Camostat Mesylate May Reduce Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sepsis: A First Observation
et al., Critical Care Explorations, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000284, Nov 2020
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
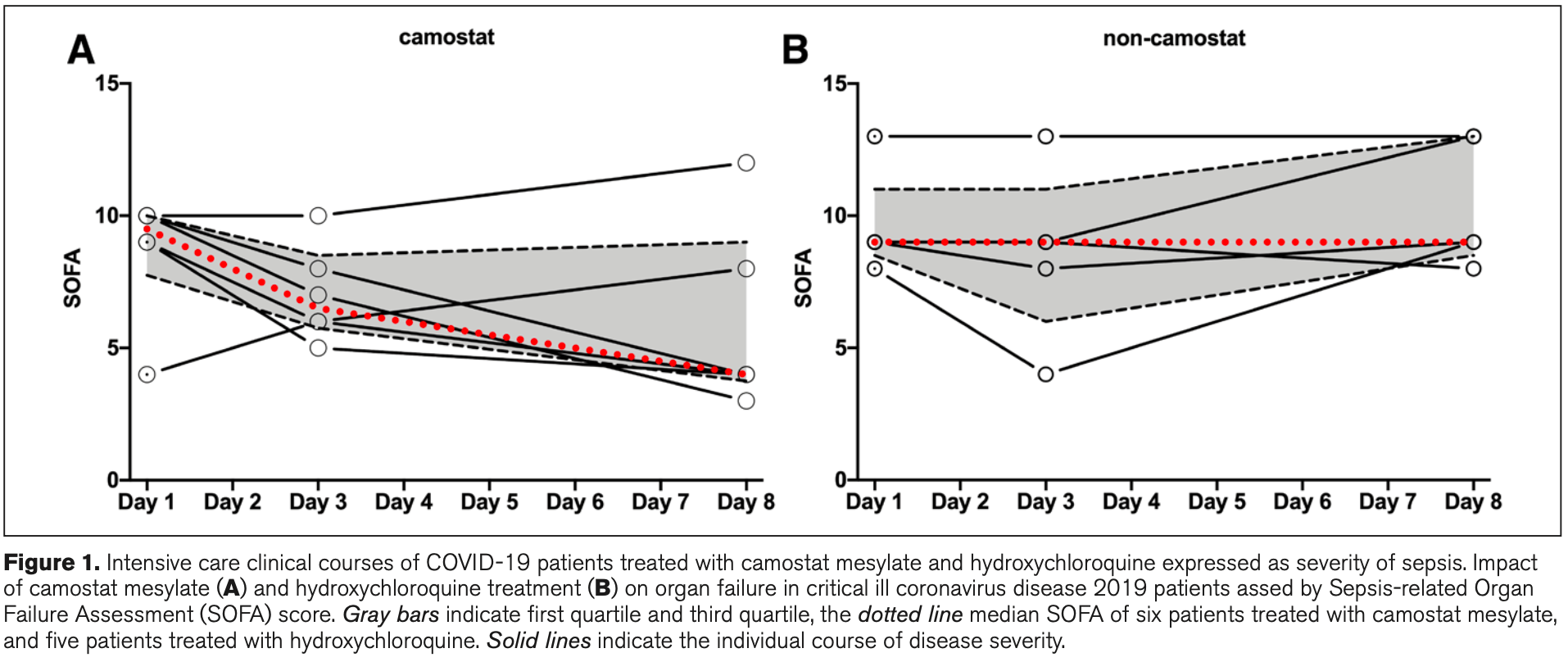
Retrospective 11 critically ill COVID-19 ICU patients with organ failure treated with camostat mesylate (6 patients) or HCQ (5 patients). Over an 8 day period, the severity of COVID-19 decreased in the camostat group as measured by a decline in the SOFA score, inflammatory markers, and improvement in oxygenation. A similar effect was not seen in the HCQ group.
Study covers camostat and HCQ.
|
risk of death, 140.0% higher, RR 2.40, p = 0.55, treatment 2 of 5 (40.0%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%).
|
|
ICU time, 157.1% higher, relative time 2.57, treatment 5, control 6.
|
|
SOFA, 125.0% higher, RR 2.25, treatment 5, control 6, day 8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hofmann-Winkler et al., 16 Nov 2020, retrospective, Germany, peer-reviewed, 19 authors, study period March 2020 - May 2020, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Camostat Mesylate May Reduce Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sepsis: A First Observation
Critical Care Explorations, doi:10.1097/cce.0000000000000284
Objectives: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry depends on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane serine protease 2 and is blocked in cell culture by camostat mesylate, a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Whether camostat mesylate is able to lower disease burden in coronavirus disease 2019 sepsis is currently unknown. Design: Retrospective observational case series. Setting: Patient treated in ICU of University hospital Göttingen, Germany. Patients: Eleven critical ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients with organ failure were treated in ICU. Interventions: Compassionate use of camostat mesylate (six patients, camostat group) or hydroxychloroquine (five patients, hydroxychloroquine group). Measurements and Main Results: Clinical courses were assessed by Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score at days 1, 3, and 8. Further, viral load, oxygenation, and inflammatory markers were determined. Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score was comparable between camostat and hydroxychloroquine groups upon ICU admission. During observation, the Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score decreased in the camostat group but remained elevated in the hydroxychloroquine group. The decline in disease severity in camostat mesylate treated patients was paralleled by a decline in inflammatory markers and improvement of oxygenation. Conclusions: The severity of coronavirus disease 2019 decreased upon camostat mesylate treatment within a period of 8 days and a similar effect was not observed in patients receiving hydroxychloroquine. Camostat mesylate thus warrants further evaluation within randomized clinical trials.
