Patient's clinical status was assessed by laboratory investigations and physical examination (from day 1 to day 12 on a 4-point ordinal scale and from day 12 to 24 on a 6-point ordinal scale). Oxygen support requirements and adverse events were recorded. The data were entered and analysed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 22.0. Results: High-flow oxygen support and non-invasive ventilation was required at baseline by lesser patients in the remdesivir group. In the end, both groups had similar outcomes after adjustment for baseline clinical status. There was no statistical difference in mortality between the two groups (p = 0.749). Patients in both groups had an equal time to recovery. There was no difference in the occurrence of adverse effects of remdesivir between the two groups. Conclusion: Remdesivir therapy for five days did not produce improvement in clinical outcomes in moderate to severe COVID-19 cases.
Conflicts of interest There are no conflicts of interest.
References
Bajwa, Editing from the dungeons of the pandemic; An editor's agonisingly painful battle with COVID-19, Indian J Anaesth
Bajwa, Sarna, Bawa, Mehdiratta, Peri-operative and critical care concerns in corona virus pandemic, Indian J Anaesth
Biegel, Tomashek, Lori, Mehta, Barry et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid -19 -Final Report, N Engl J Med
Fauci, Lane, Field Rr, Covid-19 -Navigating the uncharted, N Engl J Med
Goldman, David, Hui, Marks, Bruno et al., Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid -19, N Engl J Med
Mulangu, Dodd, Jr, Mbaya, Proschan et al., A randomized, controlled trial of Ebola virus disease therapeutics, N Engl J Med
O'keeffe, Ambler, Barber, Sample size calculations based on a difference in medians for positively skewed outcomes in health care studies, BMC Med Res Methodol, doi:10.1186/s12874-017-0426-1
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, Lopez, Cattelan et al., Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Wang, Zhang, Guanhua, Ronghui, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial, Lancet
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Meade-White, Porter et al., Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.15.043166
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ija.ija_149_21",
"ISSN": [
"0019-5049"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/ija.IJA_149_21",
"alternative-id": [
"311599"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahajan",
"given": "Lakshmi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "AP",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gifty",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Indian Journal of Anaesthesia",
"container-title-short": "Indian J Anaesth",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-20T07:59:19Z",
"timestamp": 1616227159000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-20T08:25:27Z",
"timestamp": 1616228727000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-14T19:01:44Z",
"timestamp": 1710442904431
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 46,
"issue": "13",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "13",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"member": "2581",
"original-title": [],
"page": "41",
"prefix": "10.4103",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Medknow",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2002387",
"article-title": "Covid-19 -” Navigating the uncharted",
"author": "Fauci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1268",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ija.IJA_1280_20",
"ISSN": "http://id.crossref.org/issn/0019-5049",
"article-title": "Editing from the dungeons of the pandemic; An editor's agonisingly painful battle with COVID-19",
"author": "Bajwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "831",
"issn-type": "print",
"journal-title": "Indian J Anaesth",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ija.IJA_272_20",
"ISSN": "http://id.crossref.org/issn/0019-5049",
"article-title": "Peri-operative and critical care concerns in corona virus pandemic",
"author": "Bajwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"issn-type": "print",
"journal-title": "Indian J Anaesth",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019- nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.15.043166",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-5",
"unstructured": "Williamson BN, Feldmann F, Schwarz B, Meade-White K, Porter DP, Schulz J, et al. Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020.doi: 10.1101/2020.04.15.043166."
},
{
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-6",
"unstructured": "Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Emergency use authorization (EUA) forremdesivir.May 1, 2020. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docsznda/2020/EUA%20Review%20Remdesivir_050120.pdf. [Last accessed on 2021 Feb 01]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1910993",
"article-title": "A randomized, controlled trial of Ebola virus disease therapeutics",
"author": "Mulangu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2293",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid -19 –Final Report",
"author": "Biegel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12874-017-0426-1",
"article-title": "Sample size calculations based on a difference in medians for positively skewed outcomes in health care studies?",
"author": "O'Keeffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "BMC Med Res Methodol",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.16349",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1048",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for 5 or 10 days in patients with severe Covid -19",
"author": "Goldman",
"first-page": "1827",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.4103/0019-5049.311599-12",
"year": "200;"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.ijaweb.org/text.asp?2021/65/13/41/311599"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical outcomes of using remdesivir in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A prospective randomised study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "65"
}