ACTIV-5 / Big Effect Trial (BET-C) for the Treatment of COVID-19
et al., NCT04988035, ACTIV-5 BET-C, NCT04988035, Apr 2022
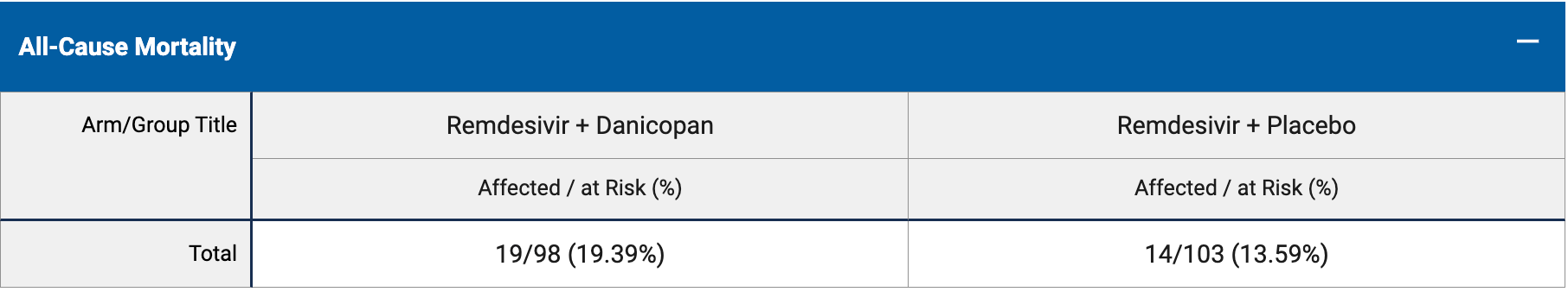
RCT 201 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing increased risk with danicopan treatment, with statistical significance for time to sustained recovery.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 42.6% higher, RR 1.43, p = 0.34, treatment 19 of 98 (19.4%), control 14 of 103 (13.6%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 16.8% higher, RR 1.17, p = 0.69, treatment 16 of 91 (17.6%), control 14 of 93 (15.1%), mechanical ventilation or ECMO.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 53.8% higher, HR 1.54, p = 0.01, treatment 96, control 99, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 37.0% higher, HR 1.37, p = 0.06, treatment 96, control 99, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, 2 categories, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 29.9% higher, HR 1.30, p = 0.11, treatment 96, control 99, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, 1 category, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
hospitalization time, 18.8% higher, relative time 1.19, p = 0.40, treatment median 9.5 IQR 19.0 n=96, control median 8.0 IQR 14.0 n=99.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Beigel et al., 23 Apr 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, preprint, 1 author, trial NCT04988035 (history) (ACTIV-5 BET-C).
Contact: jbeigel@niaid.nih.gov.