Famotidine Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study
et al., Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053, May 2020
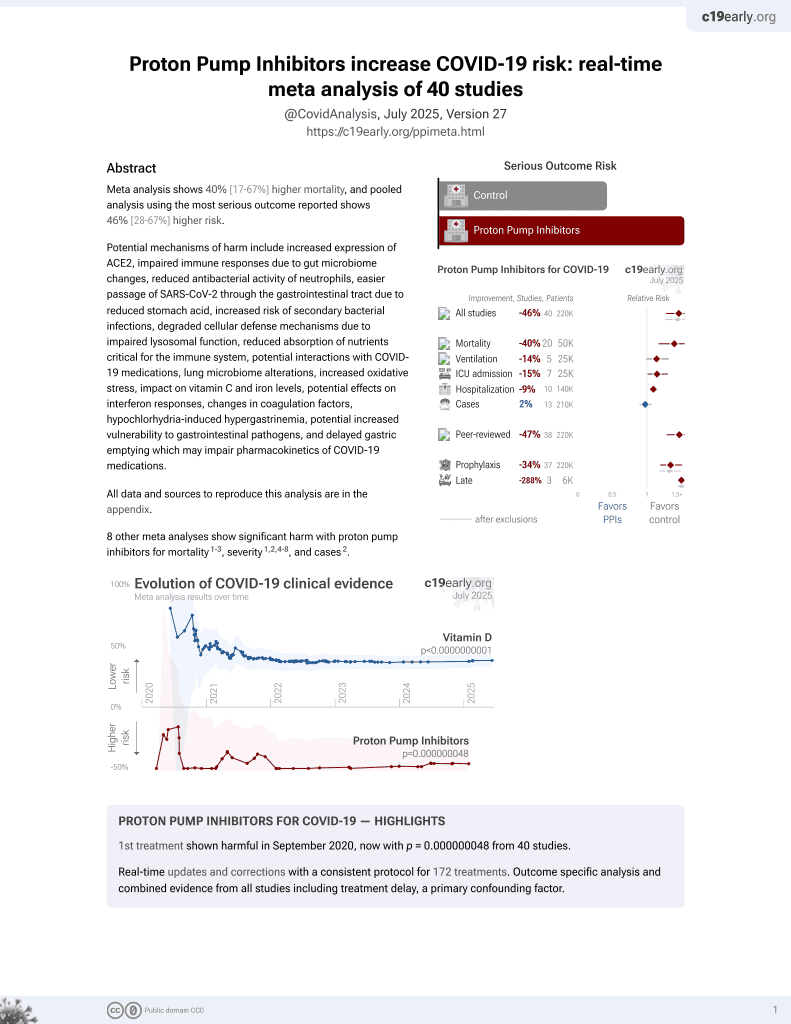
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
PSM retrospective 1,620 hospitalized patients in the USA, showing higher risk of combined death/intubation with PPI treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers proton pump inhibitors and famotidine.
|
risk of death/intubation, 34.0% higher, HR 1.34, p = 0.01, treatment 8 of 84 (9.5%), control 332 of 1,536 (21.6%), NNT 8.3, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Freedberg et al., 21 May 2020, retrospective, propensity score matching, USA, peer-reviewed, 15 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"ISSN": [
"0016-5085"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"alternative-id": [
"S0016508520347065"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Famotidine Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Gastroenterology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 by the AGA Institute"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2023-2899",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Freedberg",
"given": "Daniel E.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Conigliaro",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Timothy C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tracey",
"given": "Kevin J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callahan",
"given": "Michael V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abrams",
"given": "Julian A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sobieszczyk",
"given": "Magdalena E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Markowitz",
"given": "David D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Aakriti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O’Donnell",
"given": "Max R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jianhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tuveson",
"given": "David A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Zhezhen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "William C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landry",
"given": "Donald W.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Gastroenterology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"gastrojournal.org",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-22T01:22:26Z",
"timestamp": 1590110546000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-19T04:27:01Z",
"timestamp": 1621398421000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-19T16:47:56Z",
"timestamp": 1642610876500
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 130,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0016-5085"
}
],
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1598918400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0016508520347065?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0016508520347065?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1129-1131.e3",
"prefix": "10.1053",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Gottschlich",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib1",
"series-title": "American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0024-3205(96)00553-X",
"author": "Bourinbaiar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "PL365",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib2",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2020.02.008",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib3",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085658",
"author": "Anand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1763",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib4",
"volume": "300",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.003",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib5",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202000502",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6008",
"journal-title": "FASEB J",
"key": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053_bib6",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Gastroenterology"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Gastroenterology",
"Hepatology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Famotidine Use Is Associated With Improved Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Cohort Study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "159"
}