Multiarm multistage randomised controlled trial of inflammatory signal inhibitors (MATIS) for patients hospitalised with COVID-19 pneumonia during the UK pandemic
et al., BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583, MATIS, NCT04581954, Feb 2026
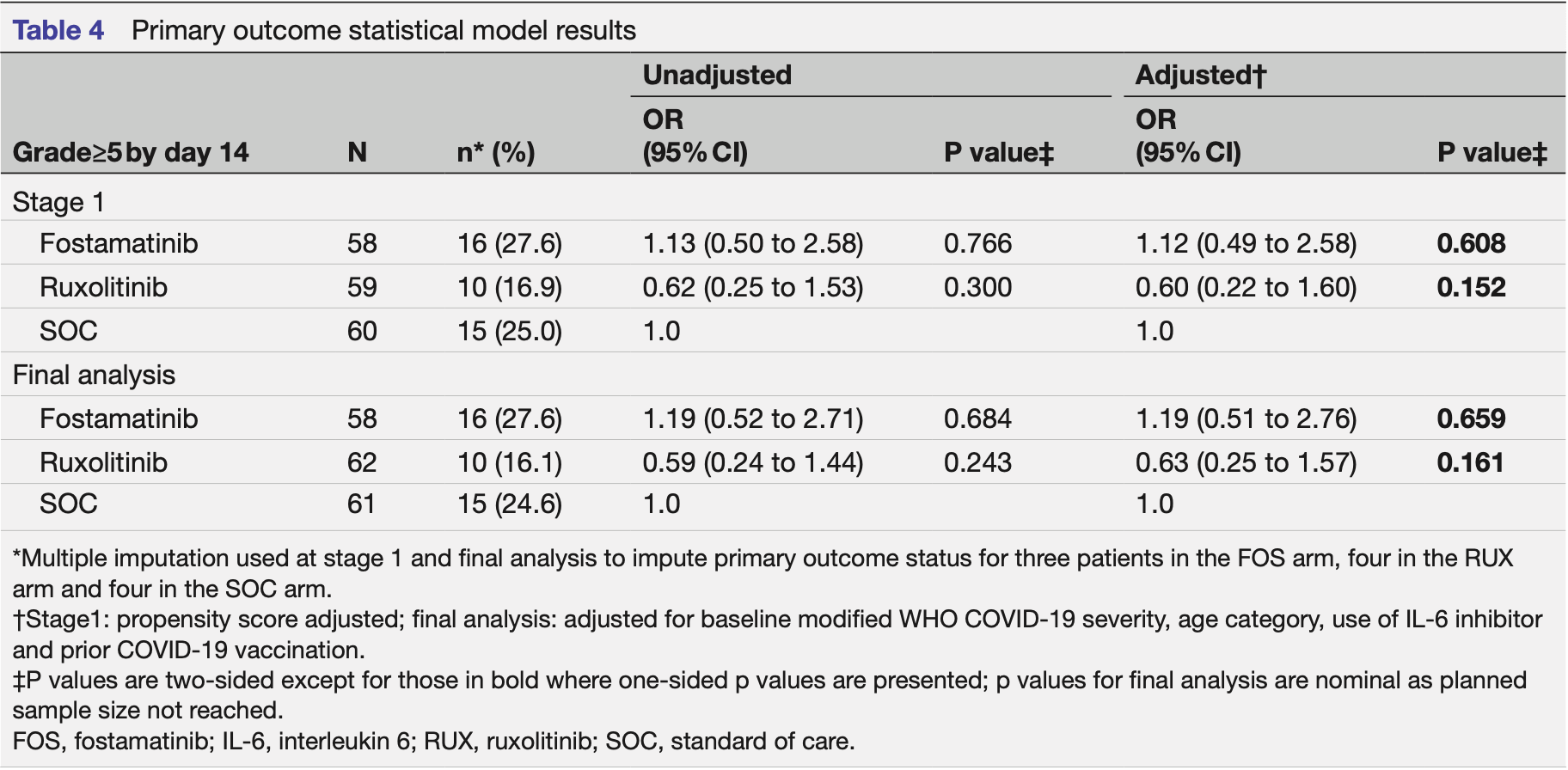
RCT 181 hospitalized COVID-19 pneumonia patients showing no significant benefit with fostamatinib and inconclusive results for ruxolitinib compared to standard care.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the United Kingdom, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
The United Kingdom focused on expensive high-profit treatments, approving only one low-cost early treatment, which required a prescription and had limited adoption. The high-cost prescription treatment strategy reduces the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminates complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 40.2% higher, RR 1.40, p = 0.71, treatment 4 of 58 (6.9%), control 3 of 61 (4.9%), day 14.
|
|
risk of severe case, 19.0% higher, OR 1.19, p = 0.66, treatment 58, control 61, adjusted per study, severe COVID-19 pneumonia, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hazell et al., 5 Feb 2026, Randomized Controlled Trial, United Kingdom, peer-reviewed, 21 authors, study period October 2020 - September 2022, average treatment delay 9.7 days, trial NCT04581954 (history) (MATIS).
