Efficacy and Safety of Pacritinib vs Placebo for Patients With Severe COVID-19
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42918, NCT04404361, Dec 2022
RCT 200 hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 showing no significant differences with pacritinib.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
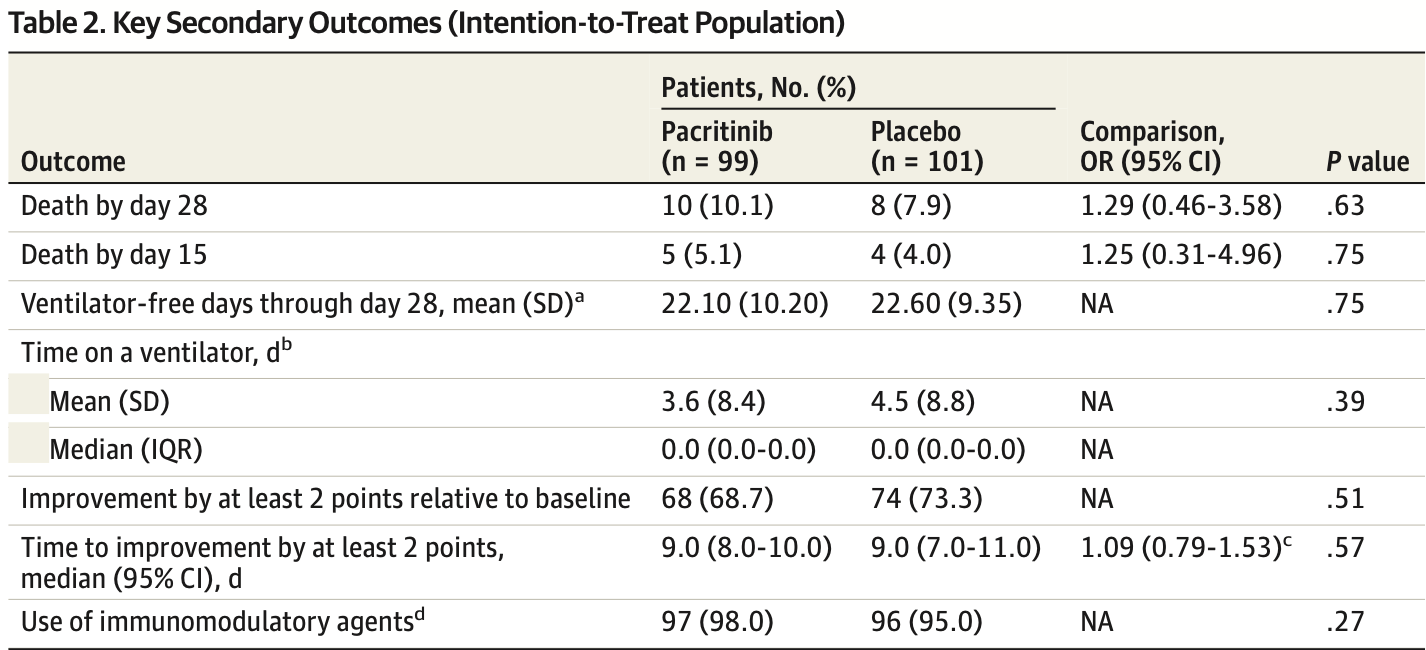
risk of death, 27.5% higher, RR 1.28, p = 0.63, treatment 10 of 99 (10.1%), control 8 of 101 (7.9%), day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 27.5% higher, RR 1.28, p = 0.75, treatment 5 of 99 (5.1%), control 4 of 101 (4.0%), day 15.
|
|
mechanical ventilation or ECMO or death, post-hoc, 24.6% lower, RR 0.75, p = 0.38, treatment 17 of 99 (17.2%), control 23 of 101 (22.8%), NNT 18, day 28, primary outcome.
|
|
mechanical ventilation or ECMO or death, prespecified, 6.1% higher, RR 1.06, p = 0.87, treatment 26 of 99 (26.3%), control 25 of 101 (24.8%), day 28, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of no improvement by 2+ points, 17.1% higher, RR 1.17, p = 0.53, treatment 31 of 99 (31.3%), control 27 of 101 (26.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cafardi et al., 5 Dec 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 59.0, 17 authors, study period June 2020 - February 2021, trial NCT04404361 (history).
Efficacy and Safety of Pacritinib vs Placebo for Patients With Severe COVID-19
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42918
IMPORTANCE The morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 remain high despite advances in standard of care therapy, and the role of anti-inflammatory agents that inhibit the interleukin 6/JAK2 pathway is still being elucidated.
