The efficacy of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
et al., Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w, IRCT20121216011763N46, Jun 2022
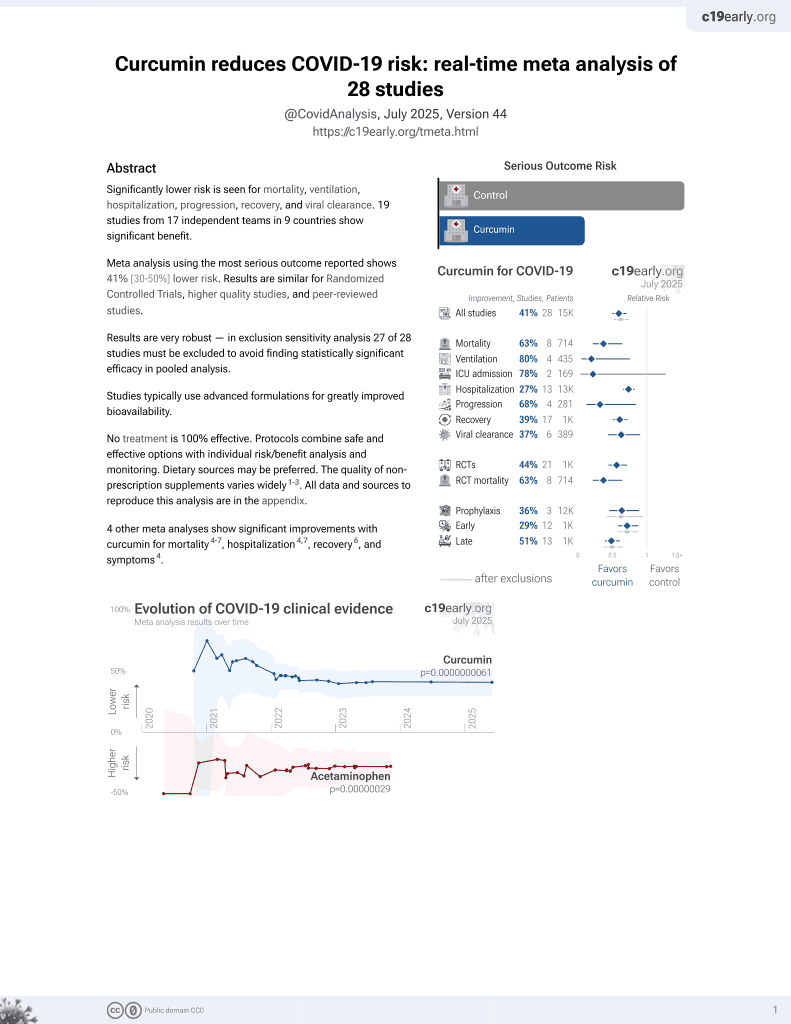
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small RCT 46 outpatients in Iran, 23 treated with curcimin-piperine, showing no significant difference in recovery. 1000mg curcumin and 10mg piperine/day for 14 days.
This is the 14th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 19th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
risk of no recovery, 26.5% lower, RR 0.74, p = 0.26, treatment 13, control 13, all symptoms combined.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 125.0% higher, RR 2.25, p = 0.58, treatment 3 of 8 (37.5%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), dyspnea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 433.3% higher, RR 5.33, p = 0.19, treatment 2 of 6 (33.3%), control 0 of 7 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), ague.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 72.9% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.04, treatment 2 of 12 (16.7%), control 8 of 13 (61.5%), NNT 2.2, weakness.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.42, treatment 3 of 10 (30.0%), control 7 of 14 (50.0%), NNT 5.0, muscular pain.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 38.5% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.65, treatment 4 of 13 (30.8%), control 4 of 8 (50.0%), NNT 5.2, headache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 71.4% higher, RR 1.71, p = 1.00, treatment 2 of 7 (28.6%), control 1 of 6 (16.7%), sore throat.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 12.5% lower, RR 0.88, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 8 (12.5%), control 1 of 7 (14.3%), NNT 56, sputum cough.
|
|
risk of no recovery, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 13 (23.1%), control 3 of 13 (23.1%), dry cough.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Askari et al., 6 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period November 2020 - April 2021, trial IRCT20121216011763N46.
