Comparison of the Different Medications for COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients
et al., Authorea, Inc., doi:10.22541/au.168777909.90198442/v1, Jun 2023
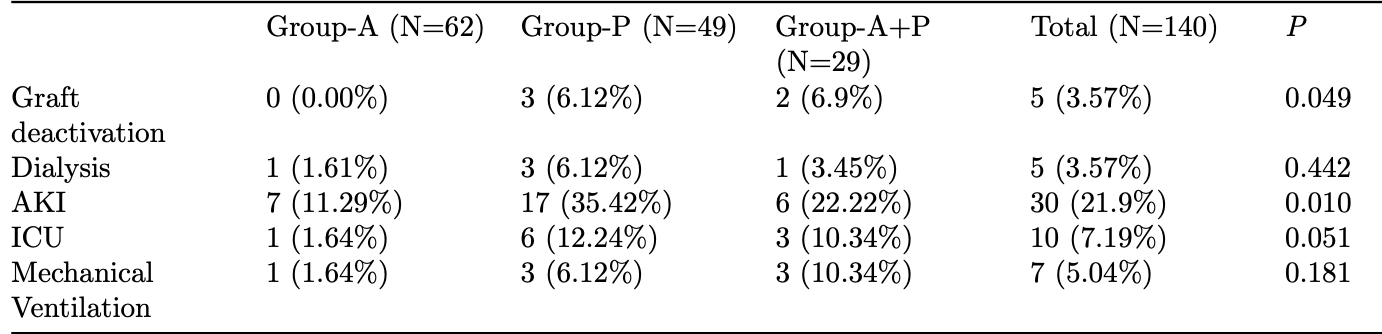
Retrospective 140 kidney transplant patients, showing higher risk of AKI with paxlovid compared with azvudine. There were more severe cases in the paxlovid group at baseline.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 279.6% higher, RR 3.80, p = 0.32, treatment 3 of 49 (6.1%), control 1 of 62 (1.6%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 659.2% higher, RR 7.59, p = 0.04, treatment 6 of 49 (12.2%), control 1 of 62 (1.6%).
|
|
AKI, 207.3% higher, RR 3.07, p = 0.005, treatment 17 of 49 (34.7%), control 7 of 62 (11.3%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Fu et al., 26 Jun 2023, retrospective, China, preprint, mean age 47.3, 8 authors, study period December 2022 - January 2023, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Comparison of the Different Medications for COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients
doi:10.22541/au.168777909.90198442/v1
Background We analyzed the effects of small-molecule antiviral treatment for coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) Omicron strain in kidney transplant recipients. Methods We enrolled 140 kidney transplant patients admitted for COVID-19-related pneumonia were treated using small-molecule antivirals. Patients were divided into three groups: azvudine (n=62), paxlovid (n=49), and a combination of azvudine+paxlovid (A+P, n=29). Differences in clinical outcomes owing to COVID-19 infections were compared among three groups. Results Paxlovid group had a higher proportion of comorbid diabetes than the other two groups (P=0.032). There were differences in the clinical typing of the coronavirus , with the highest proportion of heavy and critical cases in the A+P group (35.5%). The immunosuppression prior to infection did not differ among the groups; however, after adjusting for immunosuppression during antiviral treatment, differences were observed. Of the 140 patients, 125 (89.29%) had fever, 114 (81.43%) had cough, and 66 (47.1%) had malaise. Combination of two or more symptoms were found in 90% patients. Mean length of hospitalization was slightly longer in the combination group than in the azvudine and paxlovid groups. Four deaths, all in the A+P group; five cases of loss of function, two in the paxlovid group and three in the A+P group; and acute kidney injury occurred in 30 patients with 7 in the azvudine, 17 in paxlovid, and 6 in A+P groups. Conclusion The use of small-molecule medications may be the optimal treatment approach; however, they should be modified based on the patients' conditions, such as clinical symptoms, laboratory results, paraclinicals, and examinations.
CONCLUSION The use of small-molecule medications may be the optimal treatment approach; however, they should be modified based on the patients' conditions, such as clinical symptoms, laboratory results, paraclinicals, and examinations.
