Advances in the effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment: a comprehensive review
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072, Apr 2025
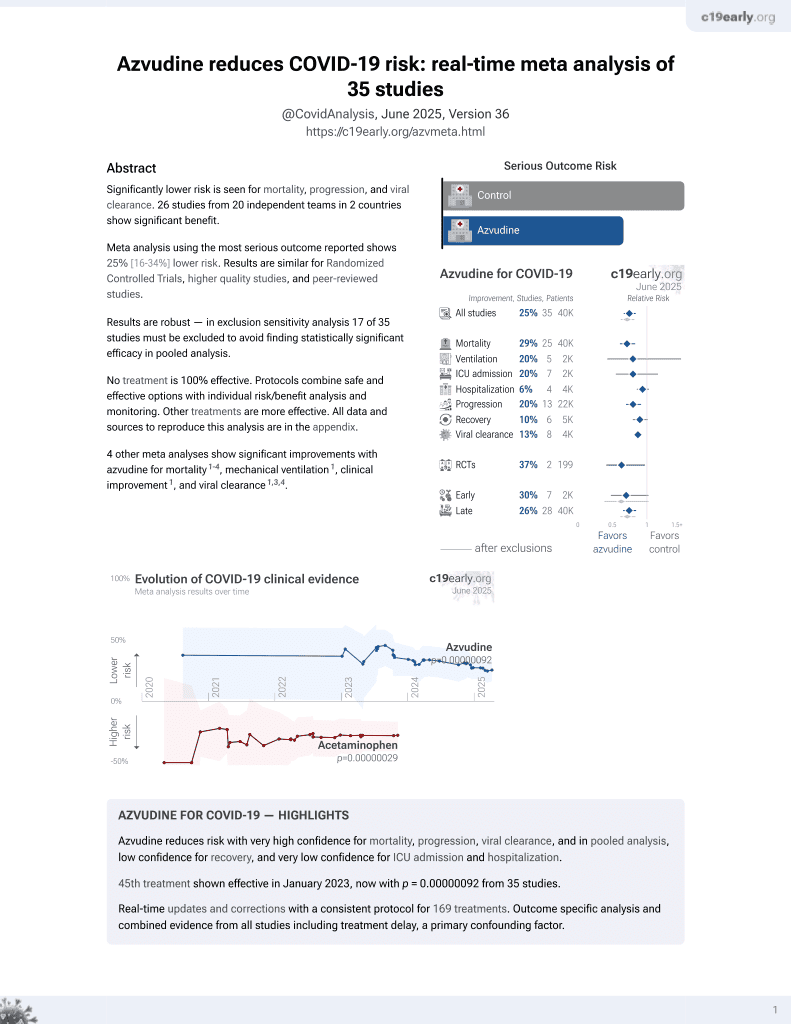
Azvudine for COVID-19
48th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2023, now with p = 0.0000000041 from 40 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
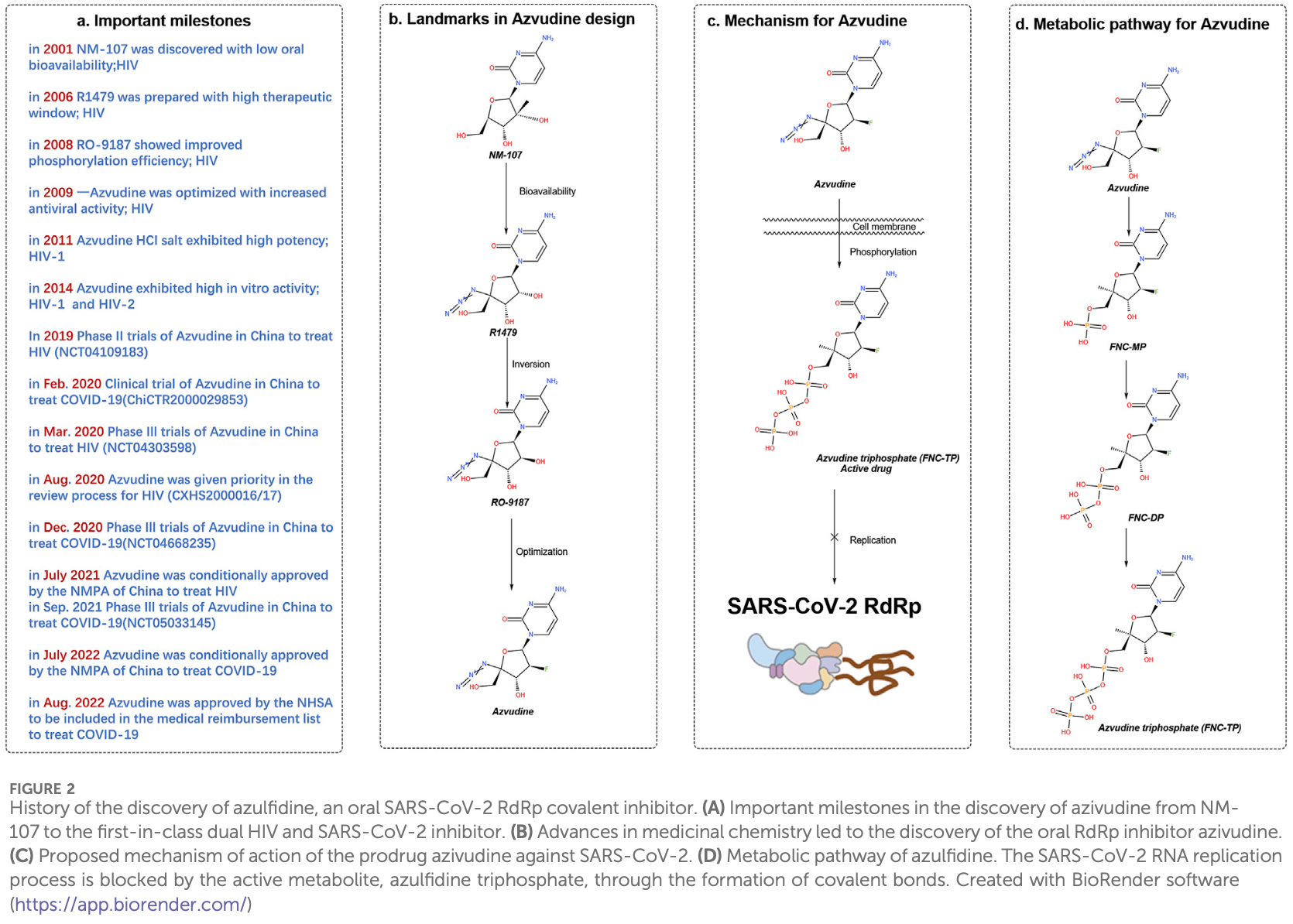
Review of azvudine as a treatment for COVID-19, highlighting its pharmacological properties, clinical effectiveness, and safety profile. Azvudine, a dual-target nucleoside drug initially developed for HIV, received conditional approval from China's National Medical Products Administration in July 2022, becoming the first oral SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor. Authors describe azvudine's mechanism of action, which involves incorporation into viral RNA by RdRp, leading to chain termination and inhibition of viral replication. Clinical trials demonstrated that azvudine reduces viral load, shortens time to viral clearance, and improves clinical outcomes.
Li et al., 25 Apr 2025, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: wenge_lee2002@126.com, zheng.alan@hotmail.com, changjunbiao@zzu.edu.cn, 18810568600@163.com.
