Use of Darunavir-Cobicistat as a Treatment Option for Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
et al., Yonsei Medical Journal, doi:10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826, Dec 2020
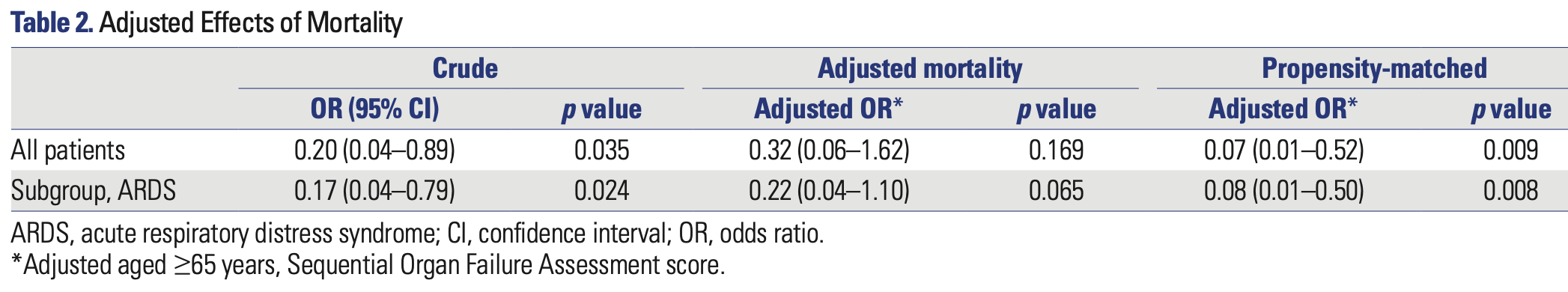
Retrospective 110 critically ill COVID-19 patients in South Korea showing lower mortality with darunavir/cobicistat treatment.
|
risk of death, 86.9% lower, RR 0.13, p = 0.009, treatment 2 of 14 (14.3%), control 14 of 28 (50.0%), NNT 2.8, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kim et al., 31 Dec 2020, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 18 February, 2020 - 5 April, 2020.
Contact: letact@yu.ac.kr.
Use of Darunavir-Cobicistat as a Treatment Option for Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Yonsei Medical Journal, doi:10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a pandemic. Until May 20, 2020, there were more than 4.9 million reported COVID-19 cases and 324869 deaths across more than 200 countries. Currently, there are no specific therapeutic agents for treating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Potential drugs for treating COVID-19 include human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 aspartate protease inhibitors, such as lopinavir and darunavir, which have been shown to inhibit SARS-CoV in vitro, the cause of SARS in humans. [1] [2] [3] [4] Cobicistat-boosted darunavir is a boosted protease inhibitor in a fixed-dose combination that is approved for use in treating HIV type 1 infection. 5, 6 Drug efficacy evaluation in cell models in vitro have revealed that darunavir is active against SARS-CoV-2. 2 At present, however, there are no clinical data on the use of these drugs for COVID-19. Cobicistat-boosted darunavir is stable as a suspension, 7 so it was considered to be suitable for administration as a nasogastric tube to critical ill patients. Here, we evaluated the effects of darunavir-cobicistat on the clinical outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19 using a risk stratification model that adjusted for potential differences between the darunavir-cobicistat treated and non-darunavir-cobicistat treated individuals. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all adults with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who were subsequently admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) at one of the
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization: Eun Young Choi. Data curation: all authors. Formal analysis: Eun Jin Kim and Sun Ha Choi.
References
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Wong, Chan et al., Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax
Curran, Pérez-Valero, Moltó, Rezolsta ® (darunavir/cobicistat): first boosted protease inhibitor co-formulated with cobicistat, AIDS Rev
Dong, Hu, Gao, Discovering drugs to treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Drug Discov Ther
Putcharoen, Do, Avihingsanon, Ruxrungtham, Rationale and clinical utility of the darunavir-cobicistat combination in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, Drug Des Devel Ther
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, Darunavir-Cobicistat with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019
Zanon, Manca, Nicolò, 'avolio, Musazzi et al., Data on the stability of darunavir/cobicistat suspension after tablet manipulation, Data Brief
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826",
"ISSN": [
"0513-5796",
"1976-2437"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"value": "2020-05-21"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"value": "2020-07-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"value": "2020-07-28"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published online",
"name": "published_online",
"value": "2020-08-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Copyright and Licensing",
"name": "Copyright_and_licensing"
},
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2020"
},
{
"explanation": {
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/"
},
"group": {
"label": "Copyright and Licensing",
"name": "Copyright_and_licensing"
},
"label": "License",
"name": "license",
"value": "This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9791-8077",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Eun Jin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9665-7466",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Sun Ha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5751-7209",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Park",
"given": "Jae Seok",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8003-7668",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kwon",
"given": "Yong Shik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8111-7320",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Jaehee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9936-7379",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Yeonjae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2121-7335",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Shin Yup",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2974-5447",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Eun Young",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Yonsei Medical Journal",
"container-title-short": "Yonsei Med J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"eymj.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-02T05:26:41Z",
"timestamp": 1599024401000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-02T05:32:01Z",
"timestamp": 1599024721000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"COVID19-DM18"
],
"name": "Daegu Metropolitan City"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-14T10:34:05Z",
"timestamp": 1747218845747,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1577836800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://eymj.org/pdf/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://eymj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://eymj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "18617",
"original-title": [],
"page": "826",
"prefix": "10.3349",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
},
"publisher": "XMLink",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref2",
"unstructured": "China News Network. Abidol and darunavir can effectively inhibit coronavirus [accessed on 2020 February 5]. Available at: http://www.sd.chinanews.com/2/2020/0205/70145.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5582/ddt.2020.01012",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov Ther",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref3",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Sanders",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Curran",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "AIDS Rev",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref5",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "Putcharoen",
"first-page": "5763",
"journal-title": "Drug Des Devel Ther",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dib.2020.105552",
"author": "Zanon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105552",
"journal-title": "Data Brief",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref7",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826_ref8",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 8,
"references-count": 8,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://eymj.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3349/ymj.2020.61.9.826"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Use of Darunavir-Cobicistat as a Treatment Option for Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3349/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "61"
}