Early Onset Favipiravir Saves Lives
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-142868/v1, Jan 2021
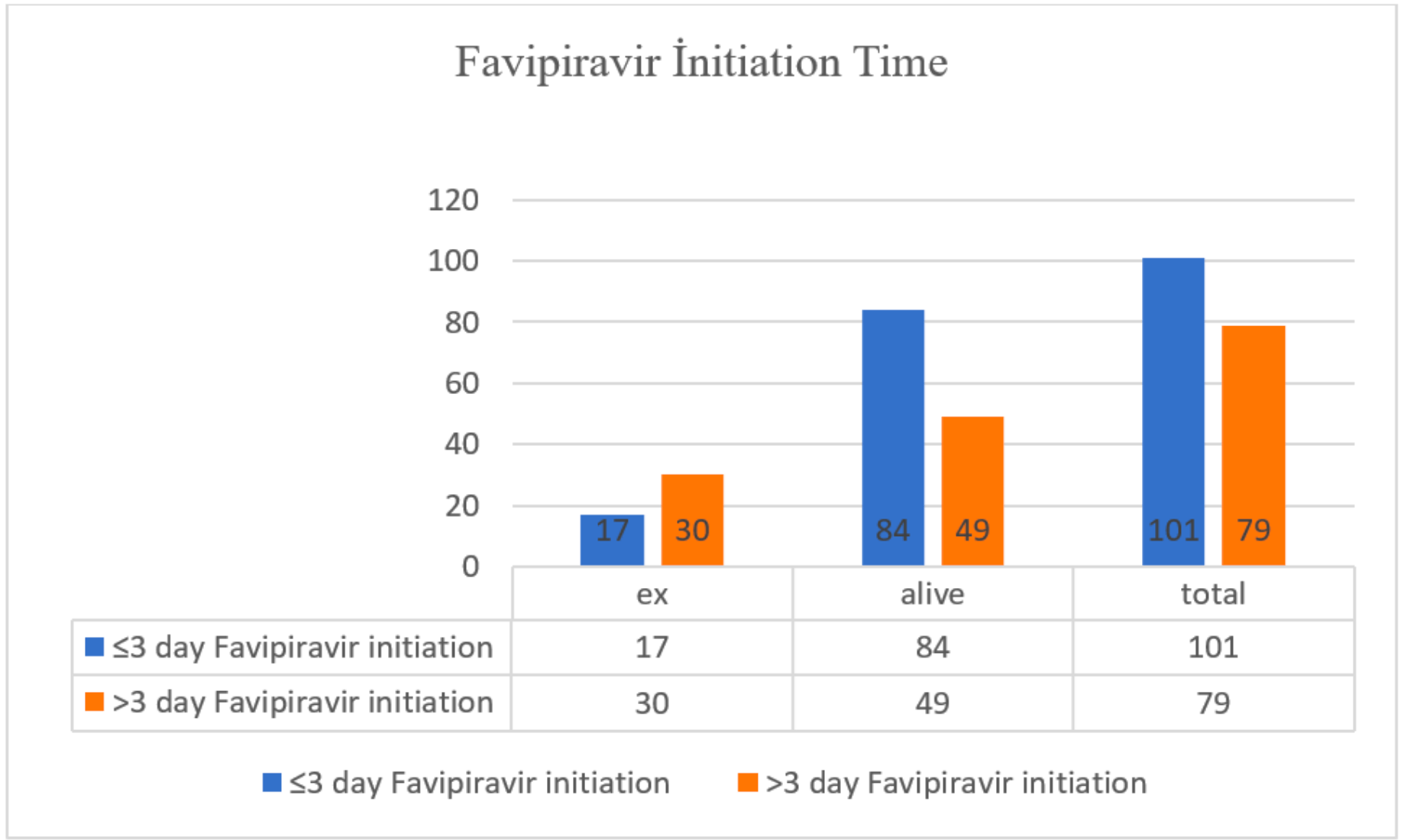
Retrospective 180 hospitalized patients showing lower mortality when Favipiravir is given earlier. 17% of patients given Favipiravir within 3 days died, compared to 38% when given after 3 days.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Karatas et al., 14 Jan 2021, preprint, 5 authors.
Early Onset Favipiravir Saves Lives
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-142868/v1
Background Favipiravir, an antiviral recommended for use in patients with tachypnea (respiratory rate 30 / min) in COVID-19 pneumonia, with SpO2 level below 90% in room air and with bilateral diffuse pneumonia on chest X-ray or tomography, or patients with treatment-resistant fever, is a new type of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitor. After the administration of Favipiravir, it contributed signi cantly to reducing mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 positive disease. We performed this study to determine the start time in Favipiravir's covid pneumonia.
Material and Method: We evaluated the effect of a total of 5 days of oral treatment as a 2 × 1600 mg loading dose and a 2 × 600 mg maintenance dose of Favipiravir added to the standard COVID-19 treatment received by patients with laboratory-radiology-clinical ndings who have advanced or severe COVID 19 pneumonia.
Results 180 patients hospitalized at Tuzla State Hospital and given Favipiravir treatment between 20/3/2020 and 30/5/2020 were examined. As of hospitalization, 17 of 101 patients (17%) who were given Favipiravir treatment in ≤ 3 days died, 30 of 79 patients (38%) who were given Favipiravir treatment for in > 3 days died (p:0.002). 33 of 47 patients (70%) who died were > 65 years old. Only 5 of the 47 (11%) patients who died had no comorbid disease. 35 had two or more comorbid diseases.
