Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial
et al., Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia, doi:10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182, IRCT20151228025732N52, Dec 2020
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
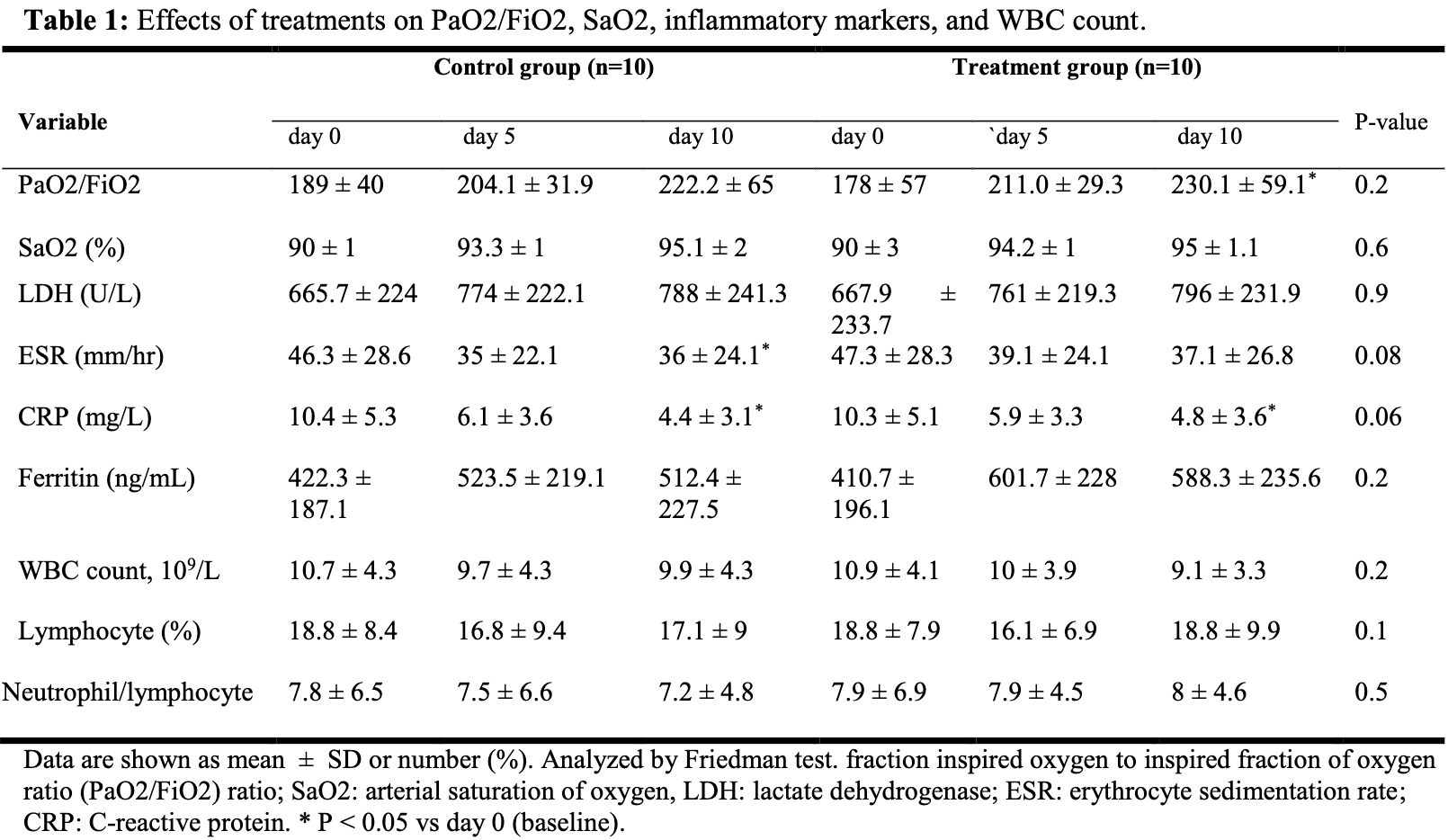
Small RCT in Iran with 20 ICU patients, 10 treated with high-dose vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc, not showing significant differences.
This is the 3rd of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0012.
