The Effects of Cyproheptadine on Severe COVID-19 From the ISPY-COVID Adaptive Platform Trial
et al., CHEST Critical Care, doi:10.1016/j.chstcc.2025.100201 (results released 1/4/2023), I-SPY COVID, NCT04488081, Jan 2023
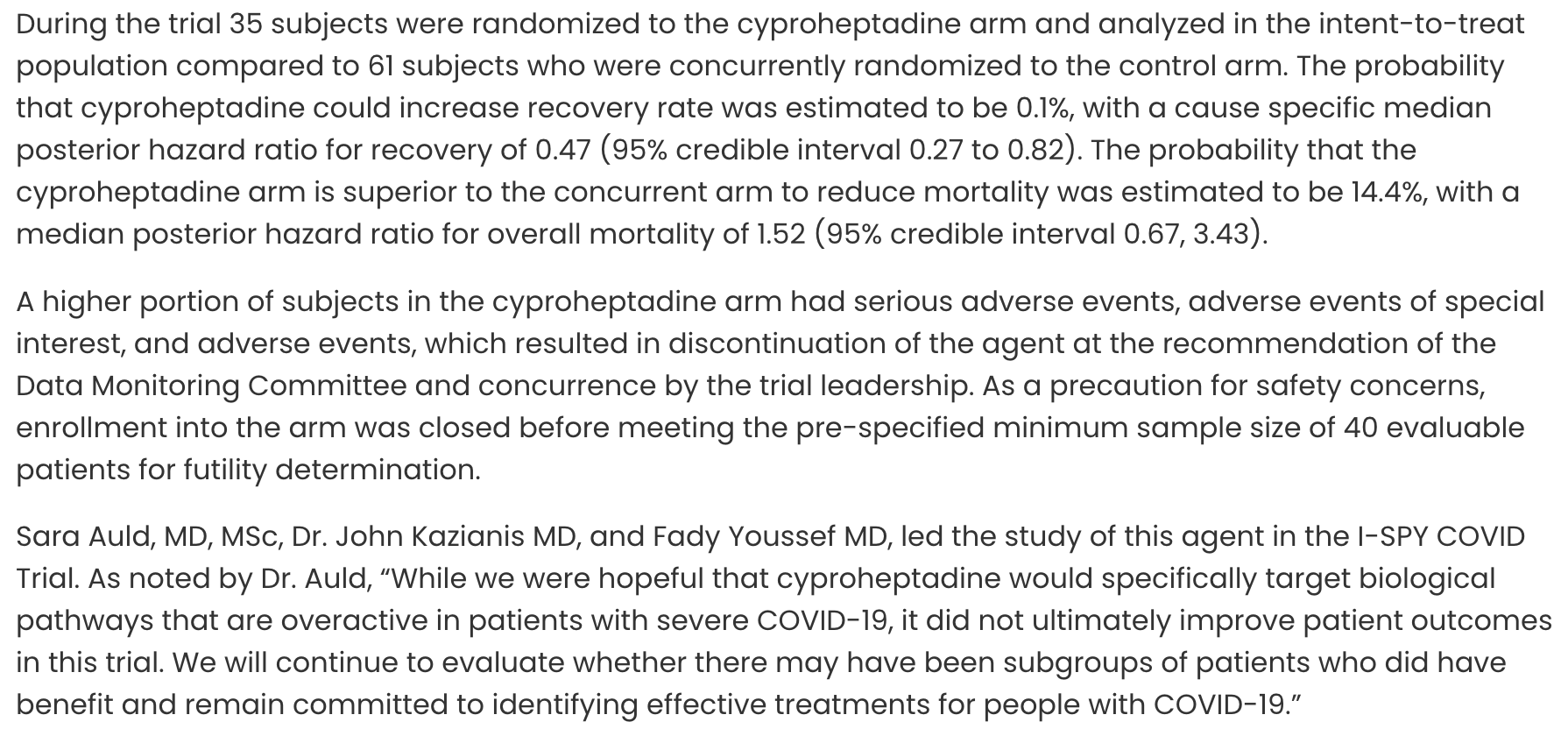
RCT 96 critically ill COVID-19 patients in the USA showing higher mortality/ventilation and worse recovery with cyproheptadine. Anticholinergic adverse events (delirium, urinary retention, bronchial obstruction/atelectasis, ileus) were higher in the cyproheptadine arm.
Cyproheptadine is a serotonin (5-HT) receptor antagonist, particularly at 5-HT2 receptors. Its effects may depend heavily on disease stage. In early disease it may reduce platelet hyperactivation: excessive platelet activation, platelet reactivity, and platelet-leukocyte aggregates are recognized as a pathogenic feature of COVID-19. Among the mediators released from activated platelet granules, serotonin is unique in that its clearance relies heavily on a healthy pulmonary endothelium, which is known to be injured in COVID-19. Cyproheptadine may also prevents serotonin accumulation: early blockade prevents the cycle of platelet activation → serotonin release → endothelial injury → more inflammation. Additionally, cyproheptadine has anti-inflammatory effects.
However in late stage disease, anticholinergic adverse events may cause significant harm. Cyproheptadine may also cause vasomotor disruption: blocking 5-HT2 receptors could worsen ventilation-perfusion matching; and loss of compensatory mechanisms: serotonin plays complex roles in vascular tone regulation that may be compensatory in severe lung injury. Once severe endothelial injury and thromboinflammation are established, blocking serotonin receptors alone cannot reverse the damage.
|
risk of death, 51.0% higher, HR 1.51, p = 0.32, treatment 35, control 61.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 206.0% higher, HR 3.06, p = 0.002, treatment 35, control 61.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 122.2% higher, HR 2.22, p = 0.004, treatment 35, control 61, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Auld et al., 4 Jan 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Sweden, peer-reviewed, median age 56.5, 29 authors, study period 10 September, 2021 - 28 December, 2021, trial NCT04488081 (history) (I-SPY COVID).