Conclusion
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests Authors' contributions EK,LA conceived this review; EK,LA,EÖ performed the literature review and wrote the paper; PEK,AD helped with the review and writing of the paper; all authors read and approved the nal manuscript.
Authors' information Ercan Karatas
References
Aktoz, Altay, Aslanger, Turkish Cardiology Association Consensus Report: COVID-19 Pandemic and Cardiovascular Diseases
Andersen, Rambaut, Lipkin, Holmes, Garry, The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Med
Chan, Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with lopinavir/ritonavir: a multicentre retrospective matched cohort study, Hong Kong Medical Journal
Corman, Muth, Niemeyer, Drosten, Hosts and Sources of Endemic Human Coronaviruses, Adv Virus Res
Doi, Hibino, Hase, A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Trial of Early versus Late Favipiravir Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
García, Immune Response, In ammation, and the Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Goyal, Lurie, Meissner, Modeling HCV cure after an ultra-short duration of therapy with direct acting agents, Antiviral Res
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, The New England journal of medicine
Hsu, Santesso, Mustafa, Brozek, Chen et al., Antivirals for treatment of in uenza: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Annals of internal medicine
Jayaweera, Perera, Gunawardana, Manatunge, Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: A critical review on the unresolved dichotomy, Environ Res
Kalil, Treating COVID-19-Off-Label Drug Use, Compassionate Use, and Randomized Clinical Trials During Pandemics, JAMA
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease
Lima, Information about the new coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Radiologia brasileira
Liu, Yan, Wan, Xiang, Le et al., Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. The Lancet, Infectious diseases
Magleby, Westblade, Trzebucki, Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load on Risk of Intubation and Mortality Among Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive care medicine
Saber-Ayad, Saleh, Abu-Gharbieh, The Rationale for Potential Pharmacotherapy of COVID-19, Pharmaceuticals
Tang, Bidon, Jaimes, Whittaker, Daniel, Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development, Antiviral Res
Uyeki, Bernstein, Bradley, Englund, File et al., Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2018 Update on Diagnosis, Treatment, Chemoprophylaxis, and Institutional Outbreak Management of Seasonal In uenzaa, Infectious Diseases Society of America
Wang, Wang, Chen, Qin, Unique epidemiological and clinical features of the emerging 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) implicate special control measures, Journal of medical virology
Weiss, Jellingsø, Sommer, Spatial and temporal dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, EBioMedicine
Wu, Li, Shi, Chen, Jiang et al., Early antiviral treatment contributes to alleviate the severity and improve the prognosis of patients with novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), J Intern Med
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Yazdanpanah, Hamblin, Rezaei, The immune system and COVID-19: Friend or foe?, Life Sci
Yu, Tian, Chu, COVID-19 patients bene t from early antiviral treatment: A comparative, retrospective study
Zhu, Chen, Gorshkov, Xu, Lo et al., RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase as a Target for COVID-19 Drug Discovery, SLAS Discov
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-142868/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-142868/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Background\n Favipiravir, an antiviral recommended for use in patients with tachypnea (respiratory rate 30 / min) in COVID-19 pneumonia, with SpO2 level below 90% in room air and with bilateral diffuse pneumonia on chest X-ray or tomography, or patients with treatment-resistant fever, is a new type of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitor. After the administration of Favipiravir, it contributed significantly to reducing mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 positive disease. We performed this study to determine the start time in Favipiravir's covid pneumonia.\nMaterial and Method:\n We evaluated the effect of a total of 5 days of oral treatment as a 2 × 1600 mg loading dose and a 2 × 600 mg maintenance dose of Favipiravir added to the standard COVID-19 treatment received by patients with laboratory-radiology-clinical findings who have advanced or severe COVID 19 pneumonia.\nResults\n 180 patients hospitalized at Tuzla State Hospital and given Favipiravir treatment between 20/3/2020 and 30/5/2020 were examined. As of hospitalization, 17 of 101 patients (17%) who were given Favipiravir treatment in ≤ 3 days died, 30 of 79 patients (38%) who were given Favipiravir treatment for in > 3 days died (p:0.002). 33 of 47 patients (70%) who died were > 65 years old. Only 5 of the 47 (11%) patients who died had no comorbid disease. 35 had two or more comorbid diseases.\nConclusion\n Patients with radiological findings indicating that COVID-19 will be severe and laboratory findings at the time of the first 3 days should be initiated with an effective dose of Favipiravir treatment without waiting for the clinical worsening.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3133-4199",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Turkiye Cumhuriyeti Saglik Bakanligi"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "KARATAS",
"given": "Ercan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Marmara Universitesi Tip Fakultesi, Family Practicies"
}
],
"family": "Aksoy",
"given": "Lacin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İstanbul Tuzla State Hospital"
}
],
"family": "Kilic",
"given": "Pinar Elbir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tuzla State Hospital: Tuzla Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Dogru",
"given": "Arzu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Acibadem Hospitals Group: Acibadem Saglik Grubu"
}
],
"family": "Ozaslan",
"given": "Ersin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-15T00:44:19Z",
"timestamp": 1610671459000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-29T00:55:12Z",
"timestamp": 1659056112000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-03T12:35:06Z",
"timestamp": 1709469306410
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
13
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1610496000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-142868/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-142868/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
13
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {
"is-preprint-of": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.3947/ic.2020.0149",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-142868/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Early Onset Favipiravir Saves Lives",
"type": "posted-content"
}