OBJECTIVE To evaluate the efficacy and safety of the oral JAK2/IRAK1 inhibitor pacritinib vs placebo in the treatment of adults with severe COVID-19. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial enrolled hospitalized adult patients with severe COVID-19 at 21 centers across the US between June 2020 and February 2021, with approximately 1.5 months of safety follow-up per patient. Data analysis was performed from September 2021 to July 2022. INTERVENTIONS Patients were randomized 1:1 to standard of care plus pacritinib (400 mg per os on day 1 followed by 200 mg twice daily on days 2-14) vs placebo, for 14 days.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary end point was death or need for invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) by day 28. All-cause mortality and safety were also assessed.
RESULTS A total of 200 patients were randomized to pacritinib (99 patients; 56 men [56.6%]; median [range] age, 60 [19-87] years) or placebo (101 patients; 64 men [63.4%]; median [range] age 59 [28-94] years). The percentage requiring supplementary oxygen was 99.0% (98 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 98.0% (99 patients) in the placebo group. The percentage who progressed to IMV, ECMO, or death was 17.2% (17 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 22.8% (23 patients) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.28-1.35; P = .23). Among patients with elevated interleukin 6, the rate was 17.5% (11 of 63 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 30.4% (21 of 96 patients) in the placebo group. The adverse event rate was similar for pacritinib vs placebo (78.1% [75 patients] vs 80.2% [81 patients]), with no excess in infection (14.6% [14 patients] vs 19.8% [20 patients]), bleeding (8.3% [8 patients] vs 10.9% [11 patients]), or thrombosis (8.3% [8 patients] vs 7.9% [8 patients]). Rates of grade 3 or higher adverse events were lower with pacritinib than placebo (29.2% [28 patients] vs 40.6% [41 patients]).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE The study did not meet its primary end point in patients with severe COVID-19. Subgroup analyses may indicate specific populations with hyperinflammation that could benefit from pacritinib, although further clinical trials would be needed to confirm these effects.
The effect size of pacritinib compared with placebo in prevention of IMV, ECMO, or death in the overall population (OR, 0.62) was comparable to the effect size for baricitinib plus remdesivir in prevention of IMV or ECMO in the ACTT-2 (A Multicenter, Adaptive, Randomized Blinded Controlled Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Investigational Therapeutics for the Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Adults) study (OR, 0.61) 21 or baricitinib in prevention of high-flow oxygen, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, IMV, ECMO, or death in the COV-BARRIER (A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Phase 3 Study of Baricitinib in Patients With COVID-19 Infection) study (OR, 0.85). 22 Both ACTT-2 and COV-BARRIER were adequately powered phase 3 confirmatory trials, with a total sample size of more than 1000 patients. PRE-VENT, by contrast, was designed as a phase 2 study, and although the results are encouraging, the study was not powered to detect the observed effect size. Since April 2020, when PRE-VENT was designed, standard of care therapy for severe COVID-19 has evolved rapidly. Almost all patients enrolled in the PRE-VENT trial received corticosteroids and prophylactic-dose or intermediate-dose anticoagulation as part of standard therapy. In November 2020, approximately 4 months before study closure, the JAK1/2 inhibitor baricitinib was approved, in combination with remdesivir, under EUA in the US. In June 2021, approximately 4 months after study..
References
Alunno, Najm, Mariette, Immunomodulatory therapies for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an update of the systematic literature review to inform EULAR points to consider, RMD Open, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001899
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Fisher, Fowles, Zhou, Oh, Inflammatory pathophysiology as a contributor to myeloproliferative neoplasms, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.683401
Fleming, Viral inhibition of the IFN-induced JAK/STAT signalling pathway: development of live attenuated vaccines by mutation of viral-encoded IFN-antagonists, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines4030023
Gerds, Savona, Scott, Determining the recommended dose of pacritinib: results from the PAC203 dose-finding trial in advanced myelofibrosis, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003314
Gordon, Mouncey, Al-Beidh, REMAP-CAP Investigators. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2100433
Guimarães, Quirk, Furtado, Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101643
Han, Antila, Ficker, Ruxolitinib in addition to standard of care for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RUXCOVID): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00044-3
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, ACTT-2 Study Group Members. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
Li, Melton, Su, Unexpected role for adaptive αβTh17 cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1500054
Magesh, John, Li, Disparities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status: a systematic-review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34147&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2022.42918
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3
Mascarenhas, Hoffman, Talpaz, Pacritinib vs best available therapy, including ruxolitinib, in patients with myelofibrosis: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Oncol, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5818&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2022.42918
Mesa, Vannucchi, Mead, Pacritinib versus best available therapy for the treatment of myelofibrosis irrespective of baseline cytopenias (PERSIST-1): an international, randomised, phase 3 trial, Lancet Haematol, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30027-3
Mikacenic, Hansen, Radella, Gharib, Stapleton et al., Interleukin-17A is associated with alveolar inflammation and poor outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001409
Pagano, Salmanton-García, Marchesi, COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: a European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA), J Hematol Oncol, doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01177-0
Piroth, Cottenet, Mariet, Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: a nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30527-0
Ranjeva, Pinciroli, Hodell, Identifying clinical and biochemical phenotypes in acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to coronavirus disease-2019, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100829
Reif, Heun-Johnson, Tysinger, Lakdawalla, Measuring the COVID-19 mortality burden in the United States: a microsimulation study, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M21-2239
Singer, Al-Fayoumi, Ma, Komrokji, Mesa et al., Comprehensive kinase profile of pacritinib, a nonmyelosuppressive Janus kinase 2 inhibitor, J Exp Pharmacol, doi:10.2147/JEP.S110702
