Clinical Characteristics of Severe COVID-19 Patients During Omicron Epidemic and a Nomogram Model Integrating Cell-Free DNA for Predicting Mortality: A Retrospective Analysis
et al., Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/IDR.S430101, Oct 2023
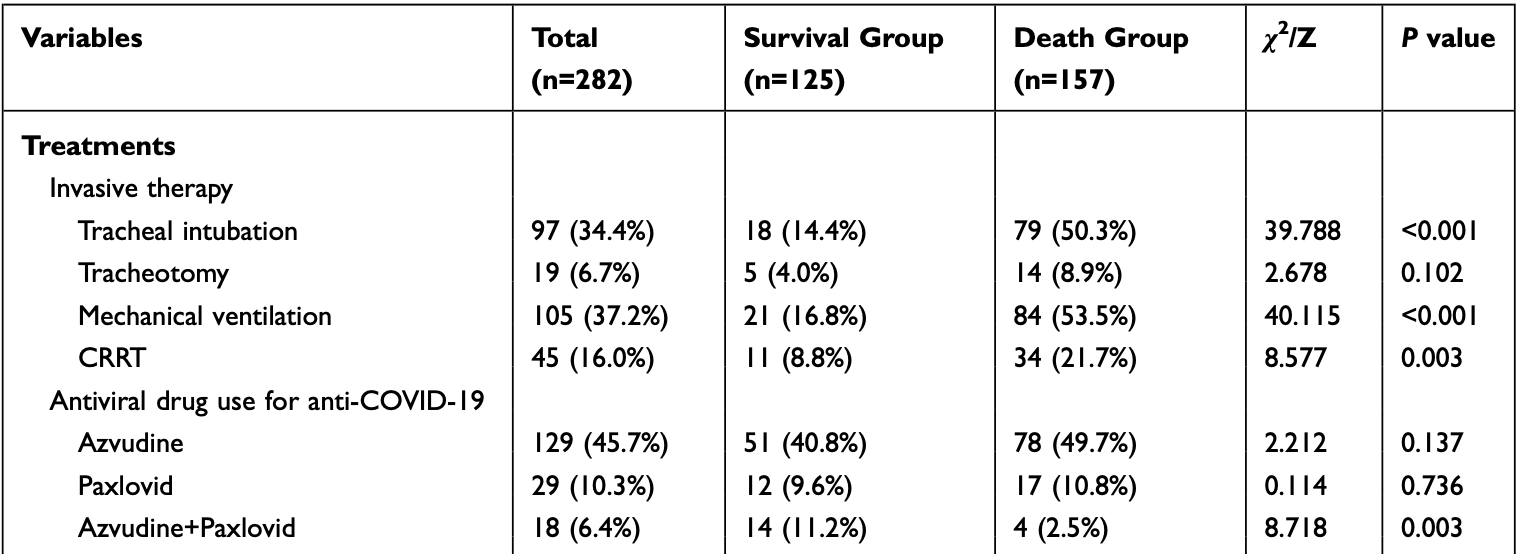
Retrospective 282 severe COVID-19 patients, showing no significant difference in mortality with paxlovid in unadjusted results.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
|
risk of death, 5.9% higher, RR 1.06, p = 0.84, treatment 17 of 29 (58.6%), control 140 of 253 (55.3%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Lu et al., 18 Oct 2023, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 26 September, 2022 - 27 April, 2023.
Contact: sypan@njmu.edu.cn.
Clinical Characteristics of Severe COVID-19 Patients During Omicron Epidemic and a Nomogram Model Integrating Cell-Free DNA for Predicting Mortality: A Retrospective Analysis
Infection and Drug Resistance, doi:10.2147/idr.s430101
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors of death in severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the epidemic of Omicron variants, assess the clinical value of plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA), and construct a prediction nomogram for patient mortality. Methods: The study included 282 patients with severe COVID-19 from December 2022 to January 2023. Patients were divided into survival and death groups based on 60-day prognosis. We compared the clinical characteristics, traditional laboratory indicators, and cfDNA concentrations at admission of the two groups. Univariate and multivariate logistic analyses were performed to identify independent risk factors for death in patients with severe COVID-19. A prediction nomogram for patient mortality was constructed using R software, and an internal validation was performed.
Results: The median age of the patients included was 80.0 (71.0, 86.0) years, and 67.7% (191/282) were male. The mortality rate was 55.7% (157/282). Age, tracheal intubation, shock, cfDNA, and urea nitrogen (BUN) were the independent risk factors for death in patients with severe COVID-19, and the area under the curve (AUC) for cfDNA in predicting patient mortality was 0.805 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.713-0.898, sensitivity 81.4%, specificity 75.6%, and cut-off value 97.67 ng/mL). These factors were used to construct a prediction nomogram for patient mortality (AUC = 0.856, 95% CI: 0.814-0.899, sensitivity 78.3%, and specificity 78.4%), C-index was 0.856 (95% CI: 0.832-0.918), mean absolute error of the calibration curve was 0.007 between actual and predicted probabilities, and Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed no statistical difference (χ2=6.085, P=0.638).