Contact: baghrerniya@nutr.mui.ac.ir (corresponding author).
The efficacy of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w
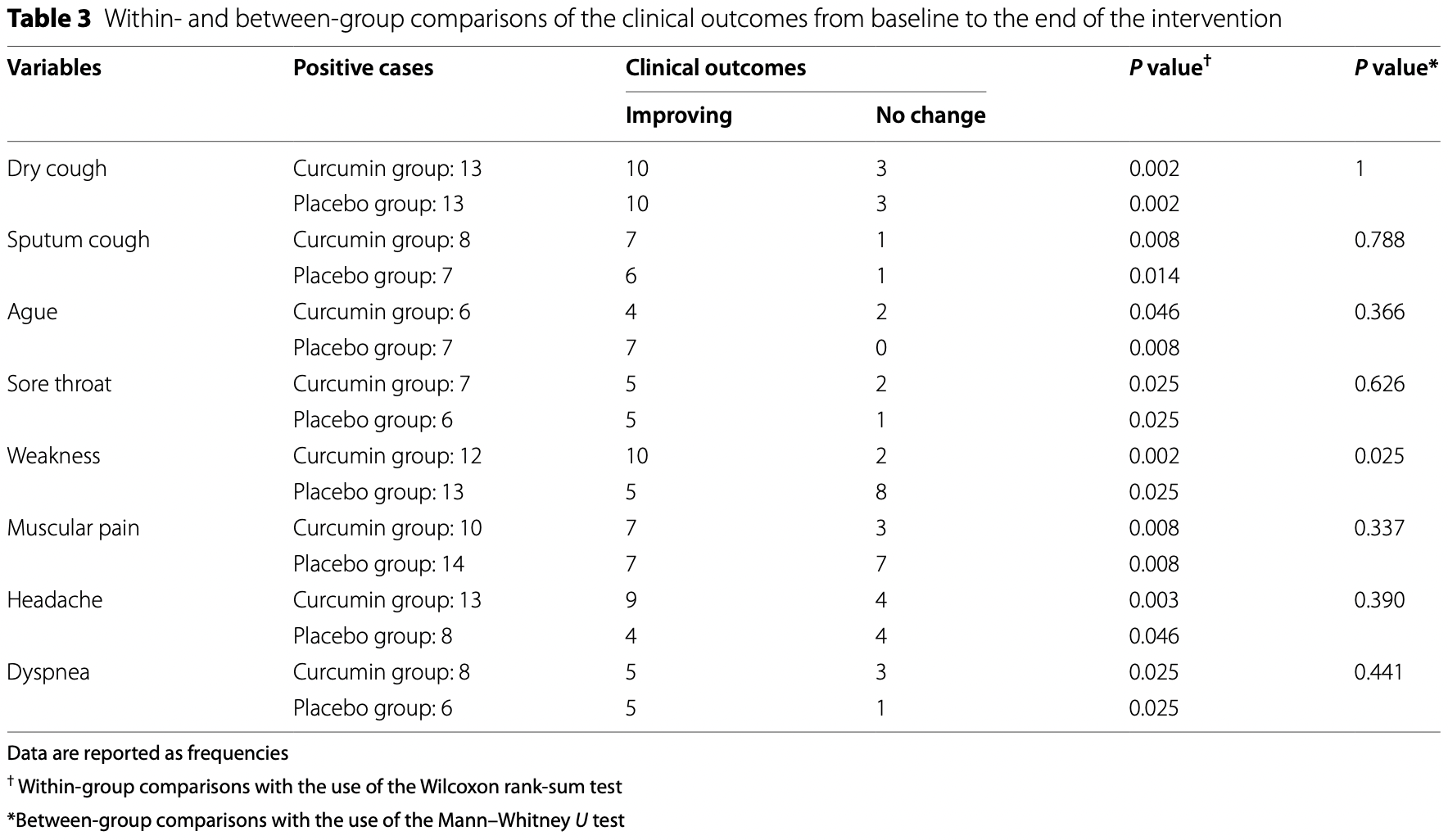
Background: COVID-19 pandemic has made the disease a major global problem by creating a significant burden on health, economic, and social status. To date, there are no effective and approved medications for this disease. Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent can have a positive effect on the control of COVID-19 complications. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of curcumin-piperine supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in patients with COVID-19. Methods: Forty-six outpatients with COVID-19 disease were randomly allocated to receive two capsules of curcumin-piperine; each capsule contained 500 mg curcumin plus 5 mg piperine or placebo for 14 days. Results: Mean changes in complete blood count, liver enzymes, blood glucose levels, lipid parameters, kidney function, and c-reactive protein (CRP) were not significantly different between the two groups. There was a significant improvement in health status, including dry cough, sputum cough, ague, sore throat, weakness, muscular pain, headache, and dyspnea at week 2 in both curcumin-piperine and placebo groups (P value < 0.05); however, the improvement in weakness was more in the curcumin-piperine group than with placebo group (P value 025).
