Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial
et al., Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia, doi:10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182, IRCT20151228025732N52, Dec 2020
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000015 from 18 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small RCT in Iran with 20 ICU patients, 10 treated with high-dose vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc, showing no significant differences.
This study has several data issues:
The study reports a mean age of 59 ± 19 years with a range of 20-65 years for 20 patients. It is mathematically impossible to achieve a standard deviation of 19 with a mean of 59 and a maximum value of 65 in a sample of 20.
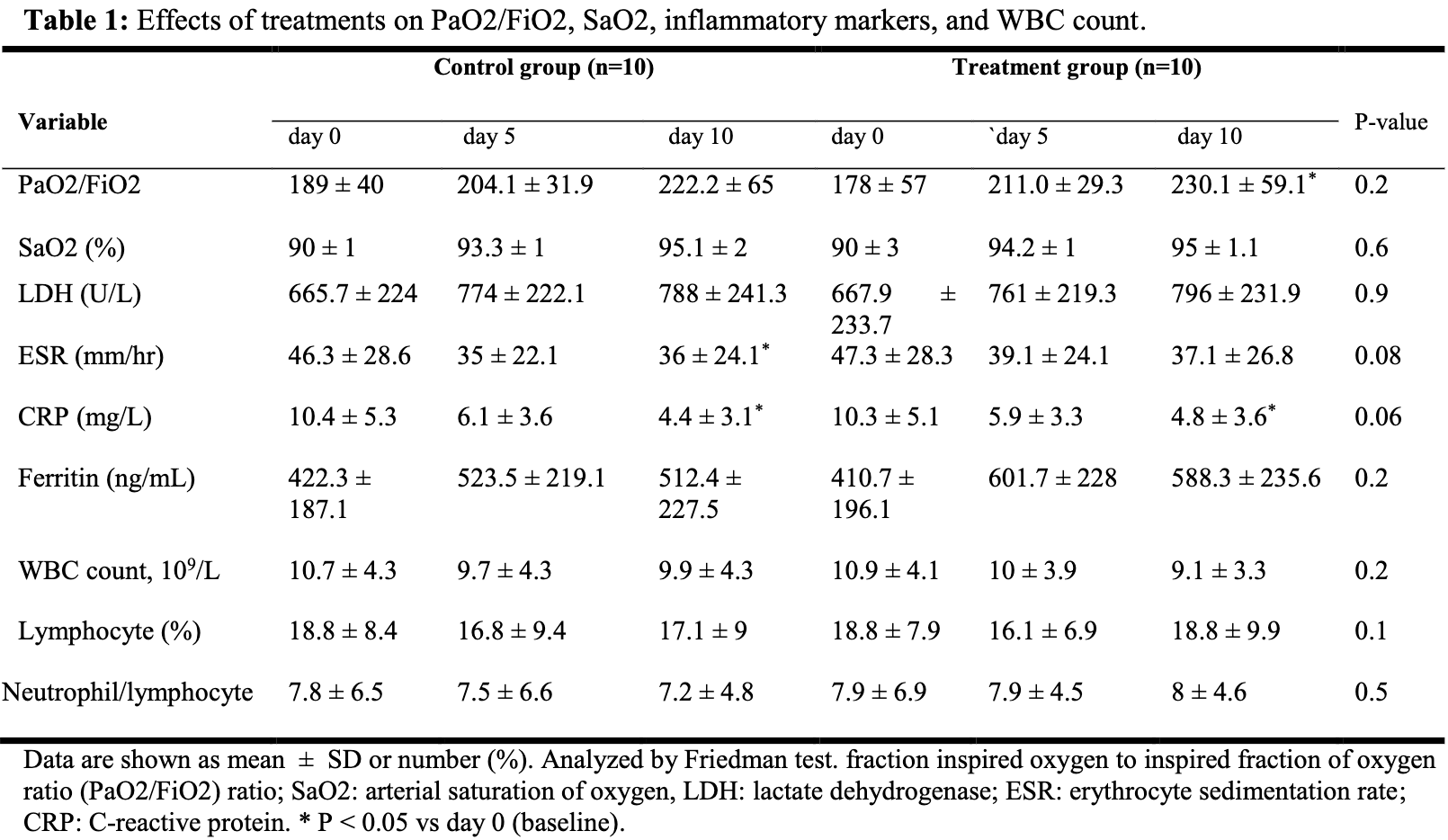
Table 1 reports p-values in the rightmost column that appear to represent between-group comparisons but are difficult to reconcile with the descriptive statistics. For example, Day 10 CRP is 4.4 ± 3.1 vs 4.8 ± 3.6 (p = 0.06) and Day 10 ESR is 36 ± 24.1 vs 37.1 ± 26.8 (p = 0.08). If these are between-group comparisons, the true p-values for such nearly identical distributions with large standard deviations and n=10 per group should be well above 0.05. The table footnote states "Analyzed by Friedman test," adding further confusion, since the Friedman test is a within-subject repeated-measures test and cannot produce between-group p-values.