Advances in the effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment: a comprehensive review
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072
The global impact of COVID-19 has highlighted the urgent need for effective therapeutic interventions against SARS-CoV-2. Azvudine, a dual-target nucleoside drug initially developed for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), has gained attention for its potential in treating COVID-19. On 25 July 2022, Azvudine received conditional approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China, making it the first oral SARS-CoV-2 RNAdependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitor for COVID-19 treatment. This review explores the pharmacological activity, antiviral mechanisms, and clinical effectiveness of azvudine in the context of COVID-19. Clinical trials have demonstrated its ability to reduce the viral load, shorten the time to nucleic acid negativity, and improve clinical outcomes in patients. Additionally, azvudine has shown excellent pharmacokinetic properties and a favorable safety profile with mild side effects. The review also addresses the importance of drug interactions and safety considerations, particularly in high-risk populations. Research should focus on optimizing second-generation inhibitors with enhanced effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 variants, improving oral bioavailability, and minimizing adverse effects, ensuring more robust treatment options for COVID-19.
Author contributions JyL: Writingoriginal draft, Writingreview and editing. BZ: Conceptualization, Writingreview and editing, Data curation. JnL: Writingreview and editing. ZD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writingreview and editing. PL: Methodology, Project administration, Writingreview and editing. WL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writingoriginal draft. CZ: Supervision, Validation, Writingreview and editing. JC: Writingreview and editing, Investigation. SS: Writingreview and editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writingoriginal draft.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Amani, Amani, Tian, Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Reviews Med. Virology, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153
Cagliari, None
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26234
Da Silva, Gebe Abreu Cabral, De Souza, Arruda, Cabral et al., Serial viral load analysis by DDPCR to evaluate FNC efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of COVID-19, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485
De Souza, Cabral, Da Silva, Arruda, Cabral et al., Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916
Deng, Li, Sun, Jin, Zhou et al., Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28756
Dian, Meng, Sun, Deng, Zeng, Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012
Fu, Pan, Chen, Li, Zheng et al., Comparison of the different medications for COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients, Authorea
Gao, Luo, Ren, Duan, Han et al., Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19
Ju, Wang, Yuan, Xu, Xue et al., Chinese expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment strategies for novel coronavirus infection in Frontiers in Pharmacology frontiersin
Kale, Shelke, Dagar, Anders, Gaikwad, How to use COVID-19 antiviral drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1053814
Klumpp, Kalayanov, Ma, Le Pogam, Leveque et al., 2′-deoxy-4′-azido nucleoside analogs are highly potent inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication despite the lack of 2′-α-hydroxyl groups, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M708929200
Klumpp, Lévêque, Le Pogam, Ma, Jiang et al., The novel nucleoside analog R1479 (4'-azidocytidine) is a potent inhibitor of NS5Bdependent RNA synthesis and hepatitis C virus replication in cell culture, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M510195200
Köklü, Tuna, Gülşen, Demir, Köksal et al., Long-term efficacy and safety of lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir for treatment of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis, Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.003
Ledford, Maxmen, African clinical trial denied access to key COVID drug Paxlovid, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-022-00919-5
Li, None
Li, fphar.2025.1524072 immunocompromised populations (2023 edition), Int. J. Rheumatic Dis, doi:10.1111/1756-185x.14998
Liu, Liu, Zhang, Peng, Huang et al., Intestinal absorption mechanisms of 2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine, a cytidine analog for AIDS treatment, and its interaction with P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistanceassociated protein 2 and breast cancer resistance protein, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2017.05.009
Liu, Wang, Peng, Liu, Ma et al., Effects of the antiretroviral drug 2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine (FNC) on P-gp, MRP2 and BCRP expressions and functions, Pharmazie, doi:10.1691/ph.2018.8555
Ma, Yip, Lui, Lai, Hui et al., Clinical outcomes following treatment for COVID-19 with nirmatrelvir/ ritonavir and Molnupiravir among patients living in nursing homes, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10887
Mazzitelli, Mengato, Sasset, Ferrari, Gardin et al., Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: tolerability, safety, and adherence in a retrospective cohort study, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15020384
Mazzitelli, Trunfio, Sasset, Scaglione, Ferrari et al., Risk of hospitalization and sequelae in patients with COVID-19 treated with 3day early remdesivir vs. controls in the vaccine and Omicron era: a real-life cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28660
Meng, Sun, Liang, Yu, Chang, 2'-Fluorinated nucleoside chemistry for new drug discovery: achievements and prospects, Natl. Sci. Rev, doi:10.1093/nsr/nwae331
Park, Kim, Seo, Jang, Shin et al., Long-term efficacy of entecavir in adefovir-refractory chronic hepatitis B patients with prior lamivudine resistance, J. Viral Hepat, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01479.x
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Ren, Luo, Yu, Song, Liang et al., A randomized, openlabel, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study, Adv. Sci. (Weinh), doi:10.1002/advs.202001435
Shang, Fu, Geng, Zhang, Zhang et al., Azvudine therapy of common COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29007
Shao, Fan, Guo, Huang, Guo et al., Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China, MICROORGANISMS, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11071859
