Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure as Long-Term Mortality Predictor in Elderly Critically Ill with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17020244, Feb 2025
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
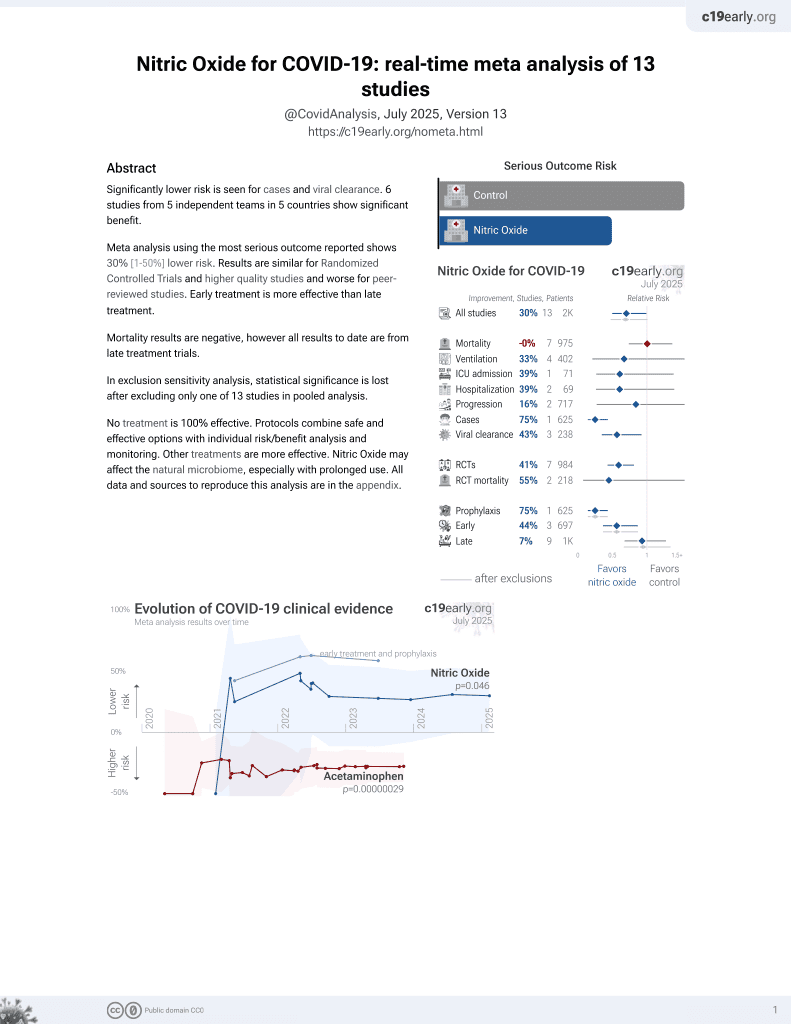
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
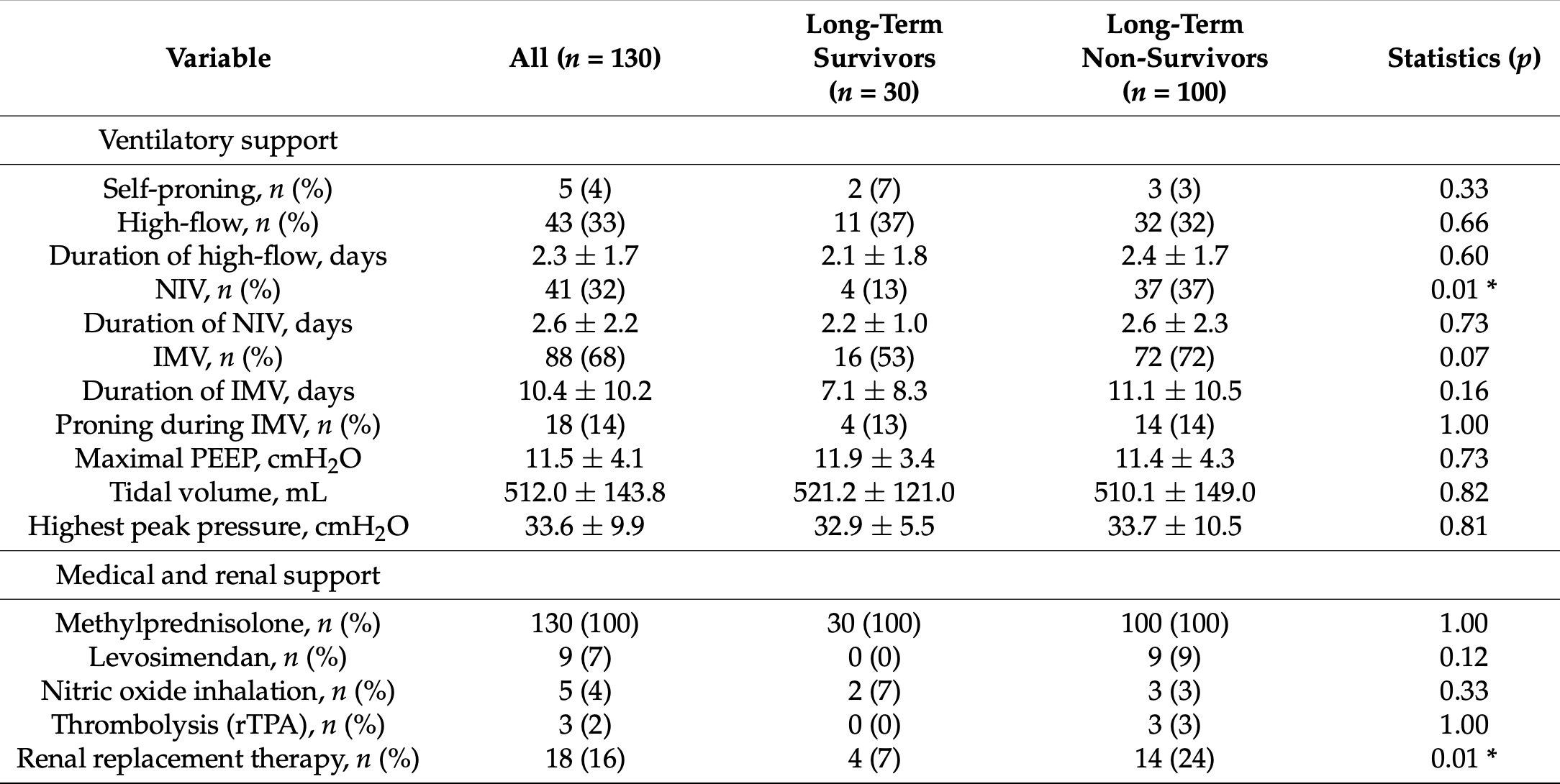
Retrospective 130 elderly (≥70 years) critically ill COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in long-term mortality with nitric oxide.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
Study covers nitric oxide and aspirin.
|
risk of death, 22.7% lower, RR 0.77, p = 0.33, treatment 3 of 5 (60.0%), control 97 of 125 (77.6%), NNT 5.7, day 1000.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kurnik et al., 11 Feb 2025, retrospective, Slovenia, peer-reviewed, mean age 76.8, 3 authors, study period October 2020 - April 2021.
Contact: marko.kurnik@sb-celje.si (corresponding author), helena.bozic@sb-celje.si, matej.podbregar@sb-celje.si.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v17020244",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v17020244",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: COVID-19 can cause acute pulmonary hypertension (PH), worsening outcomes in critically ill elderly patients. Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), assessing right ventricular hemodynamics, predicts short-term outcomes. This study examines the long-term impact of acute PH on mortality in elderly COVID-19 patients. Methods: This retrospective long-term study analyzed data from patients over 70 years old with severe COVID-19 pneumonia admitted to a mixed 25-bed, level 3 intensive care unit (ICU). POCUS focused on systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP) at admission. Mortality was evaluated 1000 days post-admission. Results: The study included 130 patients, comprising 30 long-term survivors and 100 non-survivors, with a cumulative long-term mortality rate of 77%. Non-survivors had significantly higher sPAP values (39.1 ± 12.8 vs. 30.4 ± 9.2, p = 0.04), which were associated with long-term mortality in survival analysis. Conclusion: Acute pulmonary hypertension (PH), reflected by elevated systolic pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP), is strongly associated with long-term mortality in elderly critically ill COVID-19 patients. Early assessment of sPAP via POCUS may help identify high-risk patients and guide management strategies to improve outcomes.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v17020244"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9433-2035",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Intensive Medicine, General Hospital Celje, 3000 Celje, Slovenia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kurnik",
"given": "Marko",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Intensive Medicine, General Hospital Celje, 3000 Celje, Slovenia"
}
],
"family": "Božič",
"given": "Helena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Intensive Medicine, General Hospital Celje, 3000 Celje, Slovenia"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, University of Ljubljana, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia"
