Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination against COVID‐19 caused by omicron BA.2.2 in the elderly: A single‐center large observational study
et al., Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.1232, Apr 2024
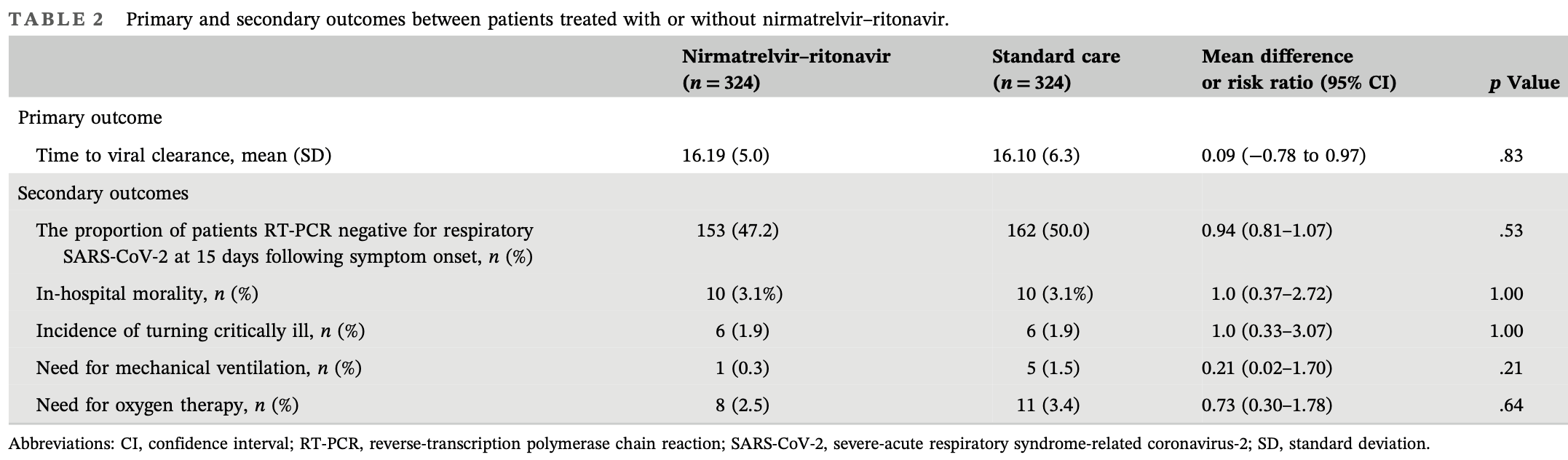
PSM retrospective 648 elderly COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in time to viral clearance with paxlovid. However, in subgroup analysis of patients treated within 10 days of symptom onset, treatment was associated with faster viral clearance. There was no significant difference in mortality, progression to critical illness, or need for oxygen therapy.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments18.
|
risk of death, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 10 of 324 (3.1%), control 10 of 324 (3.1%), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.22, treatment 1 of 324 (0.3%), control 5 of 324 (1.5%), NNT 81, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of severe case, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 6 of 324 (1.9%), control 6 of 324 (1.9%), propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 27.3% lower, RR 0.73, p = 0.64, treatment 8 of 324 (2.5%), control 11 of 324 (3.4%), NNT 108, propensity score matching.
|
|
time to viral-, 1.0% lower, relative time 0.99, p = 0.91, treatment 324, control 324, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 5.6% higher, RR 1.06, p = 0.53, treatment 171 of 324 (52.8%), control 162 of 324 (50.0%), day 15.
|
|
time to viral-, 25.9% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.004, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, ≤10 days, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
16.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Chen et al., 5 Apr 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 77.0, 8 authors, study period 26 April, 2022 - 30 June, 2022.
Contact: chen.zhangzhang@zs-hospital.sh.cn, li.xiaoyu@zs-hospital.sh.cn.
Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination against COVID‐19 caused by omicron BA.2.2 in the elderly: A single‐center large observational study
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease, doi:10.1002/iid3.1232
Background: Since coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) swept the world, a variety of novel therapeutic and prevention strategies have been developed, among which nirmatrelvir-ritonavir is highly recommended. We intended to assess the effectiveness and safety of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in the elderly mild-tomoderate COVID-19 population caused by the omicron BA.2.2 variant in realworld settings. Methods: An observational study was conducted retrospectively to review the outcomes of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 patients admitted between April 26 and June 30, 2022. Patients' baseline characteristics were collected and assessed. Participants in the intervention group were administered nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in addition to standard care, whereas those in the control group only received standard care. The primary outcome was the duration between the initial positive reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test and the subsequent conversion to a negative result. Results: The analysis included 324 patients who were administered nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and an equal number of control patients. The patient characteristics in both groups were evenly matched. The average duration from the initial positive RT-PCR to negative conversion was similar in both groups (16.2 ± 5.0 vs. 16.1 ± 6.3 days, p = .83). Control patients exhibited slower conversion in comparison to patients who received nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment within 10 days of symptom onset. Conclusions: These findings suggest that administering nirmatrelvirritonavir within 10 days of symptom onset could potentially reduce the time
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Can Chen: Investigation; methodology; writingoriginal draft; writing-review and editing. Ranyi Li: Data curation; formal analysis; software; writing-review and editing. Shuliang Xing: Project administration; resources; supervision. Lei Cao: Project administration; resources; supervision. Yue Qu: Methodology; writingreview and editing. Qianzhou Lv: Supervision. Xiaoyu Li: Conceptualization; data curation; funding acquisition; writing-review and editing. Zhangzhang Chen: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; writing-review and editing.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ETHICS STATEMENT This study adhered to STROBE guidelines and received approval from the ethics committees of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (approval number B2022-470R).
References
Dal-Ré, Becker, Bottieau, Holm, Availability of oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 infection and the requirement for an ethical prescribing approach, Lancet Infect Dis
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO clinical characterisation protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ
Drew, Donnell, Leblanc, Mcmahon, Natin, The importance of cycle threshold values in interpreting molecular tests for SARS-CoV-2, Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis
Dryden-Peterson, Kim, Kim, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir for early covid-19 in a large U.S. health system: a population-based cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kaboré, Laffont, Diop, Real-world effectiveness of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir on coronavirus disease 2019-associated hospitalization prevention: a population-based cohort study in the province of Quebec, Canada, Clin Infect Dis
Kim, Garg, 'halloran, Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the US coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated hospitalization surveillance network (COVID-NET), Clin Infect Dis
Krammer, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development, Nature
Lewnard, Mclaughlin, Malden, Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system, Lancet Infect Dis
Li, Gao, You, Association of nirmatrelvir/ ritonavir treatment on upper respiratory severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR) negative conversion rates among high-risk patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis
Martin-Blondel, Marcelin, Soulié, Time to negative PCR conversion amongst high-risk patients with mild-to-moderate omicron BA.1 and BA.2 COVID-19 treated with sotrovimab or nirmatrelvir, Clin Microbiol Infect
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19-interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Pitre, Van Alstine, Chick, Antiviral drug treatment for nonsevere COVID-19: a systematic review and network meta-analysis, Can Med Assoc J
Rao, Manissero, Steele, Pareja, A systematic review of the clinical utility of cycle threshold values in the context of COVID-19, Infect Dis Ther
Rodríguez-Grande, Jiménez, Catalán, Inference of active viral replication in cases with sustained positive reverse transcription-PCR results for SARS-CoV-2, J Clin Microbiol
Salvatore, Dawson, Wadhwa, Epidemiological correlates of polymerase chain reaction cycle threshold values in the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis
Sevrioukova, Poulos, Structure and mechanism of the complex between cytochrome P4503A4 and ritonavir, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Singh, Toussi, Hackman, Innovative randomized phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir, Clin Pharm Ther
Stein, Ramelli, Grazioli, SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy, Nature
Ullrich, Ekanayake, Otting, Nitsche, Main protease mutants of SARS-CoV-2 variants remain susceptible to nirmatrelvir, Bioorg Med Chem Lett
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res
Wong, Au, Lau, Lau, Cowling et al., Real-world effectiveness of molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir against mortality, hospitalisation, and in-hospital outcomes among community-dwelling, ambulatory patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection during the omicron wave in Hong Kong: an observational study, Lancet
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA
Zhang, Liang, Tang, Negative conversion rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection, JAMA Int Med
Zhang, Zhang, Chen, Shanghai's life-saving efforts against the current omicron wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.1232",
"ISSN": [
"2050-4527",