Smith, Kalayanov, Sund, Winqvist, Maltseva et al., The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of monofluoro and difluoro analogues of 4′-azidocytidine against hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of 4′-Azido-2′-deoxy-2′-fluorocytidine and 4′-Azido-2′-dideoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/jm801595c
Smith, Kalayanov, Sund, Winqvist, Pinho et al., The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of 4′-azidocytidine analogues against hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of 4′-azidoarabinocytidine, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/jm800981y
Smith, Martin, Klumpp, Baker, Blomgren et al., Design, synthesis, and antiviral properties of 4'-substituted ribonucleosides as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of R1479, Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett, doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.02.004
Sommadossi, Colla, Methods and compositions using modified nucleosides for treating flaviviruses and pestiviruses
Sommadossi, Colla, Preparation of antiviral nucleosides and methods for treating hepatitis C virus
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Corrigendum to 'Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102110
Sun, Jin, Dian, Shen, Zeng et al., Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981
Thompson, Wynn, O Akerele, Rostad, Anderson et al., Acute pancreatitis associated with dolutegravir and lamivudine/abacavir administration, AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000000542
Wang, Cui, Cheng, Aji, Li et al., Real-world effectiveness and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, retrospective, cohort study, Signal Transduct. Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-025-02126-w
Wang, Hu, Wang, Pan, Tao et al., Synthesis of new 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-4′-azido nucleoside analogues as potent anti-HIV agents, Eur. J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.06.020
Wang, Yang, Luo, Peng, Dai et al., Azvudine, A novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105617
Wang, Yang, Luo, Peng, Dai et al., Azvudine, A novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro, Plos One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0105617
Wei, Zeng, Wang, Gui, Zhang et al., Headto-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294
Yang, Wang, Bench-to-bedside: innovation of small molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs in China, Eur. J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115503
Yu, Chang, Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z
Yu, Chang, The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched, Innovation, doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321
Yuan, Liu, Zhan, Wei, Zhang et al., Characteristics of patients with non-severe infections of different SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants in China, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2024.1511227
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct. Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhang, Li, Wang, Liu, Lu et al., Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6
Zhao, Cheng, Zhang, Qianda, Zhouma et al., Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in tibet: a retrospective study, Infect. DRUG Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S423725
Zhao, Zheng, Han, Feng, Xia et al., Is azvudine comparable to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in real-world efficacy and safety for hospitalized patients with COVID-19? A retrospective cohort study, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7
Zheng, Zhao, Yang, Feng, Xin et al., Small-molecule antiviral treatments for COVID-19: a systematic review and network meta-analysis, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107096
Zhou, Liu, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang et al., Azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19: emulation of a randomized target trial, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29318
Zong, Zhou, Li, Jiang, Liu et al., Azvudine reduces the inhospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study, Acta Pharm. Sin. B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The global impact of COVID-19 has highlighted the urgent need for effective therapeutic interventions against SARS-CoV-2. Azvudine, a dual-target nucleoside drug initially developed for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), has gained attention for its potential in treating COVID-19. On 25 July 2022, Azvudine received conditional approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) of China, making it the first oral SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitor for COVID-19 treatment. This review explores the pharmacological activity, antiviral mechanisms, and clinical effectiveness of azvudine in the context of COVID-19. Clinical trials have demonstrated its ability to reduce the viral load, shorten the time to nucleic acid negativity, and improve clinical outcomes in patients. Additionally, azvudine has shown excellent pharmacokinetic properties and a favorable safety profile with mild side effects. The review also addresses the importance of drug interactions and safety considerations, particularly in high-risk populations. Research should focus on optimizing second-generation inhibitors with enhanced effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 variants, improving oral bioavailability, and minimizing adverse effects, ensuring more robust treatment options for COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jiayi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Bo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Jian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "Zheyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Wenge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Chunfu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Junbiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shang",
"given": "Shunlai",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-25T09:08:04Z",
"timestamp": 1745572084000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-25T09:08:07Z",
"timestamp": 1745572087000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-26T04:03:41Z",
"timestamp": 1745640221403,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1745539200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2551",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Paxlovid in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Amani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2551",
"journal-title": "Reviews Med. Virology",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "B2",
