Interim analysis of an open‐label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non‐hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019
et al., International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, doi:10.1002/alr.22703, Oct 2020
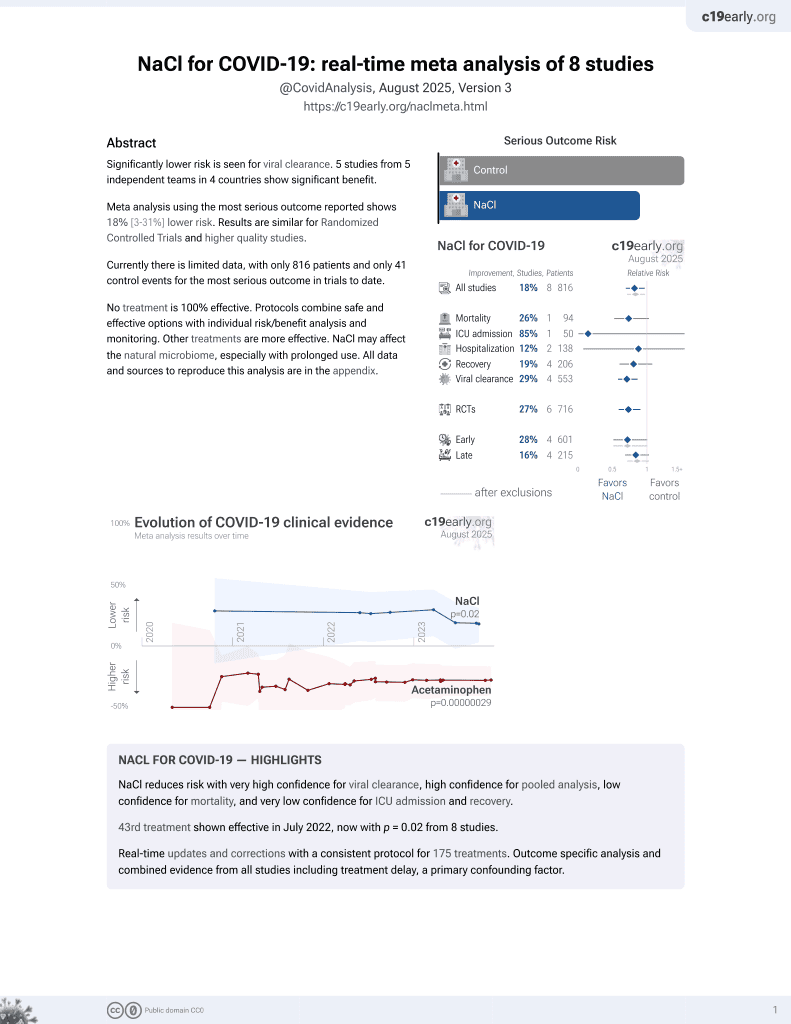
NaCl for COVID-19
44th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2022, now with p = 0.0028 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for progression and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
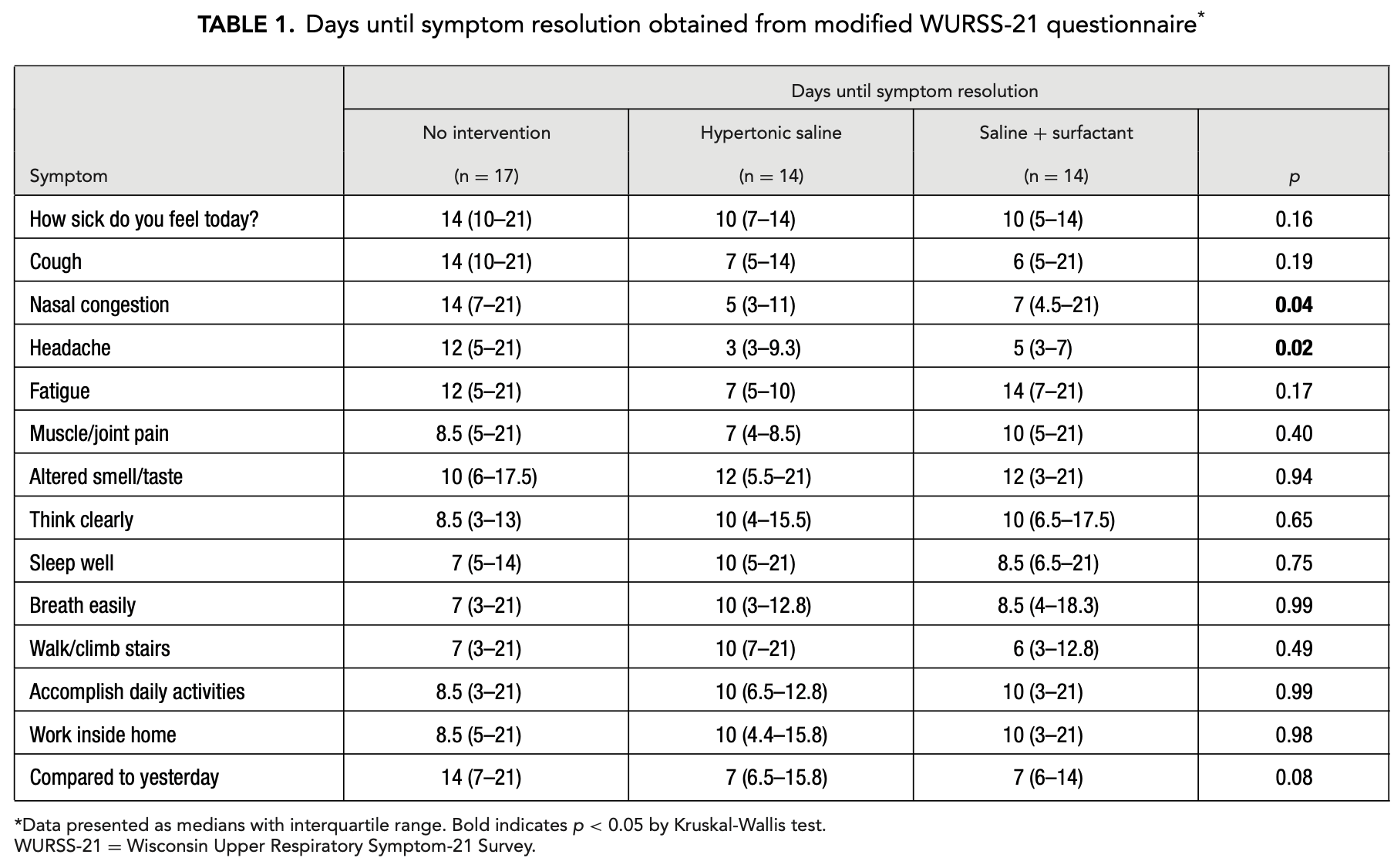
Interim analysis of an open-label RCT of 45 non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing nasal irrigation with hypertonic saline significantly reduced days to symptom resolution for nasal congestion and headache. The study compared three arms: no intervention, twice-daily irrigation with hypertonic saline (HTS), and hypertonic saline with 1% surfactant (HTSS). Patients using HTS and HTSS experienced resolution of nasal congestion (7-9 days sooner) and headache (7-9 days sooner) than the control group. There was also a trend toward earlier overall symptom resolution (14 days for control vs. 10 days for both intervention groups) and improvement in cough and fatigue, though these did not reach statistical significance. Authors recommend hypertonic saline irrigation as a safe, inexpensive intervention for symptom reduction in COVID-19 patients.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
recovery time, 28.6% lower, relative time 0.71, p = 0.16, treatment 14, control 17.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kimura et al., 20 Oct 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: justin.h.turner@vumc.org.
Interim analysis of an open‐label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non‐hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019
International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, doi:10.1002/alr.22703
ysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease Int Forum Allergy Rhinol -Response to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has primarily focused on pharmacologic and medical interventions, including antivirals, 1 convalescent sera, 2 and vaccinations, 3 with each potentially critical in the fight against COVID-19, particularly among high-risk and hospitalized populations. Non-hospitalized patients with mild to moderate disease comprise an estimated 81% of those affected with COVID-19, 4 and there are currently no widely available interventions with proven ability to hasten symptom resolution or reduce viral shedding. We started an open-label randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate the effect of nasal irrigation with hypertonic saline (HTS) or saline with surfactant on upper respiratory symptoms and viral load. Viral shedding is highest in the nasal
References
Barrett, Brown, Mundt, The Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey is responsive, reliable, and valid, J Clin Epidemiol
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, for the ACTT-1 Study Group Members. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2007764
Corbett, Flynn, Foulds, Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2024671
Farrell, Klatt-Cromwell, Schneider, Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemicwashing COVID-19 away, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Jin, Yang, Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19, Viruses
Lee, Yi, Lee, Human rhinovirus serotypes in the nasal washes and mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Ramalingam, Graham, Dove, Morrice, Sheikh, A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold, Sci Rep
Tu, Jennings, Hart, Swabs collected by patients or health care workers for SARS-CoV-2 testing, N Engl J Med
Turner, Wu, Dorminy, Chandra, Safety and tolerability of surfactant nasal irrigation, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Valk, Piechotta, Chai, Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a rapid review, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Zou, Ruan, Huang, SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.22703",
"ISSN": [