Conclusion: There was a high mortality rate among patients with severe COVID-19. cfDNA levels ≥97.67 ng/mg can significantly increase mortality. When predicting mortality in patients with severe COVID-19, a nomogram based on age, tracheal intubation, shock, cfDNA, and BUN showed high accuracy and consistency.
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Alimohamadi, Tola, Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, Janani, Sepandi, Case fatality rate of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Prev Med Hyg, doi:10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.2.1627
Andargie, Tsuji, Seifuddin, Cell-free DNA maps COVID-19 tissue injury and risk of death and can cause tissue injury, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.147610
Bello, Lasierra, Vergara, IL-6 and cfDNA monitoring throughout COVID-19 hospitalization are accurate markers of its outcomes, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-023-02426-1
Blumlein, Griffiths, Shock: aetiology, pathophysiology and management, Br J Nurs, doi:10.12968/bjon.2022.31.8.422
Chang, Wan, Fu, Severe versus common COVID-19: an early warning nomogram model, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.203832
Chen, Pan, Xie, Development and evaluation of a duplex real-time PCR assay with a novel internal standard for precise quantification of plasma DNA, Ann Lab Med, doi:10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.18
Cheng, Bai, Yang, Chou, Ning, Construction and validation of mortality risk nomograph model for severe/critical patients with COVID-19, Diagnostics
Do, Manabe, Vu, Clinical characteristics and mortality risk among critically ill patients with COVID-19 owing to the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant in Vietnam: a retrospective observational study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0279713
Fiolet, Kherabi, Macdonald, Ghosn, Peiffer-Smadja, Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: a narrative review, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.005
Fredj, Ghammem, Zammit, Risk factors for severe Covid-19 breakthrough infections: an observational longitudinal study, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-022-07859-5
Jin, Wang, Xu, Plasma cell-free DNA promise monitoring and tissue injury assessment of COVID-19, Mol Genet Genom, doi:10.1007/s00438-023-02014-4
Jing, Ding, Zhang, Trends of SARS-CoV-2 infection in rural area in sentinel community-based surveillance -China, December 2022 to January 2023, China CDC Wkly, doi:10.46234/ccdcw2023.044
Li, Wang, Liu, Exploration of prognostic factors for critical COVID-19 patients using a nomogram model, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-87373-x
Liu, Zhang, Pan, Value of dynamic plasma cell-free DNA monitoring in septic shock syndrome: a case report, World J Clin Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.200
Mckay, Meyers, Rivard, Stankewicz, Stoltzfus et al., Comparison of early and late intubation in COVID-19 and its effect on mortality, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19053075
Moghadas, Vilches, Zhang, The impact of vaccination on COVID-19 outbreaks in the United States, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.27.20240051
Moon, Kim, Kang, Yang, Lee, Prediction of COVID-19-related mortality and 30-day and 60-day survival probabilities using a nomogram, J Korean Med Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e248
Papoutsi, Giannakoulis, Xourgia, Routsi, Kotanidou et al., Effect of timing of intubation on clinical outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of non-randomized cohort studies, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03540-6
Peng, He, Xue, Yang, Liu et al., Role of hypertension on the severity of COVID-19: a review, J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000001116
Rakhsha, Azghandi, Taghizadeh-Hesary, Decision on chemotherapy amidst COVID-19 pandemic: a review and a practical approach from Iran, Infect Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2020.52.4.496
Ranucci, Cell-free DNA: applications in different diseases, Methods Mol Biol
Rhodes, Cecconi, Cell-free DNA and outcome in sepsis, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc11508
Russotto, Rahmani, Parotto, Bellani, Laffey, Tracheal intubation in the critically ill patient, Eur J Anaesthesiol, doi:10.1097/EJA.0000000000001627
Scialo, Amato, Pastore, Matera, Cazzola, ACE2: the major cell entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2, Lung, doi:10.1007/s00408-020-00408-4
Sen, Chakraborty, Kalita, Pathak, Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: understanding the association in light of current evidence, World J Clin Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8327
Shao, Li, Liu, Tian, Luo et al., Acute kidney injury is associated with severe infection and fatality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 studies and 24,527 patients, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105107
Standl, Annecke, Cascorbi, Heller, Sabashnikov et al., The nomenclature, definition and distinction of types of shock, Dtsch Arztebl Int, doi:10.3238/arztebl.2018.0757
Thakur, Ratho, OMICRON (B.1.1.529): a new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern mounting worldwide fear, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27541
Tu, Wang, Geng, Guo, Cui et al., Establishment of a clinical nomogram model to predict the progression of COVID-19 to severe disease, Ther Clin Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/TCRM.S308961
Wang, Lu, Song, Zhou, Liu et al., epidemiology of antibiotic resistance and the mechanisms of resistance development and diffusion in both hospitals and the community, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.997713
Wang, Zhong, Zhang, Liao, Cao, Risk factor analysis and nomogram construction for non-survivors among critical patients with COVID-19, Jpn J Infect Dis, doi:10.7883/yoken.JJID.2020.227
Warren-Gash, Davidson, Strongman, Severe COVID-19 outcomes by cardiovascular risk profile in England in 2020: a population-based cohort study, Lancet Region Health Europe, doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100604
Xia, Gao, Dai, Liquid biopsy for non-invasive assessment of liver injury in hepatitis B patients, World J Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3985
Yang, Zhu, Huang, Nomogram for prediction of fatal outcome in patients with severe COVID-19: a multicenter study, Military Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-021-00315-6
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the "Cytokine Storm" in COVID-19, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037
Zarębska-Michaluk, Jaroszewicz, Rogalska, Impact of kidney failure on the severity of COVID-19, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10092042
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
Zhang, Dong, Liu, Gao, Risk and protective factors for COVID-19 morbidity, severity, and mortality, Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, doi:10.1007/s12016-022-08921-5
Zhang, Zhang, Wu, Risks and features of secondary infections in severe and critical ill COVID-19 patients, Emerg Microb Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1812437
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Wang, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2147/idr.s430101",
"ISSN": [