}
],
"family": "Podbregar",
"given": "Matej",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-11T14:36:05Z",
"timestamp": 1739284565000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-13T05:50:41Z",
"timestamp": 1739425841000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-13T06:10:15Z",
"timestamp": 1739427015218,
"version": "3.37.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1739232000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/2/244/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "244",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01913-2018",
"article-title": "Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension",
"author": "Simonneau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1801913",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehac237",
"article-title": "2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension",
"author": "Humbert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3618",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1755-5922.2009.00095.x",
"article-title": "The management of acute pulmonary arterial hypertension",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Ther.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12947-023-00300-0",
"article-title": "Pulmonary hypertension at admission predicts ICU mortality in elderly critically ill with severe COVID-19 pneumonia: Retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Kurnik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Ultrasound",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.101004",
"article-title": "Severe Pulmonary Hypertension: An Important Sequel After Severe Post-Acute COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"author": "Rojas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101004",
"journal-title": "Curr. Probl. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202102.0319.v2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Alves, V.P., Casemiro, F.G., Araujo, B.G., Lima, M.A.S., Oliveira, R.S., Fernandes, F.T.S., Gomes, A.V.C., and Gregori, D. (2021). Factors Associated with Mortality among Elderly People in the COVID-19 Pandemic (SARS-CoV-2): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/echo.14837",
"article-title": "Critical care ultrasonography during COVID-19 pandemic: The ORACLE protocol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1353",
"journal-title": "Echocardiography",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hlc.2024.01.036",
"article-title": "The Effect of Pulmonary Hypertension on Mortality and Intensive Care Unit Admission in Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Papageorgiou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1136",
"journal-title": "Heart Lung Circ.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIR.0000000000000560",
"article-title": "Evaluation and Management of Right-Sided Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association",
"author": "Konstam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e578",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resinv.2023.10.001",