Conclusion: The present study results showed that curcumin-piperine co-supplementation in outpatients with COVID-19 could significantly reduce weakness. However, in this study, curcumin-piperine co-supplementation could not significantly affect the other indices, including biochemical and clinical indices.
Authors' contributions Study design: GA, AS, BI, MHR, and MB. Data gathering: DS, AM, SR, FK, and ME. Statistical analysis: GA, DS, BI, MHR, and MB. Drafting the manuscript: GA, AS, AM, SR, MM, ME, and MB. The authors read and approved the final manuscript before submission.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate This trial was accepted by the ethics committee of the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, with the ethical code: IR.MUI.MED.REC.1399.049. In this study, we only reported the data obtained from COVID-19 outpatients. This trial was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients were informed regarding the objectives and procedures of the trial, who then provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests MM is the funder of the Sami-Sabinsa Group. The other authors have nothing to disclose. Author details 1 Food Security Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, PO Box: 00983137922110, Isfahan, Iran. 2 Anesthesia and Critical Care Research Center, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. 3 Department of Community Nutrition, School of Nutrition and Food Science, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. 4 Applied Biomedical Research Center, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran. 5 Biotechnology Research Center, Pharmaceutical Technology Institute, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad,..
References
Ahmadi, Salari, Sharifi, Reihani, Rostamiani et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID-19: a randomized triple-blind placebocontrolled clinical trial, Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2226
Alamdari, Neal, Hasselgren, Curcumin and muscle wasting: a new role for an old drug?, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2008.09.002
Ali, Hanif, Haider, Ahmed, Sundas et al., Treatment options for COVID-19: a review, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00480
Alikiaii, Bagherniya, Askari, Sathyapalan, Sahebkar, Evaluation of the effect of curcumin on pneumonia: a systematic review of preclinical studies, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6939
Alwi, Santoso, Suyono, Sutrisna, Suyatna et al., The effect of curcumin on lipid level in patients with acute coronary syndrome, Acta Med Indones
Anand, Kunnumakkara, Newman, Aggarwal, Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises, Mol Pharm, doi:10.1021/mp700113r
Avasarala, Zhang, Liu, Wang, London et al., Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0134982
Babaei, Nassiri-Asl, Hosseinzadeh, Curcumin (a constituent of turmeric): New treatment option against COVID-19, Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1002/fsn3.1858
Bagherniya, Khedmatgozar, Fakheran, Xu, Johnston et al., Medicinal plants and bioactive natural products as inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7118
Bani-Sadr, Hentzien, Pascard, 'guyen, Servettaz et al., Corticosteroid therapy for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: a before-after study, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106077
Bhutani, Bishnoi, Kulkarni, Anti-depressant like effect of curcumin and its combination with piperine in unpredictable chronic stressinduced behavioral, biochemical and neurochemical changes, Pharmacol Biochem Behav, doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.10.007
Bourbour, Dahka, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus, Arch Physiol Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188
Brem, Viardot, Nylund, Implications of the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak for innovation: which technologies will improve our lives?, Technol Forecast Soc Chang, doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120451
Cai, Frantz, Ne, Melendez, Oh et al., IKKβ/NF-κB activation causes severe muscle wasting in mice, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.027
Cevik, Bamford, Ho, COVID-19 pandemic-a focused review for clinicians, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.023
Chin, Huebbe, Frank, Rimbach, Pallauf, Curcumin may impair iron status when fed to mice for six months, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2014.01.018
Farhood, Mortezaee, Goradel, Khanlarkhani, Salehi et al., Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent: implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, J Cell Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.27442
Feingold, Grunfeld, The Effect of Inflammation and Infection on Lipids and Lipoproteins
Ferguson, Stojanovski, Macdonald-Wicks, Garg, Curcumin potentiates cholesterol-lowering effects of phytosterols in hypercholesterolaemic individuals. A randomised controlled trial, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2017.12.009
Ford, Red blood cell morphology, Int J Lab Hematol, doi:10.1111/ijlh.12082
García-Escobar, Ingelmo, Red cell volume distribution width as another biomarker, Card Fail Rev, doi:10.15420/cfr.2019.13.1
Gupta, Patchva, Koh, Aggarwal, Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice, and its miraculous biological activities, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05648.x