"1178-6973"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S430101",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6514-7095",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Yanfei",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2359-1379",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Wenying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miao",
"given": "Shuxian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Ting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Fang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Jian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2759-6858",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mu",
"given": "Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Bingfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Shiyang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infection and Drug Resistance",
"container-title-short": "IDR",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-18T05:35:06Z",
"timestamp": 1697607306000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-18T05:35:18Z",
"timestamp": 1697607318000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-19T05:19:36Z",
"timestamp": 1697692776055
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/getfile.php?fileID=93566",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/getfile.php?fileID=93566",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "6735-6745",
"prefix": "10.2147",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.2.1627",
"author": "Alimohamadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E311",
"journal-title": "J Prev Med Hyg",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.203832",
"author": "Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "544",
"journal-title": "Aging",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.46234/ccdcw2023.044",
"author": "Jing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "China CDC Wkly",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100604",
"author": "Warren-Gash",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100604",
"journal-title": "Lancet Region Health Europe",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10092042",
"author": "Zarębska-Michaluk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2042",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2020.52.4.496",
"author": "Rakhsha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "496",
"journal-title": "Infect Chemother",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v9.i28.8327",
"author": "Sen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8327",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/FJC.0000000000001116",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e648",
"journal-title": "J Cardiovasc Pharmacol",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27541",
"author": "Thakur",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1821",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40779-021-00315-6",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Military Med Res",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e248",
"author": "Moon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e248",
"journal-title": "J Korean Med Sci",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.200",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "200",
"journal-title": "World J Clin Cases",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-023-02426-1",
"author": "Bello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.3985",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3985",
"journal-title": "World J Gastroenterol",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc11508",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "170",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.147610",
"author": "Andargie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00438-023-02014-4",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "Mol Genet Genom",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "298",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.18",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "Ann Lab Med",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "General Office of the National Health Commission PGD, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment Plan for novel coronavirus infection (trial version 10). China Med. 2023;02:161–166."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0279713",
"author": "Do",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0279713",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7883/yoken.JJID.2020.227",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "452",
"journal-title": "Jpn J Infect Dis",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-87373-x",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8192",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics12102562",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2562",
"journal-title": "Diagnostics",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-022-07859-5",
"author": "Ben Fredj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S308961",
"author": "Tu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "553",
"journal-title": "Ther Clin Risk Manag",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.005",
"author": "Fiolet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.27.20240051",
"author": "Moghadas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/dmrr.3377",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3377",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Res Rev",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00408-020-00408-4",
"author": "Scialo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "Lung",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12016-022-08921-5",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Clin Rev Allergy Immunol",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "607",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-8973-7_1",
"author": "Ranucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "1909",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03540-6",
"author": "Papoutsi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EJA.0000000000001627",
"author": "Russotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Eur J Anaesthesiol",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19053075",
"author": "McKay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3075",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1812437",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1958",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microb Infect",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12968/bjon.2022.31.8.422",
"author": "Blumlein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "422",
"journal-title": "Br J Nurs",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3238/arztebl.2018.0757",
"author": "Standl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Dtsch Arztebl Int",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105107",
"author": "Shao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "105107",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.997713",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "997713",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.dovepress.com/clinical-characteristics-of-severe-covid-19-patients-during-omicron-ep-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-IDR"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical Characteristics of Severe COVID-19 Patients During Omicron Epidemic and a Nomogram Model Integrating Cell-Free DNA for Predicting Mortality: A Retrospective Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "Volume 16"
}