"article-title": "Outcomes of patients with elevated pulmonary artery systolic pressure on echocardiography due to chronic lung diseases",
"author": "Salahuddin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Respir. Investig.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/mje.2000.104535",
"article-title": "Doppler-determined peak systolic tricuspid pressure gradient in persons with normal pulmonary function and tricuspid regurgitation",
"author": "Aessopos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "645",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2020.1808462",
"article-title": "MATH+ protocol for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: The scientific rationale",
"author": "Marik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.05.022",
"article-title": "Predicting success of high-flow nasal cannula in pneumonia patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure: The utility of the ROX index",
"author": "Roca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200",
"journal-title": "J. Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20503121231187755",
"article-title": "Pulmonary hypertension predicts higher mortality in patients admitted with severe COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Minkin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20503121231187755",
"journal-title": "SAGE Open Med.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-014-0028-6",
"article-title": "Pulmonary vascular dysfunction in ARDS",
"author": "Ryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/echo.15351",
"article-title": "The role of expert focus echocardiography during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "McPhail",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "701",
"journal-title": "Echocardiography",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5772/67151",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Charolidi, N., and Carroll, V.A. (2017). Hypoxia and Pulmonary Hypertension. Hypoxia and Human Diseases, InTech."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjcard.2023.05.035",
"article-title": "Pulmonary Hypertension in Pulmonary Embolism",
"author": "Arrigo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.49.1.152",
"article-title": "Experimental pulmonary embolism; effect on pulmonary blood volume and vascular compliance",
"author": "Alpert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "49",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77641-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Trecarichi, E.M., Mazzitelli, M., Serapide, F., Pelle, M.C., Tassone, B., Arrighi, E., Perri, G., Fusco, P., Scaglione, V., and Davoli, C. (2020). Clinical characteristics and predictors of mortality associated with COVID-19 in elderly patients from a long-term care facility. Sci. Rep., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0293883",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Santos, M.M.S., Pereira, I.J., Cuboia, N., Reis-Pardal, J., Adriao, D., Cardoso, T., Aragao, I., Santos, L., Sarmento, A., and Rosa, R.G. (2023). Predictors of early and long-term mortality after ICU discharge in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE, 18."