Hassaniazad, Eftekhar, Inchehsablagh, Kamali, Tousi et al., A triple-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin-containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7294
Holbrook, Weakness and fatigue
Honarkar Shafie, Taheri, Alijani, Okhovvat, Goudarzi et al., Effect of nanocurcumin supplementation on the severity of symptoms and length of hospital stay in patients with COVID-19: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7374
Hong, Kim, Youm, Choi, Kim et al., Elevated red blood cell distribution width is associated with morphometric vertebral fracture in community-dwelling older adults, independent of anemia, inflammation, and nutritional status: the Korean Urban Rural Elderly (KURE) study, Calcif Tissue Int, doi:10.1007/s00223-018-0470-9
Hu, Chen, Wu, He, Ye, Low serum cholesterol level among patients with COVID-19 infection in Wenzhou, SSRN Electron J, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3544826
Jain, Rains, Croad, Larson, Jones, Curcumin supplementation lowers TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 secretion in high glucose-treated cultured monocytes and blood levels of TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, glucose, and glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetic rats, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2008.2140
Keihanian, Saeidinia, Bagheri, Johnston, Sahebkar, Curcumin, hemostasis, thrombosis, and coagulation, J Cell Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.26249
Kulkarni, Bhutani, Bishnoi, Antidepressant activity of curcumin: involvement of serotonin and dopamine system, Psychopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1300-y
Ladner, Guttridge, Tumor necrosis factor-regulated biphasic activation of NF-κB is required for cytokine-induced loss of skeletal muscle gene products, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M207129200
Lake, What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research, Clin Med, doi:10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron
Li, Reid, NF-κB mediates the protein loss induced by TNF-α in differentiated skeletal muscle myotubes, Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.2000.279.4.R1165
Liu, Cong, Wang, Mei, Peng et al., Risk of malnutrition is common in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: a cross-sectional study, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxab009
Maurya, Kumar, Prasad, Bhatt, Saxena, Structure-based drug designing for potential antiviral activity of selected natural products from Ayurveda against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and its cellular receptor, Virusdisease, doi:10.1007/s13337-020-00598-8
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Miryan, Bagherniya, Sahebkar, Soleimani, Rouhani et al., Effects of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical signs, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in patients with COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04924-9
Miryan, Soleimani, Askari, Jamialahmadi, Guest et al., Curcumin and piperine in COVID-19: a promising duo to the rescue? In
Miryan, Soleimani, Askari, Jamialahmadi, Guest et al., Curcumin and piperine in COVID-19: a promising duo to the rescue?, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_16
Moghadamtousi, Kadir, Hassandarvish, Tajik, Abubakar et al., A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/186864
Pawar, Mastud, Pawar, Pawar, Bhoite et al., Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.669362
Pawar, Mastud, Pawar, Pawar, Bhoite et al., Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.669362
Penner, Gang, Wray, Fischer, Hasselgren, The transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 are differentially regulated in skeletal muscle during sepsis, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4497
Rafiq, Raza, Younas, Naeem, Adeeb et al., Molecular targets of curcumin and future therapeutic role in leukemia, J Biosci Med, doi:10.4236/JBM.2018.64003
Rattis, Ramos, Celes, Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.675287
Richardson, Griffin, Tucker, Smith, Oechsle et al., Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4
Rocha, De Assis, Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6745
Rothenberg, Coronavirus disease 19 from the perspective of ageing with focus on nutritional status and nutrition management-a narrative review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13041294
Saber-Moghaddam, Salari, Hejazi, Amini, Taherzadeh et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: an open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7004
Sarma, Chapter, Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations
Sfera, Osorio, Campo, Pereida, Maurer et al., Endothelial senescence and chronic fatigue syndrome, a COVID-19 based hypothesis, Front Cell Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.673217
Smith, Ashar, Iron deficiency anemia due to high-dose turmeric, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.3858
Sohrabi, Alsafi, Neill, Khan, Kerwan et al., World Health Organization declares global emergency: a review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19), Int J Surg, doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034
Soni, Mehta, Ratre, Tiwari, Amit et al., Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19?, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551
Strandberg, CHAPTER VII: The influence of corticosteroid therapy on hematological values, bone marrow iron and iron absorption in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Acta Med Scand, doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb01372.x