Contact: n.cooper@imperial.ac.uk.
Multiarm multistage randomised controlled trial of inflammatory signal inhibitors (MATIS) for patients hospitalised with COVID-19 pneumonia during the UK pandemic
BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583
Objectives To determine the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib (RUX) and fostamatinib (FOS) compared with standard of care (SOC) in patients requiring hospital admission for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia. Design Adaptive multiarm, multistage, randomised, openlabel trial (three arm, two stage). Setting Five hospitals in England between October 2020 and September 2022. Participants Hospitalised patients (≥18 years) with COVID-19 pneumonia defined by a modified WHO COVID-19 severity grade of 3 or 4. Interventions Participants were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to receive RUX (10 mg two times per day for 7 days then 5 mg two times per day for 7 days), FOS (150 mg two times per day for 7 days then 100 mg two times per day for 7 days) or SOC. Main outcome measures Primary outcome was development of severe COVID-19 pneumonia (modified WHO severity grade≥5) within 14 days of randomisation. Secondary outcomes included mortality, invasive and noninvasive ventilation, venous thromboembolism, duration of hospital stay, readmissions, inflammatory markers and serious adverse events (SAEs). Results At stage 1, 181 patients were randomised, with 4 assessed as ineligible post randomisation. FOS was stopped early for futility with 16 participants (27.6%, n=58) developing severe COVID-19 pneumonia compared with 15 (25.0%, n=60) in the SOC arm (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) compared with SOC: 1.12; 95% CI 0.49 to 2.58; p=0.608). RUX progressed to stage 2 but the trial was stopped early due to slow recruitment. At the final analysis, 10 participants (16.1%, n=62) developed severe COVID-19 pneumonia in the RUX arm compared with 15 (24.6%, n=61) in the SOC arm (aOR: 0.63; 95% CI 0.25 to 1.57; p=0.161). Four (7.4%) participants in the FOS arm, none in the RUX arm and three (5.5%) in the SOC arm died within 14 days of randomisation. Infections were the most frequently reported SAE and were numerically higher in the FOS (10, 17.2%) and RUX (10, 16.1%) arms compared with SOC (7, 11.5%). Two unexpected serious adverse reactions occurred in the RUX arm only. Conclusions We found no evidence that FOS was superior to SOC for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients requiring hospital admission. Due to early stopping, the trial was underpowered to establish RUX's effect in this population. Further study is needed.
Ethics approval This study involves human participants. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.The Surrey Research Ethics Committee (REC) and Health Regulator Authority (HRA) reviewed and granted approval for this trial (IRAS ID 282552). Informed consent was obtained for each participant either by the participant themselves or from a relative or an independent treating clinician acting as their legally designated personal representative in the event that the participant lacked capacity to provide consent. Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed. Data availability statement Data are available upon reasonable request. Deidentified participant-level data (excluding free text fields) and supporting documentation (including the MATIS study protocol, Statistical Analysis Plan and data dictionary) can be made available on reasonable request from the corresponding author ( https://profiles.imperial.ac.uk/n.cooper ) for the purposes of scientific research including secondary analysis of the data or for individual participant meta-analysis with appropriate human research ethics approvals and data transfer agreements in place. Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all..