"2042-6976",
"2042-6984"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/alr.22703",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/alr.22703"
],
"archive": [
"Portico"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-08-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-09-08"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-10-20"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Kimura",
"given": "Kyle S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "Michael H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Wessinger",
"given": "Bronson C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Veerain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Sheng",
"given": "Quanhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Li Ching",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Von Wahlde",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine Division of Microbiology and Infectious Disease Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Suman R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Naweed I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5501-9900",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville TN"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Justin H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-27T12:12:58Z",
"timestamp": 1601208778000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-07T07:20:40Z",
"timestamp": 1607325640000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"R21 AI142321"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-24T07:26:06Z",
"timestamp": 1643009166313
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 17,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2042-6976"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2042-6984"
}
],
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1603152000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1603152000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/alr.22703",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/alr.22703",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/alr.22703",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1325-1328",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid‐19—preliminary report",
"author": "Beigel JH",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_5_2_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID‐19: a rapid review",
"author": "Valk SJ",
"first-page": "CD013600",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "e_1_2_5_3_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of the mRNA‐1273 vaccine against SARS‐CoV‐2 in nonhuman primates",
"author": "Corbett KS",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_5_4_1"
},
{
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)",
"key": "e_1_2_5_5_1",
"volume-title": "Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001737",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-37703-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.11.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2016321",
"article-title": "Swabs collected by patients or health care workers for SARS‐CoV‐2 testing",
"author": "Tu YP",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "494",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_5_9_1",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1622",
"article-title": "Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic—washing COVID‐19 away",
"author": "Farrell NF",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "787",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "e_1_2_5_10_1",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.21959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12040372",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/alr.21472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_5_13_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Int Forum Allergy Rhinol."
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Otorhinolaryngology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Interim analysis of an open‐label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non‐hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}