Subhan, Khalil, Zeeshan, Haider, Tauseef et al., Curcumin: from ancient spice to modern anti-viral drug in COVID-19 pandemic, Life Sci
Sultana, Haque, Sultana, Ahmed, Value of red cell distribution width (RDW) and RBC indices in the detection of iron deficiency anemia, Mymensingh Med J
Sun, Zhou, Ye, White blood cells and severe COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization study, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.14.20212993
Tahmasebi, Saeed, Temirgalieva, Yumashev, El-Esawi et al., Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437
Ternullo, Gagnat, Julin, Johannessen, Basnet et al., Liposomes augment biological benefits of curcumin for multitargeted skin therapy, Eur J Pharm Biopharm, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.016
Thimmulappa, Kumar, Shivamallu, Subramaniam, Radhakrishnan et al., Antiviral and immunomodulatory activity of curcumin: a case for prophylactic therapy for COVID-19, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06350
Townsend, Dyer, Jones, Dunne, Mooney et al., Persistent fatigue following SARS-CoV-2 infection is common and independent of severity of initial infection, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0240784
Utku, Budak, Karabay, Güçlü, Okan et al., Main symptoms in patients presenting in the COVID-19 period, Scott Med J, doi:10.1177/0036933020949253
Vahedian-Azimi, Abbasifard, Rahimi-Bashar, Guest, Majeed et al., Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review of clinical trials, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020256
Valizadeh, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Danshina, Gencer, Ammari et al., Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088
Wang, Li, Wang, Sarcopenia: an underlying treatment target during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.111104
Wilson, Concern coronavirus may trigger post-viral fatigue syndromes, New Sci, doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30746-6
Wyke, Russell, Tisdale, Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-κ B activation, Br J Cancer, doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602165
Yong, Long COVID or post-COVID-19 syndrome: putative pathophysiology, risk factors, and treatments, Infect Dis, doi:10.1080/23744235.2021.1924397
Zahedipour, Hosseini, Sathyapalan, Majeed, Jamialahmadi et al., Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6738
Zha, Li, Pan, Tefsen, Li et al., Corticosteroid treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Med J Aust, doi:10.5694/mja2.50577
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w",
"ISSN": [
"1745-6215"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>COVID-19 pandemic has made the disease a major global problem by creating a significant burden on health, economic, and social status. To date, there are no effective and approved medications for this disease. Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent can have a positive effect on the control of COVID-19 complications. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of curcumin-piperine supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in patients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Forty-six outpatients with COVID-19 disease were randomly allocated to receive two capsules of curcumin-piperine; each capsule contained 500 mg curcumin plus 5 mg piperine or placebo for 14 days.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Mean changes in complete blood count, liver enzymes, blood glucose levels, lipid parameters, kidney function, and c-reactive protein (CRP) were not significantly different between the two groups. There was a significant improvement in health status, including dry cough, sputum cough, ague, sore throat, weakness, muscular pain, headache, and dyspnea at week 2 in both curcumin-piperine and placebo groups (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> value < 0.05); however, the improvement in weakness was more in the curcumin-piperine group than with placebo group (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> value 025).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The present study results showed that curcumin-piperine co-supplementation in outpatients with COVID-19 could significantly reduce weakness. However, in this study, curcumin-piperine co-supplementation could not significantly affect the other indices, including biochemical and clinical indices.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.irct.ir/trial/47529\">IRCT20121216011763N46</jats:ext-link>. 2020-10-31</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"6375"
],
"article-number": "472",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "29 August 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2 May 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "6 June 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This trial was accepted by the ethics committee of the Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, with the ethical code: IR.MUI.MED.REC.1399.049. In this study, we only reported the data obtained from COVID-19 outpatients. This trial was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients were informed regarding the objectives and procedures of the trial, who then provided written informed consent."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "MM is the funder of the Sami-Sabinsa Group. The other authors have nothing to disclose."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Askari",