References
Alimova, Sidhom, Satyam, A High Content Screen for Mucin-1-Reducing Compounds Identifies Fostamatinib as a Candidate for Rapid Repurposing for Acute Lung Injury During the COVID-19 Pandemic, bioRxiv, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3650600
Broglie, Pommert, Rao, Ruxolitinib for treatment of refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2017007526
Cao, Wei, Zou, Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019
Cook, Maclennan, Palmer, Instrumental variable methods for a binary outcome were used to informatively address noncompliance in a randomized trial in surgery, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.11.011
Elliott, Whitaker, Tang, Design and Implementation of a National SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring Program in England: REACT-1 Study, Am J Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2023.307230
Gotur, Malik, Markovtsov, Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Who Required Oxygen Supplementation: Results of a Phase 3 Trial, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004
Guimarães, Quirk, Furtado, Tofacitinib in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101643
Hammersen, Birndt, Döhner, The JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in patients with COVID-19 triggered hyperinflammation: the RuxCoFlam trial, Leukemia, doi:10.1038/s41375-023-01979-w
Han, Antila, Ficker, Ruxolitinib in addition to standard of care for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RUXCOVID): a randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00044-3
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
Lhermusier, Van Rottem, Garcia, The Syk-kinase inhibitor R406 impairs platelet activation and monocyte tissue factor expression triggered by heparin-PF4 complex directed antibodies, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04470.x
Malik, Tóth, Teng, Distorted TCR repertoires define multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0274289
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3
Nadeem, Ahmad, No, Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase signaling protects against acute lung injury through blockade of NADPH oxidase and IL-17A in neutrophils and γδ T cells respectively in mice, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.062
Novartis, Jakavi 10mg tablets
Pp, Human, Experimentation, None, Br Med J, doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5402.177
Rein, Calero, Shah, Randomized Phase 3 Trial of Ruxolitinib for COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005682
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Correction to: Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06028-z
Schulz, Altman, Moher, 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.c332
Selvaraj, Finn, Lal, Baricitinib in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101489
Siddiqi, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: A clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant, doi:10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012
Spalton, Mori, Pollitt, The novel Syk inhibitor R406 reveals mechanistic differences in the initiation of GPVI and CLEC-2 signaling in platelets, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03451.x
Strich, Tian, Samour, Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab732
Velavan, Pallerla, Rüter, Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103629
Vergis, Phillips, Cornelius, Multi-arm Trial of Inflammatory Signal Inhibitors (MATIS) for hospitalised patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05190-z
White, Royston, Wood, Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.4067
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583",
"ISSN": [
"2044-6055",
"2044-6055"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To determine the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib (RUX) and fostamatinib (FOS) compared with standard of care (SOC) in patients requiring hospital admission for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Design</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Adaptive multiarm, multistage, randomised, open-label trial (three arm, two stage).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Setting</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Five hospitals in England between October 2020 and September 2022.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Participants</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Hospitalised patients (≥18 years) with COVID-19 pneumonia defined by a modified WHO COVID-19 severity grade of 3 or 4.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Interventions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Participants were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to receive RUX (10 mg two times per day for 7 days then 5 mg two times per day for 7 days), FOS (150 mg two times per day for 7 days then 100 mg two times per day for 7 days) or SOC.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Main outcome measures</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Primary outcome was development of severe COVID-19 pneumonia (modified WHO severity grade≥5) within 14 days of randomisation. Secondary outcomes included mortality, invasive and non-invasive ventilation, venous thromboembolism, duration of hospital stay, readmissions, inflammatory markers and serious adverse events (SAEs).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>At stage 1, 181 patients were randomised, with 4 assessed as ineligible post randomisation. FOS was stopped early for futility with 16 participants (27.6%, n=58) developing severe COVID-19 pneumonia compared with 15 (25.0%, n=60) in the SOC arm (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) compared with SOC: 1.12; 95% CI 0.49 to 2.58; p=0.608). RUX progressed to stage 2 but the trial was stopped early due to slow recruitment. At the final analysis, 10 participants (16.1%, n=62) developed severe COVID-19 pneumonia in the RUX arm compared with 15 (24.6%, n=61) in the SOC arm (aOR: 0.63; 95% CI 0.25 to 1.57; p=0.161). Four (7.4%) participants in the FOS arm, none in the RUX arm and three (5.5%) in the SOC arm died within 14 days of randomisation. Infections were the most frequently reported SAE and were numerically higher in the FOS (10, 17.2%) and RUX (10, 16.1%) arms compared with SOC (7, 11.5%). Two unexpected serious adverse reactions occurred in the RUX arm only.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We found no evidence that FOS was superior to SOC for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia in patients requiring hospital admission. Due to early stopping, the trial was underpowered to establish RUX’s effect in this population. Further study is needed.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration number</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"clintrialgov\" xlink:href=\"NCT04581954\">NCT04581954</jats:ext-link>\n ; EUDRA-CT:\n <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2020-001750-22/GB\">https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2020-001750-22/GB</jats:ext-link>\n .\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
18
]
]
},
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5962-0648",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Clinical Trials Unit, Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hazell",
"given": "Lorna",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Pillay",
"given": "Clio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Clinical Trials Unit, Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Cornelius",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Clinical Trials Unit, Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Charania",
"given": "Asad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4691-126X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Population Health Sciences Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wason",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Population Health Sciences Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK"
}
],
"family": "Cherlin",
"given": "Svetlana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Immunology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, Leeds, UK"
},
{
"name": "University of Leeds, Leeds, West Yorkshire, UK"
}
],
"family": "Savic",
"given": "Sinisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases and Acute Medicine, Northwick Park Hospital, Harrow, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Whittington",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Haemato-Oncology, Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust, Reading, UK"