Singer, Al-Fayoumi, Taylor, Velichko, Mahony, Comparative phenotypic profiling of the JAK2 inhibitors ruxolitinib, fedratinib, momelotinib, and pacritinib reveals distinct mechanistic signatures, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0222944
Sterne, Murthy, Diaz, WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group. Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2020.17023&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2022.42918
Witalisz-Siepracka, Klein, Prinz, Loss of JAK1 drives innate immune deficiency, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.03108
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Yu, Ji, Yan, The ratio of Th17/Treg cells as a risk indicator in early acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-015-0811-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42918",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42918",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>The morbidity and mortality associated with COVID-19 remain high despite advances in standard of care therapy, and the role of anti-inflammatory agents that inhibit the interleukin 6/JAK2 pathway is still being elucidated.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To evaluate the efficacy and safety of the oral JAK2/IRAK1 inhibitor pacritinib vs placebo in the treatment of adults with severe COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>This phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial enrolled hospitalized adult patients with severe COVID-19 at 21 centers across the US between June 2020 and February 2021, with approximately 1.5 months of safety follow-up per patient. Data analysis was performed from September 2021 to July 2022.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Patients were randomized 1:1 to standard of care plus pacritinib (400 mg per os on day 1 followed by 200 mg twice daily on days 2-14) vs placebo, for 14 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary end point was death or need for invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) by day 28. All-cause mortality and safety were also assessed.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 200 patients were randomized to pacritinib (99 patients; 56 men [56.6%]; median [range] age, 60 [19-87] years) or placebo (101 patients; 64 men [63.4%]; median [range] age 59 [28-94] years). The percentage requiring supplementary oxygen was 99.0% (98 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 98.0% (99 patients) in the placebo group. The percentage who progressed to IMV, ECMO, or death was 17.2% (17 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 22.8% (23 patients) in the placebo group (odds ratio, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.28-1.35; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .23). Among patients with elevated interleukin 6, the rate was 17.5% (11 of 63 patients) in the pacritinib group vs 30.4% (21 of 96 patients) in the placebo group. The adverse event rate was similar for pacritinib vs placebo (78.1% [75 patients] vs 80.2% [81 patients]), with no excess in infection (14.6% [14 patients] vs 19.8% [20 patients]), bleeding (8.3% [8 patients] vs 10.9% [11 patients]), or thrombosis (8.3% [8 patients] vs 7.9% [8 patients]). Rates of grade 3 or higher adverse events were lower with pacritinib than placebo (29.2% [28 patients] vs 40.6% [41 patients]).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>The study did not meet its primary end point in patients with severe COVID-19. Subgroup analyses may indicate specific populations with hyperinflammation that could benefit from pacritinib, although further clinical trials would be needed to confirm these effects.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04404361\">NCT04404361</jats:ext-link></jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Carl and Edyth Lindner Center for Research and Education at The Christ Hospital, Cincinnati, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Cafardi",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ascension St Agnes Cancer Institute, Baltimore, Maryland"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Carole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ascension St John Newland Medical Associates, Southfield, Michigan"
}
],
"family": "Terebelo",
"given": "Howard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ascension Medical Group St Vincent Carmel Infectious Disease, Carmel, Indiana"
}
],
"family": "Tewell",
"given": "Chad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Benzaquen",
"given": "Sadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Providence St Jude Medical Center, Providence Medical Foundation, Fullerton, California"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lifespan Cancer Institute, Rhode Island Hospital, Providence"
}
],
"family": "Egan",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ascension St John Hospital, Detroit, Michigan"
}
],
"family": "Lebovic",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Bone Marrow Transplant & Leukemia Clinic, C. S. Mott Children’s Hospital, Ann Arbor, Michigan"
}
],
"family": "Pettit",
"given": "Kristen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Atlantic Health System, Morristown, New Jersey"
}
],
"family": "Whitman",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Tremblay",
"given": "Douglas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Feld",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CTI BioPharma, Seattle, Washington"
}
],
"family": "Buckley",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CTI BioPharma, Seattle, Washington"
}
],
"family": "Roman-Torres",
"given": "Karisse",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CTI BioPharma, Seattle, Washington"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CTI BioPharma, Seattle, Washington"
}
],
"family": "Craig",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tisch Cancer Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Mascarenhas",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T16:03:03Z",
"timestamp": 1670256183000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-05T16:03:07Z",
"timestamp": 1670256187000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-06T00:14:47Z",
"timestamp": 1720224887896
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2799198/cafardi_2022_oi_221209_1669647622.34377.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2242918",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30527-0",
"article-title": "Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: a nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study.",
"author": "Piroth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "251",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "zoi221209r1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-2239",
"article-title": "Measuring the COVID-19 mortality burden in the United States: a microsimulation study.",
"author": "Reif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1700",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "zoi221209r2",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100829",
"article-title": "Identifying clinical and biochemical phenotypes in acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to coronavirus disease-2019.",