},
{
"article-title": "Short- and long-term survival of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 in relation to cardiovascular risk factors and established cardiovascular disease: The Cor-Cardio study",
"author": "Ostrowska",
"first-page": "16441",
"journal-title": "Pol. Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "ARDS Definition of Task Force, Ranieri, V.M., Rubenfeld, G.D., Thompson, B.T., Ferguson, N.D., Caldwell, E., Fan, E., Camporota, L., and Slutsky, A.S. (2012). Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA, 307, 2526–2533."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-18991-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Benes, J., Jankowski, M., Szuldrzynski, K., Zahorec, R., Lainscak, M., Ruszkai, Z., Podbregar, M., Zatloukal, J., Kletecka, J., and Kusza, K. (2022). SepsEast Registry indicates high mortality associated with COVID-19 caused acute respiratory failure in Central-Eastern European intensive care units. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina57101070",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Feng, T., James, A., Doumlele, K., White, S., Twardzik, W., Zahid, K., Sattar, Z., Ukponmwan, O., Nakeshbandi, M., and Chow, L. (2021). Procalcitonin Levels in COVID-19 Patients Are Strongly Associated with Mortality and ICU Acceptance in an Underserved, Inner City Population. Medicina, 57."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.08.20056598",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Izcovich, A., Ragusa, M.A., Tortosa, F., Lavena Marzio, M.A., Agnoletti, C., Bengolea, A., Ceirano, A., Espinosa, F., Saavedra, E., and Sanguine, V. (2020). Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: A systematic review. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2019.51.3.263",
"article-title": "Prognostic Value of Serum Procalcitonin level for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections in Critically-ill Patients",
"author": "Leelasupasri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Infect. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Long-Term Survival Following Sepsis",
"author": "Schmidt",
"first-page": "775",
"journal-title": "Dtsch. Arztebl. Int.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01426-2022",
"article-title": "Effects of intubation timing in patients with COVID-19 throughout the four waves of the pandemic: A matched analysis",
"author": "Riera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2201426",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.50039",
"article-title": "Risk factors for mortality of critically ill patients with COVID-19 receiving invasive ventilation",
"author": "Tu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1198",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2110-5820-1-6",
"article-title": "Septic cardiomyopathy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Prognostic value of lung ultrasound score performed in the Emergency Department in COVID-19 patients: A prospective multicenter study in central Italy",
"author": "Barbieri",
"first-page": "12268",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Care J.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201002-0250OC",
"article-title": "Pulmonary vascular dysfunction is associated with poor outcomes in patients with acute lung injury",
"author": "Bull",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1123",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM197703032960903",
"article-title": "Pulmonary hypertension in severe acute respiratory failure",
"author": "Zapol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "476",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "296",
"year": "1977"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2045893217753415",
"article-title": "Hemodynamic profile of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in ARDS",
"author": "Calcaianu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2045893217753415",
"journal-title": "Pulm. Circ.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-008-1307-1",
"article-title": "Incidence and prognostic value of right ventricular failure in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Osman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.3762",
"article-title": "Outcomes of Hospitalizations with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with and without Pulmonary Hypertension: An Analysis from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "A5831",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03591-9",
"article-title": "The impact of right ventricular injury on the mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Sato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehx504.P3532",
"article-title": "P3532 Impact of systolic pulmonary artery pressure on long-term all-cause mortality in cardiovascular octogenarian patients",
"author": "Barywani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ehx504.P3532",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12947-020-00198-y",
"article-title": "Prognostic implications of tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion/pulmonary arterial systolic pressure ratio in septic shock patients",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc. Ultrasound",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Long-term predictive value of cardiac biomarkers in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Sabanoglu",
"first-page": "6396",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.09.054",
"article-title": "Onset and frequency of depression in post-COVID-19 syndrome: A systematic review",
"author": "Lui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "J. Psychiatr. Res.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2324709620925571",
"article-title": "Atrial Arrhythmias in a Patient Presenting With Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) Infection",
"author": "Seecheran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2324709620925571",
"journal-title": "J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.radi.2021.10.012",
"article-title": "COVID-19 follow-up: Chest X-ray findings with clinical and radiological relationship three months after recovery",
"author": "Fogante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Radiography",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12041536",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Niebauer, J.H., Binder-Rodriguez, C., Iscel, A., Schedl, S., Capelle, C., Kahr, M., Cadjo, S., Schamilow, S., Badr-Eslam, R., and Lichtenauer, M. (2023). Cardiopulmonary Long-Term Sequelae in Patients after Severe COVID-19 Disease. J. Clin. Med., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2020.1743182",
"article-title": "The long-lasting effects of the acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Mart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/2/244"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure as Long-Term Mortality Predictor in Elderly Critically Ill with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}