}
],
"family": "Neelakantan",
"given": "Pratap",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Sheffield, UK"
}
],
"family": "Collini",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Willicome",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Milojkovic",
"given": "Dragana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2647-4688",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Respiratory Medicine, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London, London, UK"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kon",
"given": "Onn Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College London, London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Youngstein",
"given": "Taryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Innes",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction, Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Thursz",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Imperial College London, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "Graham S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Vergis",
"given": "Nikhil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology and Inflammation, Imperial College London, London, UK"
},
{
"name": "Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Nichola",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct04581954",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "BMJ Open",
"container-title-short": "BMJ Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-05T13:51:16Z",
"timestamp": 1770299476000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-16T17:46:22Z",
"timestamp": 1771263982000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013342",
"award": [
"Not applicable"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"Not applicable"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100013342",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "NIHR Imperial Biomedical Research Centre"
},
{
"award": [
"Not applicable"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"Not applicable"
]
}
],
"name": "Rigel"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004336",
"award": [
"Not applicable"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"Not applicable"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100004336",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Novartis"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-16T18:35:21Z",
"timestamp": 1771266921662,
"version": "3.50.1"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 4,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1770249600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e100583",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03451.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04470.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.5"
},
{
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.6",
"unstructured": "Novartis . Jakavi 10mg tablets. 2022. Available: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/7786/smpc#gref"
},
{
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.7",
"unstructured": "Grifols UK Ltd . Tavlesse 100 mg film-coated tablets 2023. Available: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/11479/smpc#gref [Accessed 7 Aug 2024]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.2.5402.177",
"article-title": "HUMAN EXPERIMENTATION. CODE OF ETHICS OF THE WORLD MEDICAL ASSOCIATION. DECLARATION OF HELSINKI",
"author": "RICKHAM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.8",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1964"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4324/9781003120254-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.9",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation . COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis. Geneva Switzerland: World Health Organisation, 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05190-z",
"article-title": "Multi-arm Trial of Inflammatory Signal Inhibitors (MATIS) for hospitalised patients with mild or moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Vergis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.10",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.c332",
"article-title": "CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials",
"author": "Schulz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.11",
"volume": "340",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.4067",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.11.011",
"article-title": "Instrumental variable methods for a binary outcome were used to informatively address noncompliance in a randomized trial in surgery",
"author": "Cook",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.13",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2105/AJPH.2023.307230",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00044-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000005682",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2017007526",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2101643",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2031994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101489",
"article-title": "Baricitinib in hospitalised patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Selvaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.21",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01109-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial",
"author": "Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.24",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration . Letter of authorization: eua for baricitinib (olumiant) for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019. 2022. Available: https://www.fda.gov/media/143822/download [Accessed 23 Dec 2024]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.062",
"article-title": "Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase signaling protects against acute lung injury through blockade of NADPH oxidase and IL-17A in neutrophils and γδ T cells respectively in mice",
"author": "Nadeem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.26",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3650600",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.27",
"unstructured": "Alimova M , Sidhom E-H , Satyam A . A High Content Screen for Mucin-1-Reducing Compounds Identifies Fostamatinib as a Candidate for Rapid Repurposing for Acute Lung Injury During the COVID-19 Pandemic. bioRxiv 2020;2020. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3650600"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab732",
"article-title": "Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Adults With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized Trial",
"author": "Strich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e491",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.28",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.29",
"unstructured": "Gotur DB , Malik A , Markovtsov V , et al . 88. Fostamatinib for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Who Required Oxygen Supplementation: Results of a Phase 3 Trial. Open Forum Infect Dis 2023;10. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad500.004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41375-023-01979-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103629",
"article-title": "Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity",
"author": "Velavan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103629",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.31",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0274289",
"article-title": "Distorted TCR repertoires define multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children",
"author": "Malik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.32",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06028-z",
"article-title": "Correction to: Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1294",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "2026021609454013000_16.2.e100583.33",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmjopen.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmjopen-2025-100583"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Multiarm multistage randomised controlled trial of inflammatory signal inhibitors (MATIS) for patients hospitalised with COVID-19 pneumonia during the UK pandemic",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "16"
}