Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and COVID-19 Mortality and Hospitalization Among Patients With Vulnerability to COVID-19 Complications
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36678, Oct 2023
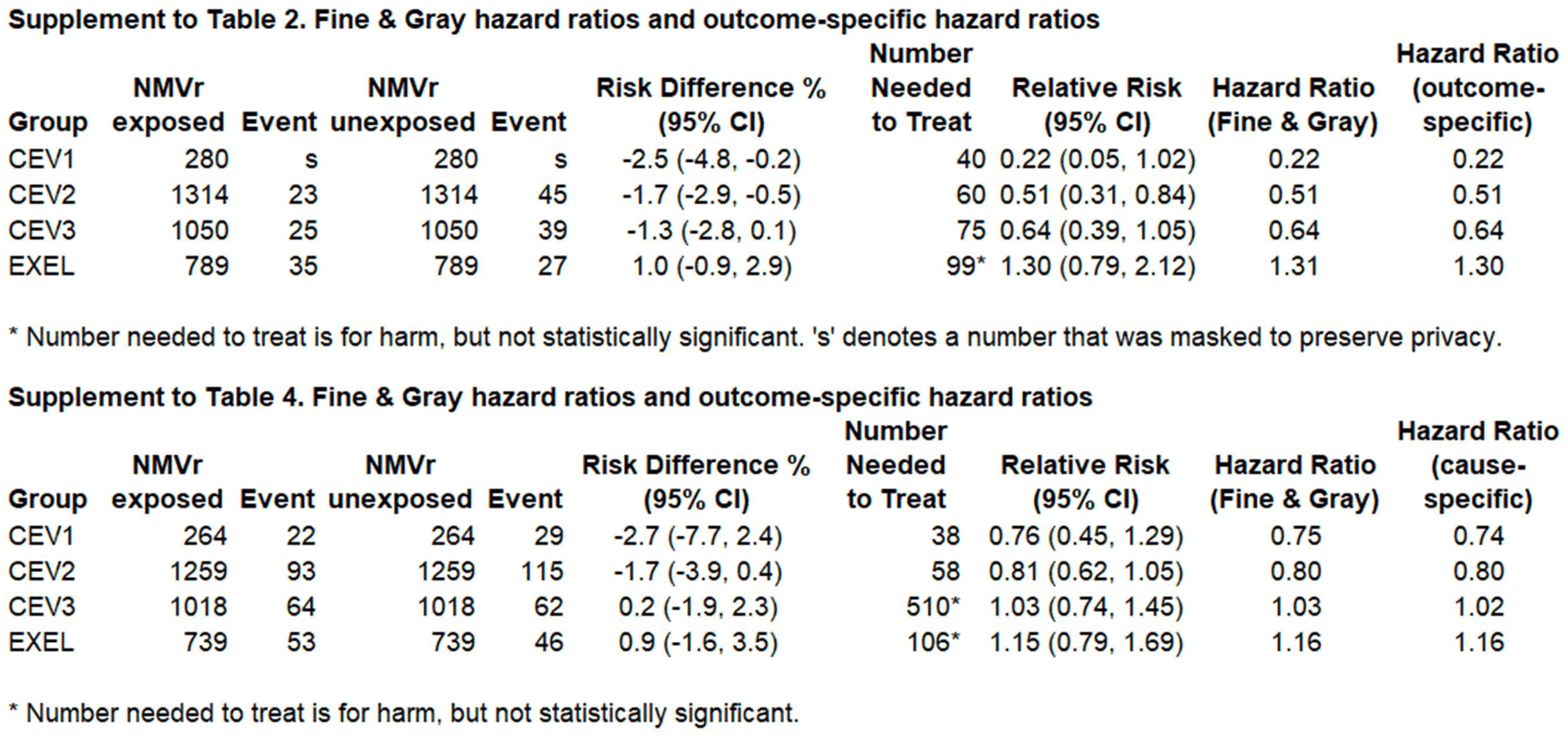
Retrospective 3,433 high-risk patients and matched controls in Canada showing lower mortality with paxlovid use. Patients were divided into four groups based on risk, with improved results as risk increased. Authors did not exclude all contraindicated patients, and do not address confounding by adjuvant treatments, therefore the results are expected to overestimate benefit. (Exclusions are not clear - the paper notes exclusion for severe kidney disease, but this is not in the detailed exclusion list in the appendix, while it is in the inclusion list for CEV2. Contraindications to paxlovid are not mentioned). Confounding may potentially remove all of the benefit seen. The worse results for protection against ER visits is consistent with the confounding being significant - the overestimation of benefit due to confounding based on inclusion of contraindicated patients is expected to increase for more severe outcomes.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending paxlovid also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out paxlovid is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Malden et al. confirm significant bias in the use of paxlovid, showing that treated
patients are more likely to be from affluent neighborhoods, be more health-conscious, and
have better access to care. Campion et al. also show that female patients were more
likely to receive paxlovid, and studies show that female patients are significantly more
likely to be health-conscious, for example being more likely to take additional
non-prescription treatments.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid6-13. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID14. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid15. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid16. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury17 and liver injury18,19. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound20-22.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
only a fraction of eligible patients received treatment and these patients may be more likely to follow other recommendations, receive additional care, and more more likely to use additional untracked treatments such as vitamin D and nasal/oral hygiene; inclusion of contraindicated patients in the control group.