"unstructured": "Center for drug evaluation\n \n \n 2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20153",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of azvudine in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e20153",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26234",
"article-title": "Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2249",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1143485",
"article-title": "Serial viral load analysis by DDPCR to evaluate FNC efficacy and safety in the treatment of mild cases of COVID-19",
"author": "da Silva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1143485",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1215916",
"article-title": "Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: a study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients",
"author": "de Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1215916",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28756",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of Azvudine versus nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e28756",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.05.012",
"article-title": "Azvudine versus Paxlovid for oral treatment of COVID-19 in Chinese patients with pre-existing comorbidities",
"author": "Dian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e24",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.168777909.90198442/v1",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B9",
"volume-title": "Comparison of the different medications for COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.023",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e158",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B12",
"unstructured": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1756-185x.14998",
"article-title": "Chinese expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment strategies for novel coronavirus infection in immunocompromised populations (2023 edition)",
"author": "Ju",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Rheumatic Dis.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1053814",
"article-title": "How to use COVID-19 antiviral drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease",
"author": "Kale",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1053814",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M510195200",
"article-title": "The novel nucleoside analog R1479 (4'-azidocytidine) is a potent inhibitor of NS5B-dependent RNA synthesis and hepatitis C virus replication in cell culture",
"author": "Klumpp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3793",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M708929200",
"article-title": "2′-deoxy-4′-azido nucleoside analogs are highly potent inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication despite the lack of 2′-α-hydroxyl groups",
"author": "Klumpp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2167",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2012.10.003",
"article-title": "Long-term efficacy and safety of lamivudine, entecavir, and tenofovir for treatment of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis",
"author": "Köklü",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-022-00919-5",
"article-title": "African clinical trial denied access to key COVID drug Paxlovid",
"author": "Ledford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "412",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2017.05.009",
"article-title": "Intestinal absorption mechanisms of 2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine, a cytidine analog for AIDS treatment, and its interaction with P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 and breast cancer resistance protein",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1691/ph.2018.8555",
"article-title": "Effects of the antiretroviral drug 2'-deoxy-2'-β-fluoro-4'-azidocytidine (FNC) on P-gp, MRP2 and BCRP expressions and functions",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "Pharmazie",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10887",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes following treatment for COVID-19 with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and Molnupiravir among patients living in nursing homes",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2310887",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28660",
"article-title": "Risk of hospitalization and sequelae in patients with COVID-19 treated with 3-day early remdesivir vs. controls in the vaccine and Omicron era: a real-life cohort study",
"author": "Mazzitelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e28660",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "95",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15020384",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: tolerability, safety, and adherence in a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Mazzitelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "15",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nsr/nwae331",
"article-title": "2'-Fluorinated nucleoside chemistry for new drug discovery: achievements and prospects",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "nwae331",
"journal-title": "Natl. Sci. Rev.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2893.2011.01479.x",
"article-title": "Long-term efficacy of entecavir in adefovir-refractory chronic hepatitis B patients with prior lamivudine resistance",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e475",
"journal-title": "J. Viral Hepat.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2001435",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci. (Weinh)",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "7",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202001435",
"article-title": "A randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trial of azvudine tablets in the treatment of mild and common COVID-19, a pilot study",
"author": "Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2001435",
"journal-title": "Adv. Sci.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "7",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29007",
"article-title": "Azvudine therapy of common COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients",
"author": "Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e29007",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11071859",
"article-title": "Composite interventions on outcomes of severely and critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Shanghai, China",
"author": "Shao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1859",
"journal-title": "MICROORGANISMS",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.02.004",
"article-title": "Design, synthesis, and antiviral properties of 4'-substituted ribonucleosides as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of R1479",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2570",