References
References
Akalin, Azzi, Bartash, Covid-19 and kidney transplantation[J], N Engl J Med
Ao, Wang, Qi, The association between severe or death COVID-19 and solid organ transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Transplant Rev (Orlando)
Baig, Khaleeq, Ali, Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms [J], ACS Chemical Neuroscience
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Callaway, Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert [J], Nature
Chaplin, Paxlovid: antiviral combination for the treatment of COVID-19, Prescriber
Chen, Shi, Dong, SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant: spatiotemporal distribution and potential, Zoonoses
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, J]. Lancet
Farouk, Fiaccadori, Cravedi, COVID-19 and the kidney: what we think we know so far and what we don't [J], J Nephrol
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe covid-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med
Hammitt, Dagan, Yuan, Nirsevimab for prevention of RSV in healthy late-preterm and term infants [J], New Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for highrisk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hirose R, Itoh, Differences in environmental stability among SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: both omicron BA.1and BA.2 have higher stability, J]. Clin Microbiol Infect
Hui, Zumla, Severe acute respiratory syndrome historical, epidemiologic, and clinical features, Infect Dis Clin N Am
Loo, Mctamney, Arends R H, The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans [J], Science translational medicine
Piechotta, Iannizzi, Chai, Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Plante, Liu, Liu, Author Correction: Spike mutation D614G alters SARS-CoV-2 fitness [J], Nature
Pulliam, Van Schalkwyk, Govender, Increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection associated with emergence of Omicron in South Africa, Science
Van Doremalen N, Bushmaker, Dh, Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-Cov-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1 [J], N Engl J Med
Yokota, Miyamae, Imagawa, Therapeutic efficacy of humanized recombinant anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody in children with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Arthritis & Rheumatism
Zhang, Wang, Guo, Treatment of CD20-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor-modified T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: an early phase IIa trial report, Signal Transduction & Targeted Therapy
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.168777909.90198442/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.22541/au.168777909.90198442/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:p id=\"p1\">Background We analyzed the effects of small-molecule antiviral treatment\nfor coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) Omicron strain in kidney\ntransplant recipients. Methods We enrolled 140 kidney transplant\npatients admitted for COVID-19-related pneumonia were treated using\nsmall-molecule antivirals. Patients were divided into three groups:\nazvudine (n=62), paxlovid (n=49), and a combination of azvudine+paxlovid\n(A+P, n=29). Differences in clinical outcomes owing to COVID-19\ninfections were compared among three groups. Results Paxlovid group had\na higher proportion of comorbid diabetes than the other two groups\n(P=0.032). There were differences in the clinical typing of the\ncoronavirus , with the highest proportion of heavy and critical cases in\nthe A+P group (35.5%). The immunosuppression prior to infection did not\ndiffer among the groups; however, after adjusting for immunosuppression\nduring antiviral treatment, differences were observed. Of the 140\npatients, 125 (89.29%) had fever, 114 (81.43%) had cough, and 66\n(47.1%) had malaise. Combination of two or more symptoms were found in\n90% patients. Mean length of hospitalization was slightly longer in the\ncombination group than in the azvudine and paxlovid groups. Four deaths,\nall in the A+P group; five cases of loss of function, two in the\npaxlovid group and three in the A+P group; and acute kidney injury\noccurred in 30 patients with 7 in the azvudine, 17 in paxlovid, and 6 in\nA+P groups. Conclusion The use of small-molecule medications may be the\noptimal treatment approach; however, they should be modified based on\nthe patients’ conditions, such as clinical symptoms, laboratory results,\nparaclinicals, and examinations.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2247-8684",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Yingxin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Jianyong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Weijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Zheng",
"given": "Yitao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Zixuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Yongdong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Yuanzheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Hongzhou",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-26T11:31:39Z",
"timestamp": 1687779099000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-26T11:31:39Z",
"timestamp": 1687779099000
},
"group-title": "Preprints",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-27T04:35:24Z",
"timestamp": 1687840524403
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Authorea, Inc."
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
]
},
"member": "9829",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.22541",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Authorea, Inc.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.authorea.com/users/632878/articles/651497-comparison-of-the-different-medications-for-covid-19-in-kidney-transplant-recipients?commit=ab4741e389c91904de90a9ce527e183d368e45d0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Comparison of the Different Medications for COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients",
"type": "posted-content"
}