Contact: sauld@emory.edu.
The Effects of Cyproheptadine on Severe COVID-19 From the ISPY-COVID Adaptive Platform Trial
CHEST Critical Care, doi:10.1016/j.chstcc.2025.100201
Background: Severe COVID-19 has been associated with hypercoagulability and platelet activation, which is known to result in excessive accumulation of serotonin. However, few studies have evaluated whether serotonergic blockade may improve clinical outcomes among those with COVID-19. Research Question: Does cyproheptadine, an anti-serotonergic drug most commonly used to treat serotonin syndrome, improve time to clinical recovery in patients with severe COVID-19? Study Design and Methods: I-SPY COVID is a phase 2, multicenter, adaptive, open-label,
Concurrent Control (N=61) Total (N=96) Age (years) -median (IQR) 56.5 (47.9-61.9) 54.9 (43.0-63.8) 55. 4 (%) 3 (9) 3 ( 5 ) *Time from first known positive PCR to enrollment was missing for four participants enrolled as concurrent controls. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Asare, Ja, Rocca, Collins, Collins et al., COVID-19 Trial eSource Data Capture Efficiencies Using OneSource
Block, Early metabolic changes in response to lung injury: extrapolation from animals to humans, J Toxicol Environ Health
Boniatti, Nedel, Rihl, Effect of Cyproheptadine on Ventilatory Supportfree Days in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: An Open-label, Randomized Clinical Trial, Indian J Crit Care Med
Cardot-Leccia, Hubiche, Dellamonica, Burel-Vandenbos, Passeron, Pericyte alteration sheds light on micro-vasculopathy in COVID-19 infection, Intensive Care Med
Collins, Aa, Rocca, OneSource -Automating Capture of Regulatory-Grade Structured Data in Multicenter Clinical Trials
Consortium, Clinical trial design during and beyond the pandemic: the I-SPY COVID trial, Nat Med
Files, Matthay, Calfee, I-SPY COVID adaptive platform trial for COVID-19 acute respiratory failure: rationale, design and operations, BMJ Open
Grommes, Alard, Drechsler, Disruption of platelet-derived chemokine heteromers prevents neutrophil extravasation in acute lung injury, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Hariri, North, Shih, Lung Histopathology in Coronavirus Disease 2019 as Compared With Severe Acute Respiratory Sydrome and H1N1 Influenza: A Systematic Review, Chest
Hart, Block, Lung serotonin metabolism, Clin Chest Med
Helms, Tacquard, Severac, High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study, Intensive Care Med
Hottz, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Palhinha, Platelet activation and plateletmonocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19, Blood
J O U R N A L P R E, None
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis, Thromb Res
Looney, Nguyen, Hu, Van Ziffle, Lowell et al., Platelet depletion and aspirin treatment protect mice in a two-event model of transfusion-related acute lung injury, J Clin Invest
Manne, Denorme, Middleton, Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19, Blood
Marshall, Murthy, Diaz, A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Middeldorp, Coppens, Van Haaps, Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Thromb Haemost
Middleton, Rondina, Schwertz, Zimmerman, Amicus or Adversary Revisited: Platelets in Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol
Moores, Tritschler, Brosnahan, Thromboprophylaxis in Patients With COVID-19: A Brief Update to the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report, CHEST
Poissy, Goutay, Caplan, Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 Patients: Awareness of an Increased Prevalence, Circulation
Rapkiewicz, Mai, Carsons, Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series
Rudolph, Paul, Pulmonary and systemic vascular response to continuous infusion of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the dog, Am J Physiol
Schulz, Chalmers, Hayes, Altman, Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials, Jama
Zaid, Puhm, Allaeys, Platelets Can Associate with SARS-Cov-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19, Circ Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chstcc.2025.100201",
"ISSN": [
"2949-7884"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chstcc.2025.100201",
"alternative-id": [
"S2949788425000747"
],
"article-number": "100201",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The Effects of Cyproheptadine on Severe COVID-19 From the ISPY-COVID Adaptive Platform Trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "CHEST Critical Care"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chstcc.2025.100201"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the American College of Chest Physicians."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8972-3736",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Auld",
"given": "Sara C.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Youssef",
"given": "Fady A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albertson",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beitler",
"given": "Jeremy R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Berger",
"given": "Paul A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burnham",
"given": "Ellen L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cobb",
"given": "Nathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Friedman",
"given": "Eliot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gandotra",
"given": "Sheetal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gibbs",
"given": "Kevin W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hayanga",
"given": "Jeremiah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hyzy",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Malik M.H.S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koff",
"given": "Jonathan L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Richard A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meyer",
"given": "Nuala J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Obermiller",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Quill",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samavedam",
"given": "Sandhya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Kenneth K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wunderink",
"given": "Richard G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Russell",
"given": "Derek W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eklund",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Calfee",
"given": "Carolyn S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matthay",
"given": "Michael A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Files",
"given": "D. Clark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Kathleen D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esserman",
"given": "Laura J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "CHEST Critical Care",
"container-title-short": "CHEST Critical Care",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"chestcc.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-06T23:01:14Z",
"timestamp": 1754521274000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-06T23:01:15Z",
"timestamp": 1754521275000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-06T23:40:03Z",
"timestamp": 1754523603464,
"version": "3.41.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2949788425000747?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2949788425000747?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "100201",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2949788425000747"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Effects of Cyproheptadine on Severe COVID-19 From the ISPY-COVID Adaptive Platform Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}