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 29.2% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.02, treatment 85 of 3,433 (2.5%), control 120 of 3,433 (3.5%), NNT 98, all high-risk patients.
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 77.8% lower, RR 0.22, p = 0.06, treatment 2 of 280 (0.7%), control 9 of 280 (3.2%), NNT 40, CEV1.
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 48.9% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.009, treatment 23 of 1,314 (1.8%), control 45 of 1,314 (3.4%), NNT 60, CEV2.
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 35.9% lower, RR 0.64, p = 0.10, treatment 25 of 1,050 (2.4%), control 39 of 1,050 (3.7%), NNT 75, CEV3.
|
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 29.6% higher, RR 1.30, p = 0.36, treatment 35 of 789 (4.4%), control 27 of 789 (3.4%), EXEL.
|
|
ER visit, 7.9% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.37, treatment 232 of 3,280 (7.1%), control 252 of 3,280 (7.7%), NNT 164, all high-risk patients.
|
|
ER visit, 24.1% lower, RR 0.76, p = 0.38, treatment 22 of 264 (8.3%), control 29 of 264 (11.0%), NNT 38, CEV1.
|
|
ER visit, 19.1% lower, RR 0.81, p = 0.13, treatment 93 of 1,259 (7.4%), control 115 of 1,259 (9.1%), NNT 57, CEV2.
|
|
ER visit, 3.2% higher, RR 1.03, p = 0.93, treatment 64 of 1,018 (6.3%), control 62 of 1,018 (6.1%), CEV3.
|
|
ER visit, 15.2% higher, RR 1.15, p = 0.53, treatment 53 of 739 (7.2%), control 46 of 739 (6.2%), EXEL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Malden et al., Predictors of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir receipt among COVID-19 patients in a large US health system, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57633-7.
5.
Campion et al., Disparities in the Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1809.
6.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
7.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
8.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
9.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
10.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
11.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
12.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
13.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
14.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
15.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
16.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
17.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
18.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
19.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
20.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Dormuth et al., 2 Oct 2023, retrospective, Canada, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 1 February, 2022 - 3 February, 2023.
Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and COVID-19 Mortality and Hospitalization Among Patients With Vulnerability to COVID-19 Complications
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36678
IMPORTANCE Postmarket analysis of individuals who receive nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (Paxlovid [Pfizer]) is essential because they differ substantially from individuals included in published clinical trials. OBJECTIVE To examine the association of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir with prevention of death or admission to hospital in individuals with different risks of complications from COVID-19 infection. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This is a cohort study of adult patients in British Columbia, Canada, between February 1, 2022, and February 3, 2023. Patients were eligible if they belonged to 1 of 4 higher-risk groups of individuals who received priority for COVID-19 vaccination. Two groups included clinically extremely vulnerable (CEV) people who were severely (CEV1) or moderately immunocompromised (CEV2). CEV3 individuals were not immunocompromised but had medical conditions associated with a high risk for complications from COVID-19. A fourth expanded eligibility (EXEL) group was added to allow wider access to nirmatrelvir and ritonavir for certain other higherrisk individuals who were not in a CEV group, such as those older than 70 years who were unvaccinated. EXPOSURES Patients with COVID-19 who received nirmatrelvir and ritonavir were matched to patients in the same vulnerability group; who were of the same sex, age, and propensity score for nirmatrelvir and ritonavir treatment; and who were also infected within 1 month of the individual treated with nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was death from any cause or emergency hospitalization with COVID-19 within 28 days. RESULTS There were 6866 individuals included in the study, of whom 3888 (56.6%) were female and whose median (IQR) age was 70 (57-80) years. Compared with unexposed controls, treatment with nirmatrelvir and ritonavir was associated with statistically significant relative reductions in the primary outcome in the CEV1 group (560 patients; risk difference [RD], -2.5%, 95% CI, -4.8% to -0.2%) and the CEV2 group (2628 patients; RD, -1.7%; 95% CI, -2.9% to -0.5%). In the CEV3 group, the RD was -1.3%, but the findings were not statistically significant (2100 patients; 95% CI, -2.8% to 0.1%). In the EXEL group, treatment was associated with higher risk of the outcome (RD, 1.0%), but the findings were not statistically significant (1578 patients; 95% CI, -0.9% to 2.9%).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In this cohort study of 6866 individuals in British Columbia, nirmatrelvir and ritonavir treatment was associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 hospitalization or death in CEV individuals, with the greatest benefit observed in severely immunocompromised (continued) Key Points Question What is the association of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir exposure with the risk of death or COVID-19-related hospitalization when accounting for patient vulnerability to complications from COVID-19 infection? Findings In this cohort study of 6866 individuals with COVID-19,..
ARTICLE INFORMATION
References
Austin, Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies, Pharm Stat, doi:10.1002/pst.433
Bc Covid, Committee, Clinical practice guide for the use of therapeutics in mild-moderate COVID-19
Clinicaltrials, Gov, Evaluation of protease inhibition for covid-19 in standard-risk patients (EPIC-SR)
Fine, Gray, A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk, J Am Stat Assoc, doi:10.1080/01621459.1999.10474144
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Kabore, Laffont, Diop, Tardif, Turgeon et al., Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ ritonavir on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated hospitalization prevention: a population-based cohort study in the province of quebec, canada, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad287
Latouche, Allignol, Beyersmann, Labopin, Fine, A competing risks analysis should report results on all cause-specific hazards and cumulative incidence functions, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.09.017
Lin, Wei, Ying, Checking the Cox model with cumulative sums of martingale-based residuals, Biometrika, doi:10.1093/biomet/80.3.557
Pfizer, Pfizer reports additional data on Paxlovid supporting upcoming new drug application submission to, U.S. FDA
Schneeweiss, Rassen, Glynn, Avorn, Mogun et al., High-dimensional propensity score adjustment in studies of treatment effects using health care claims data, Epidemiology, doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a663cc
Schwartz, Wang, Tadrous, Population-based evaluation of the effectiveness of nirmatrelvirritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19, CMAJ, doi:10.1503/cmaj.221608
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36678",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36678",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-4\"><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>Postmarket analysis of individuals who receive nirmatrelvir and ritonavir (Paxlovid [Pfizer]) is essential because they differ substantially from individuals included in published clinical trials.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-5\"><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To examine the association of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir with prevention of death or admission to hospital in individuals with different risks of complications from COVID-19 infection.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-6\"><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>This is a cohort study of adult patients in British Columbia, Canada, between February 1, 2022, and February 3, 2023. Patients were eligible if they belonged to 1 of 4 higher-risk groups of individuals who received priority for COVID-19 vaccination. Two groups included clinically extremely vulnerable (CEV) people who were severely (CEV1) or moderately immunocompromised (CEV2). CEV3 individuals were not immunocompromised but had medical conditions associated with a high risk for complications from COVID-19. A fourth expanded eligibility (EXEL) group was added to allow wider access to nirmatrelvir and ritonavir for certain other higher-risk individuals who were not in a CEV group, such as those older than 70 years who were unvaccinated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-7\"><jats:title>Exposures</jats:title><jats:p>Patients with COVID-19 who received nirmatrelvir and ritonavir were matched to patients in the same vulnerability group; who were of the same sex, age, and propensity score for nirmatrelvir and ritonavir treatment; and who were also infected within 1 month of the individual treated with nirmatrelvir and ritonavir.