References
Bardou, Menou, François, Membrane-anchored serine protease matriptase is a trigger of pulmonary fibrogenesis, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate Covid-19, New Engl J Med
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill
Das, Bhowmick, Tiwari, An updated systematic review of the therapeutic role of hydroxychloroquine in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19), Clin Drug Investig
Gibo, Ito, Kawabe, Camostat mesilate attenuates pancreatic fibrosis via inhibition of monocytes and pancreatic stellate cells activity, Lab Invest
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Hoffmann, Mösbauer, Hofmann-Winkler, Chloroquine does not inhibit infection of human lung cells with SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Iwata-Yoshikawa, Okamura, Shimizu, TMPRSS2 contributes to virus spread and immunopathology in the airways of murine models after coronavirus infection, J Virol
Maisonnasse, Guedj, Contreras, Hydroxychloroquine use against SARS-CoV-2 infection in non-human primates, Nature
Puelles, Lütgehetmann, Lindenmeyer, Multiorgan and renal tropism of SARS-CoV-2, N Engl J Med
Wu, Wang, Kuo, An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19, Curr Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s40495-020-00216-7
Zhou, Vedantham, Lu, Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry, Antiviral Res
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team: A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/cce.0000000000000284",
"ISSN": [
"2639-8028"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000284",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry depends on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane serine protease 2 and is blocked in cell culture by camostat mesylate, a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Whether camostat mesylate is able to lower disease burden in coronavirus disease 2019 sepsis is currently unknown.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Design:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Retrospective observational case series.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Setting:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Patient treated in ICU of University hospital Göttingen, Germany.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Patients:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Eleven critical ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients with organ failure were treated in ICU.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Interventions:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Compassionate use of camostat mesylate (six patients, camostat group) or hydroxychloroquine (five patients, hydroxychloroquine group).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Measurements and Main Results:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Clinical courses were assessed by Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score at days 1, 3, and 8. Further, viral load, oxygenation, and inflammatory markers were determined. Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score was comparable between camostat and hydroxychloroquine groups upon ICU admission. During observation, the Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment score decreased in the camostat group but remained elevated in the hydroxychloroquine group. The decline in disease severity in camostat mesylate treated patients was paralleled by a decline in inflammatory markers and improvement of oxygenation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The severity of coronavirus disease 2019 decreased upon camostat mesylate treatment within a period of 8 days and a similar effect was not observed in patients receiving hydroxychloroquine. Camostat mesylate thus warrants further evaluation within randomized clinical trials.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center-Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Hofmann-Winkler",
"given": "Heike",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Moerer",
"given": "Onnen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Alt-Epping",
"given": "Sabine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Bräuer",
"given": "Anselm",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Büttner",
"given": "Benedikt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Müller",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Fricke",
"given": "Torben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Grundmann",
"given": "Julian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Harnisch",
"given": "Lars-Olav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Heise",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Kernchen",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Pressler",
"given": "Meike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Neurophysiology, University Medicine Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Stephani",
"given": "Caspar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology, University Medicine Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Tampe",
"given": "Björn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center-Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Kaul",
"given": "Artur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center-Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Gärtner",
"given": "Sabine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center-Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Kramer",
"given": "Stefanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infection Biology Unit, German Primate Center-Leibniz Institute for Primate Research, Göttingen, Germany."
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Biology and Psychology, University Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Pöhlmann",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Emergency and Intensive Care Medicine, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany."
}
],
"family": "Winkler",
"given": "Martin Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Critical Care Explorations",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-17T17:53:24Z",
"timestamp": 1605635604000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-27T20:12:08Z",
"timestamp": 1698437528000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-06T12:35:20Z",
"timestamp": 1722947720476
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 38,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604188800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000284",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0284",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019.",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R1-20231027",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor.",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "R2-20231027",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-020-00927-1",
"article-title": "An updated systematic review of the therapeutic role of hydroxychloroquine in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "591",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "R3-20231027",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19.",
"author": "Wu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "R4-20231027",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045",
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR.",
"author": "Corman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2000045",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "R5-20231027",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate Covid-19.",
"author": "Cavalcanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "New Engl J Med",
"key": "R6-20231027",
"year": "2020 Jul 23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2575-3",
"article-title": "Chloroquine does not inhibit infection of human lung cells with SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "588",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "R7-20231027",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2558-4",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine use against SARS-CoV-2 infection in non-human primates.",
"author": "Maisonnasse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "584",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "R8-20231027",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/labinvest.3700203",
"article-title": "Camostat mesilate attenuates pancreatic fibrosis via inhibition of monocytes and pancreatic stellate cells activity.",
"author": "Gibo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Lab Invest",
"key": "R9-20231027",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201502-0299OC",
"article-title": "Membrane-anchored serine protease matriptase is a trigger of pulmonary fibrogenesis.",
"author": "Bardou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "847",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "R10-20231027",
"volume": "193",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01815-18",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 contributes to virus spread and immunopathology in the airways of murine models after coronavirus infection.",
"author": "Iwata-Yoshikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01815",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "R11-20231027",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2011400",
"article-title": "Multiorgan and renal tropism of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Puelles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "590",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R12-20231027",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.01.011",
"article-title": "Protease inhibitors targeting coronavirus and filovirus entry.",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "R13-20231027",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 13,
"references-count": 13,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/CCE.0000000000000284"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Camostat Mesylate May Reduce Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sepsis: A First Observation",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2"
}
hofmannwinkler