"author": "Ranjeva",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "zoi221209r3",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-015-0811-2",
"article-title": "The ratio of Th17/Treg cells as a risk indicator in early acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "82",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "zoi221209r4",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000001409",
"article-title": "Interleukin-17A is associated with alveolar inflammation and poor outcomes in acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Mikacenic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "zoi221209r5",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1500054",
"article-title": "Unexpected role for adaptive aßTh17 cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "zoi221209r6",
"volume": "195",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "420",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "zoi221209r7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JEP",
"article-title": "Comprehensive kinase profile of pacritinib, a nonmyelosuppressive Janus kinase 2 inhibitor.",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "J Exp Pharmacol",
"key": "zoi221209r8",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30027-3",
"article-title": "Pacritinib versus best available therapy for the treatment of myelofibrosis irrespective of baseline cytopenias (PERSIST-1): an international, randomised, phase 3 trial.",
"author": "Mesa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e225",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol",
"key": "zoi221209r9",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5818",
"article-title": "Pacritinib vs best available therapy, including ruxolitinib, in patients with myelofibrosis: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Mascarenhas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Oncol",
"key": "zoi221209r10",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003314",
"article-title": "Determining the recommended dose of pacritinib: results from the PAC203 dose-finding trial in advanced myelofibrosis.",
"author": "Gerds",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5825",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv",
"key": "zoi221209r11",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.683401",
"article-title": "Inflammatory pathophysiology as a contributor to myeloproliferative neoplasms.",
"author": "Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "zoi221209r12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0222944",
"article-title": "Comparative phenotypic profiling of the JAK2 inhibitors ruxolitinib, fedratinib, momelotinib, and pacritinib reveals distinct mechanistic signatures.",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "zoi221209r13",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.03108",
"article-title": "Loss of JAK1 drives innate immune deficiency.",
"author": "Witalisz-Siepracka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3108",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "zoi221209r14",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines4030023",
"article-title": "Viral inhibition of the IFN-induced JAK/STAT signalling pathway: development of live attenuated vaccines by mutation of viral-encoded IFN-antagonists.",
"author": "Fleming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "zoi221209r15",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis.",
"author": "Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1330",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi221209r16",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi221209r17",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial.",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1637",
"issue": "10285",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi221209r18",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001899",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory therapies for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: an update of the systematic literature review to inform EULAR points to consider.",
"author": "Alunno",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "zoi221209r19",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1491",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi221209r20",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031994",
"article-title": "Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19.",
"author": "Kalil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "795",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi221209r21",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00331-3",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial.",
"author": "Marconi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1407",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "zoi221209r22",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2101643",
"article-title": "Tofacitinib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 pneumonia.",
"author": "Guimarães",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "406",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi221209r23",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00044-3",
"article-title": "Ruxolitinib in addition to standard of care for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RUXCOVID): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial.",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e351",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "zoi221209r24",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"article-title": "World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects.",
"author": "World Medical Association",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2191",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi221209r25",
"volume": "310",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19.",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi221209r26",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34147",
"article-title": "Disparities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status: a systematic-review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Magesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi221209r28",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01177-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: a European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA).",
"author": "Pagano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "168",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Hematol Oncol",
"key": "zoi221209r29",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "zoi221209r27",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration Office of Minority Health. Collection of race and ethnicity data in clinical trials: guidance for industry and Food and Drug Administration staff. October 26, 2016. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/75453/download"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2799198"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [
"A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Pacritinib vs Placebo for Patients With Severe COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "5"
}