"2050-4527"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iid3.1232",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Since coronavirus 2019 (COVID‐19) swept the world, a variety of novel therapeutic and prevention strategies have been developed, among which nirmatrelvir–ritonavir is highly recommended. We intended to assess the effectiveness and safety of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in the elderly mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 population caused by the omicron BA.2.2 variant in real‐world settings.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>An observational study was conducted retrospectively to review the outcomes of mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 patients admitted between April 26 and June 30, 2022. Patients' baseline characteristics were collected and assessed. Participants in the intervention group were administered nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in addition to standard care, whereas those in the control group only received standard care. The primary outcome was the duration between the initial positive reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) test and the subsequent conversion to a negative result.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The analysis included 324 patients who were administered nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and an equal number of control patients. The patient characteristics in both groups were evenly matched. The average duration from the initial positive RT‐PCR to negative conversion was similar in both groups (16.2 ± 5.0 vs. 16.1 ± 6.3 days, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .83). Control patients exhibited slower conversion in comparison to patients who received nirmatrelvir–ritonavir treatment within 10 days of symptom onset.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>These findings suggest that administering nirmatrelvir–ritonavir within 10 days of symptom onset could potentially reduce the time it takes for SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected patients to negative RT‐PCR results, thereby expanding the current usage guidelines for nirmatrelvir–ritonavir.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/iid3.1232"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-11-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-03-14"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-04-05"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Can",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ranyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Science and Education Office Shanghai Geriatric Medical Center Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Xing",
"given": "Shuliang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Administration Office, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Lei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases The Alfred Hospital and Monash University Clayton Australia"
}
],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Yue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Qianzhou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xiaoyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0009-9468-7782",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University Shanghai China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Zhangzhang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Immunity, Inflammation and Disease",
"container-title-short": "Immunity Inflam &amp; Disease",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T12:14:31Z",
"timestamp": 1712319271000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T12:14:35Z",
"timestamp": 1712319275000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-06T00:55:43Z",
"timestamp": 1712364943687
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 4,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712275200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/iid3.1232",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2798-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_12_4_1",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID‐19. Accessed January 26 2024.https://reliefweb.int/attachments/d44a29d7-fdee-4045-ac26-fc632f98fcde/WHO-2019-nCoV-therapeutics-2023.2-eng.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.220471",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128629",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2603",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00119-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1010693107",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-2141",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.12.016",
"article-title": "Time to negative PCR conversion amongst high‐risk patients with mild‐to‐moderate omicron BA.1 and BA.2 COVID‐19 treated with sotrovimab or nirmatrelvir",
"author": "Martin‐Blondel G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "543.e5",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "e_1_2_12_15_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac600",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad287",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01586-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_18_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_12_19_1",
"unstructured": "National Medical Products Administration of China. Emergency conditional approval of Pfizer's COVID‐19 therapy:nirmatrelvir tablet/ritonavir tablet combination package (i.e. Paxlovid) importation registration [in Chinese]. Accessed April 27 2022.https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/yaowen/ypjgyw/20220212085753142"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00838-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_20_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_12_21_1",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID‐19 (trial version 9) [in Chinese]. Accessed June 20 2022.http://www.nhc.gov.cn/cms-search/xxgk/getManuscriptXxgk.htm?id=b74ade1ba4494583805a3d2e40093d88"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115130",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.7201",
"article-title": "Negative conversion rate of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"author": "Zhang R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "566",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Int Med",
"key": "e_1_2_12_26_1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1469",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00324-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05542-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_12_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.02277-20",
"article-title": "Inference of active viral replication in cases with sustained positive reverse transcription‐PCR results for SARS‐CoV‐2",
"author": "Rodríguez‐Grande C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_30_1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/iid3.1232"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir combination against COVID‐19 caused by omicron BA.2.2 in the elderly: A single‐center large observational study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}