"journal-title": "Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm800981y",
"article-title": "The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of 4′-azidocytidine analogues against hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of 4′-azidoarabinocytidine",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "52",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm801595c",
"article-title": "The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of monofluoro and difluoro analogues of 4′-azidocytidine against hepatitis C virus replication: the discovery of 4′-Azido-2′-deoxy-2′-fluorocytidine and 4′-Azido-2′-dideoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2971",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "52",
"year": ""
},
{
"article-title": "Methods and compositions using modified nucleosides for treating flaviviruses and pestiviruses",
"author": "Sommadossi",
"journal-title": "Novirio Pharm. Ltd. Univ. Degli Studi Di Cagliari",
"key": "B33",
"year": ""
},
{
"article-title": "Preparation of antiviral nucleosides and methods for treating hepatitis C virus",
"author": "Sommadossi",
"journal-title": "Novirio Pharm. Ltd. Univ. Degli Studi Di Cagliari",
"key": "B34",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101981",
"article-title": "Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101981",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "59",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102110",
"article-title": "Corrigendum to ‘Oral Azvudine for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and pre-existing conditions: a retrospective cohort study.’ [EClinicalMedicine 59 (2023) 101981]",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102110",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "62",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0000000000000542",
"article-title": "Acute pancreatitis associated with dolutegravir and lamivudine/abacavir administration",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "390",
"journal-title": "AIDS",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.06.020",
"article-title": "Synthesis of new 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-4′-azido nucleoside analogues as potent anti-HIV agents",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4178",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0105617",
"article-title": "Azvudine, A novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e105617",
"journal-title": "Plos One",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "9",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0105617",
"article-title": "Azvudine, A novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor showed good drug combination features and better inhibition on drug-resistant strains than lamivudine in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e105617",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "9",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-025-02126-w",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness and safety of oral azvudine versus nirmatrelvir‒ritonavir (Paxlovid) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a multicenter, retrospective, cohort study",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1274294",
"article-title": "Head-to-head comparison of azvudine and nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for the hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a real-world retrospective cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1274294",
"journal-title": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115503",
"article-title": "Bench-to-bedside: innovation of small molecule anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs in China",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "115503",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "257",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00351-z",
"article-title": "Azvudine (FNC): a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xinn.2022.100321",
"article-title": "The first Chinese oral anti-COVID-19 drug Azvudine launched",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100321",
"journal-title": "Innovation",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2024.1511227",
"article-title": "Characteristics of patients with non-severe infections of different SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants in China",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1511227",
"journal-title": "Front. Med. (Lausanne)",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "6",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "6",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00835-6",
"article-title": "Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "414",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "6",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-023-00845-7",
"article-title": "Is azvudine comparable to nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in real-world efficacy and safety for hospitalized patients with COVID-19? A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2087",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Ther.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "12",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S423725",
"article-title": "Efficacy of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir versus azvudine for COVID-19 treatment in tibet: a retrospective study",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6053",
"journal-title": "Infect. DRUG Resist.",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "16",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107096",
"article-title": "Small-molecule antiviral treatments for COVID-19: a systematic review and network meta-analysis",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107096",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29318",
"article-title": "Azvudine and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalized patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19: emulation of a randomized target trial",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e29318",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2023.07.007",
"article-title": "Azvudine reduces the in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4655",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm. Sin. B",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 54,
"references-count": 54,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1524072/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Advances in the effectiveness and safety of azvudine treatment: a comprehensive review",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "16"
}