This is the 8th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
very late stage, ICU patients.
|
risk of progression, 33.3% lower, RR 0.67, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 10 (20.0%), control 3 of 10 (30.0%), NNT 10.
|
|
ICU time, 6.0% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.30, treatment 10, control 10.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Darban et al., 15 Dec 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 7 April, 2020 - 8 June, 2020, dosage 2000mg qid days 1-10, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with melatonin and zinc) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial IRCT20151228025732N52.
Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial
doi:10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182
Background: We aimed to investigate the efficacy of high-dose vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc in patients with severe Covid-19. Materials and Methods: Twenty-one adult patients were randomized 1:1 to standard care alone or standard care plus IV vitamin C (2 g, q6hr), oral melatonin (6 mg, q6hr), and oral zinc sulfate (50 mg, q6hr) for 10 days. Patients were monitored for changes in hypoxemia and inflammatory markers. Results: Both treatment modalities were effective to improve PaO2/FiO2 and oxygen saturation. However, there were no significant differences between the 2 study groups (P>0.05). There were reductions in CRP, ESR, and LDH levels in both study groups, although were not significant. No significant difference was noted in the length of ICU stay between the 2 study groups (P=0.3).
Conclusion: Our study suggests that the addition of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc to standard care is not associated with considerable improvement in patients with severe Covid-19.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Jamalimoghadamsiahkali, Zarezade, Koolaji, Seyedalinaghi, Zendehdel et al., Safety and effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID-19: a randomized open-label clinical trial, Eur J Med Res
Kuhn, Meissner, Mayes, Bartels, Vitamin C in sepsis, Curr Opin Anaesthesiol
Nooraee, Fathi, Edalat, Behnaz, Mohajerani et al., Effect of Vitamin C on Serum Cortisol after Etomidate Induction of Anesthesia, J Cell Mol Anesth
Rajaei, Dabbagh, The immunologic basis of COVID-19: a clinical approach, J Cell Mol Anesth
Rodic, Mccudden, Van Walraven, The Prognostic Value of Serum Zinc Levels in Acutely Hospitalized Patients: a Systematic Review, Biol Trace Elem Res
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of High-Dose Zinc and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation vs Usual Care on Symptom Length and Reduction Among Ambulatory Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The COVID A to Z Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wongchitrat, Shukla, Sharma, Govitrapong, Reiter, Role of Melatonin on Virus-Induced Neuropathogenesis-A Concomitant Therapeutic Strategy to Understand SARS-CoV-2
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., Pilot trial of high-dose vitamin C in critically ill COVID-19 patients, Ann Intensive Care
Ziaie, Koucheck, Miri, Salarian, Shojaei et al., Review of Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of COVID-19, J Cell Mol Anesth
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182",
"ISSN": "24765120, 25382462",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22037/jcma.v6i2.32182",
"abstract": "INTRODUCTION: Our aim was to investigate the efficacy of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc in patients with severe Covid-19. METHODS: Twenty-one adult patients were randomized 1:1 to standard care alone or standard care plus IV vitamin C (2 g, q6hr), oral melatonin (6 mg, q6hr), and oral zinc sulfate (50 mg, q6hr) for 10 days. Patients were monitored for changes in hypoxemia and inflammatory markers. RESULTS: Both treatment modalities were effective to improve PaO2/FiO2 and oxygen saturation. However, there were no significant differences between 2 groups (P > 0.05). There were reductions in CRP, ESR, and LDH levels in both study groups, although not significant. No significant difference was noted in length of ICU stay between 2 groups (P = 0.3). CONCLUSION: Our study suggests that addition of vitamin C, melatonin, and zinc to standard care is not associated with considerable improvement in patients with severe Covid-19. ",
"author": [
{
"family": "Darban",
"given": "Mahboubeh"
},
{
"family": "Malek",
"given": "Farhad"
},
{
"family": "Memarian",
"given": "Mohammad"
},
{
"family": "Gohari",
"given": "Ali"
},
{
"family": "Kiani",
"given": "Arda"
},
{
"family": "Emadi",
"given": "Alireza"
},
{
"family": "Lavvaf",
"given": "Samaneh"
},
{
"family": "Bagheri",
"given": "Bahador"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Cellular & Molecular Anesthesia",
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
15
]
]
},
"language": "eng",
"medium": "JB",
"page": "164-167",
"page-first": "164",
"publisher": "Anesthesiology Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Efficacy of High Dose Vitamin C, Melatonin and Zinc in Iranian Patients with Acute Respiratory Syndrome due to Coronavirus Infection: A Pilot Randomized Trial",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "6"
}
darban