The Data Analysis section states that Chi-square, Fisher's exact, and Friedman's tests were used, yet Table 1 contains between-group comparisons of continuous variables requiring independent t-tests or Mann-Whitney U tests. None of the stated tests is appropriate for the reported between-group comparisons.
Despite the small sample size (n=10 per group), several continuous baseline variables are very closely matched across multiple variables simultaneously - for example, baseline lymphocyte (%) is 18.8 ± 8.4 vs 18.8 ± 7.9, CRP is 10.4 ± 5.3 vs 10.3 ± 5.1, and WBC is 10.7 ± 4.3 vs 10.9 ± 4.1. While any single match could occur by chance, this degree of concordance across multiple variables with only 10 patients per group is unusual.
The abstract states 21 patients were randomized 1:1, but 21 cannot be split equally. The results state 20 patients were observed and 1 dropped out due to hypersensitivity. However, Table 1 shows n=10 per group with no indication of which group lost the patient or whether they were excluded post-randomization, which would raise intention-to-treat concerns.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
data issues pending author response.
|
risk of progression, 33.3% lower, RR 0.67, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 10 (20.0%), control 3 of 10 (30.0%), NNT 10.
|
|
ICU time, 6.0% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.30, treatment 10, control 10.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Darban et al., 15 Dec 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 7 April, 2020 - 8 June, 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with vitamin C and zinc) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial IRCT20151228025732N52.
Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial
doi:10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182
Background: We aimed to investigate the efficacy of high-dose vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc in patients with severe Covid-19. Materials and Methods: Twenty-one adult patients were randomized 1:1 to standard care alone or standard care plus IV vitamin C (2 g, q6hr), oral melatonin (6 mg, q6hr), and oral zinc sulfate (50 mg, q6hr) for 10 days. Patients were monitored for changes in hypoxemia and inflammatory markers. Results: Both treatment modalities were effective to improve PaO2/FiO2 and oxygen saturation. However, there were no significant differences between the 2 study groups (P>0.05). There were reductions in CRP, ESR, and LDH levels in both study groups, although were not significant. No significant difference was noted in the length of ICU stay between the 2 study groups (P=0.3).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that the addition of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc to standard care is not associated with considerable improvement in patients with severe Covid-19.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Zarezade, Koolaji, Seyedalinaghi, Zendehdel et al., Safety and effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a randomized open-label clinical trial, Eur J Med Res
Kuhn, Meissner, Mayes, Bartels, Vitamin C in sepsis, Curr Opin Anaesthesiol
Nooraee, Fathi, Edalat, Behnaz, Mohajerani et al., Effect of Vitamin C on Serum Cortisol after Etomidate Induction of Anesthesia, J Cell Mol Anesth
Rajaei, Dabbagh, The immunologic basis of COVID-19: a clinical approach, J Cell Mol Anesth
Rodic, Mccudden, Van Walraven, The Prognostic Value of Serum Zinc Levels in Acutely Hospitalized Patients: a Systematic Review, Biol Trace Elem Res
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wongchitrat, Shukla, Sharma, Govitrapong, Reiter, Role of Melatonin on Virus-Induced Neuropathogenesis-A Concomitant Therapeutic Strategy to Understand SARS-CoV-2
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann Intensive Care
Ziaie, Koucheck, Miri, Salarian, Shojaei et al., Review of Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of COVID-19, J Cell Mol Anesth
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182",
"ISSN": "24765120, 25382462",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182",
"abstract": "INTRODUCTION: Our aim was to investigate the efficacy of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc in patients with severe Covid-19. METHODS: Twenty-one adult patients were randomized 1:1 to standard care alone or standard care plus IV vitamin C (2 g, q6hr), oral melatonin (6 mg, q6hr), and oral zinc sulfate (50 mg, q6hr) for 10 days. Patients were monitored for changes in hypoxemia and inflammatory markers. RESULTS: Both treatment modalities were effective to improve PaO2/FiO2 and oxygen saturation. However, there were no significant differences between 2 groups (P > 0.05). There were reductions in CRP, ESR, and LDH levels in both study groups, although not significant. No significant difference was noted in length of ICU stay between 2 groups (P = 0.3). CONCLUSION: Our study suggests that addition of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc to standard care is not associated with considerable improvement in patients with severe Covid-19. ",
"author": [
{
"family": "Darban",
"given": "Mahboubeh"
},
{
"family": "Malek",
"given": "Farhad"
},
{
"family": "Memarian",
"given": "Mohammad"
},
{
"family": "Gohari",
"given": "Ali"
},
{
"family": "Kiani",
"given": "Arda"
},
{
"family": "Emadi",
"given": "Alireza"
},
{
"family": "Lavvaf",
"given": "Samaneh"
},
{
"family": "Bagheri",
"given": "Bahador"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia",
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
15
]
]
},
"language": "eng",
"medium": "JB",
"page": "164-167",
"page-first": "164",
"publisher": "Anesthesiology Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "6"
}