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-8\"><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was death from any cause or emergency hospitalization with COVID-19 within 28 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-9\"><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>There were 6866 individuals included in the study, of whom 3888 (56.6%) were female and whose median (IQR) age was 70 (57-80) years. Compared with unexposed controls, treatment with nirmatrelvir and ritonavir was associated with statistically significant relative reductions in the primary outcome in the CEV1 group (560 patients; risk difference [RD], −2.5%, 95% CI, −4.8% to −0.2%) and the CEV2 group (2628 patients; RD, −1.7%; 95% CI, −2.9% to −0.5%). In the CEV3 group, the RD was −1.3%, but the findings were not statistically significant (2100 patients; 95% CI, −2.8% to 0.1%). In the EXEL group, treatment was associated with higher risk of the outcome (RD, 1.0%), but the findings were not statistically significant (1578 patients; 95% CI, −0.9% to 2.9%).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"ab-zoi231060-10\"><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>In this cohort study of 6866 individuals in British Columbia, nirmatrelvir and ritonavir treatment was associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 hospitalization or death in CEV individuals, with the greatest benefit observed in severely immunocompromised individuals. No reduction in the primary outcome was observed in lower-risk individuals, including those aged 70 years or older without serious comorbidities.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Therapeutics Initiative, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Dormuth",
"given": "Colin R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Therapeutics Initiative, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Jason D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Therapeutics Initiative, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Fisher",
"given": "Anat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
},
{
"name": "BC COVID Therapeutics Committee, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Piszczek",
"given": "Jolanta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Laboratory and Blood Services Division, British Columbia Ministry of Health, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Kuo",
"given": "I Fan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-02T15:01:27Z",
"timestamp": 1696258887000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-14T16:02:54Z",
"timestamp": 1707926574000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-28T16:38:35Z",
"timestamp": 1711643915051
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2809972/dormuth_2023_oi_231060_1707500836.98378.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2336678",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi231060r2",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.221608",
"article-title": "Population-based evaluation of the effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir for reducing hospital admissions and mortality from COVID-19.",
"author": "Schwartz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E220",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "CMAJ",
"key": "zoi231060r5",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad287",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–associated hospitalization prevention: a population-based cohort study in the province of quebec, canada.",
"author": "Kabore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "zoi231060r6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi231060r7",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181a663cc",
"article-title": "High-dimensional propensity score adjustment in studies of treatment effects using health care claims data.",
"author": "Schneeweiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "512",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology",
"key": "zoi231060r10",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pst.v10.2",
"article-title": "Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies.",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "150",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Pharm Stat",
"key": "zoi231060r11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01621459.1999.10474144",
"article-title": "A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk.",
"author": "Fine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "496",
"journal-title": "J Am Stat Assoc",
"key": "zoi231060r12",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.09.017",
"article-title": "A competing risks analysis should report results on all cause-specific hazards and cumulative incidence functions.",
"author": "Latouche",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "648",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "zoi231060r13",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/biomet/80.3.557",
"article-title": "Checking the Cox model with cumulative sums of martingale-based residuals.",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "557",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biometrika",
"key": "zoi231060r14",
"volume": "80",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"key": "zoi231060r1",
"unstructured": "Government of Canada. Summary basis of decision—Paxlovid—Health Canada. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://covid-vaccine.canada.ca/info/summary-basis-decision-detailTwo.html?linkID=SBD00577"
},
{
"key": "zoi231060r3",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. Evaluation of protease inhibition for covid-19 in standard-risk patients (EPIC-SR). August 18, 2021. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05011513"
},
{
"key": "zoi231060r4",
"unstructured": "Pfizer. Pfizer reports additional data on Paxlovid supporting upcoming new drug application submission to U.S. FDA. June 14, 2022. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-reports-additional-data-paxlovidtm-supporting"
},
{
"key": "zoi231060r8",
"unstructured": "BC COVID Therapeutics Committee. Clinical practice guide for the use of therapeutics in mild-moderate COVID-19. January 10, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2023. http://www.bccdc.ca/Health-Professionals-Site/Documents/COVID-treatment/ClinicalPracticeGuide_Therapeutics_MildModerateCOVID.pdf"
},
{
"key": "zoi231060r9",
"unstructured": "National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI). Guidance on COVID-19 vaccine booster doses: initial considerations for 2023. January 20, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2023. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/immunization/national-advisory-committee-on-immunization-naci/guidance-covid-19-vaccine-booster-doses-initial-considerations-2023.html"
}
],
"reference-count": 14,
"references-count": 14,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2809972"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and COVID-19 Mortality and Hospitalization Among Patients With Vulnerability to COVID-19 Complications",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "6"
}