"given": "Gholamreza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahebkar",
"given": "Amirhossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Soleimani",
"given": "Davood",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahdavi",
"given": "Atena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rafiee",
"given": "Sahar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majeed",
"given": "Muhammed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khorvash",
"given": "Farzin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Iraj",
"given": "Bijan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elyasi",
"given": "Mahshid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rouhani",
"given": "Mohammad Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5861-6129",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bagherniya",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Trials",
"container-title-short": "Trials",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-06T06:02:29Z",
"timestamp": 1654495349000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-06T18:06:16Z",
"timestamp": 1654538776000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003970",
"award": [
"199014"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Isfahan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-06T18:41:58Z",
"timestamp": 1654540918749
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654473600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1654473600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034",
"author": "C Sohrabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Int J Surg (London, England)",
"key": "6375_CR1",
"unstructured": "Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O’Neill N, Khan M, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, et al. World Health Organization declares global emergency: a review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int J Surg (London, England). 2020;76:71–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034.",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6375_CR2",
"unstructured": "BourBour F, Mirzaei Dahka S, Gholamalizadeh M, Akbari ME, Shadnoush M, Haghighi M, et al. Nutrients in prevention, treatment, and management of viral infections; special focus on Coronavirus. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13041294",
"author": "E Rothenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1294",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "6375_CR3",
"unstructured": "Rothenberg E. Coronavirus disease 19 from the perspective of ageing with focus on nutritional status and nutrition management—a narrative review. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1294. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041294.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron",
"author": "MA Lake",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Med",
"key": "6375_CR4",
"unstructured": "Lake MA. What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research. Clin Med. 2020;20(2):124. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120451",
"author": "A Brem",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120451",
"journal-title": "Technol Forecast Soc Chang",
"key": "6375_CR5",
"unstructured": "Brem A, Viardot E, Nylund PA. Implications of the coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak for innovation: which technologies will improve our lives? Technol Forecast Soc Chang. 2021;163:120451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120451.",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"author": "F Zahedipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2911",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR6",
"unstructured": "Zahedipour F, Hosseini SA, Sathyapalan T, Majeed M, Jamialahmadi T, Al-Rasadi K, et al. Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection. Phytother Res. 2020;34(11):2911–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6738.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "6375_CR7",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1033–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6375_CR8",
"unstructured": "Saber-Moghaddam N, Salari S, Hejazi S, Amini M, Taherzadeh Z, Eslami S, et al. Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: an open label nonrandomized clinical trial. Phytother Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7004."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4",
"author": "P Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e30",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "6375_CR9",
"unstructured": "Richardson P, Griffin I, Tucker C, Smith D, Oechsle O, Phelan A, et al. Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10223):e30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.27442",
"author": "B Farhood",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5728",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Cell Physiol",
"key": "6375_CR10",
"unstructured": "Farhood B, Mortezaee K, Goradel NH, Khanlarkhani N, Salehi E, Nashtaei MS, et al. Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent: implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5728–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27442.",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.016",
"author": "S Ternullo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharm Biopharm",
"key": "6375_CR11",
"unstructured": "Ternullo S, Gagnat E, Julin K, Johannessen M, Basnet P, Vanić Ž, et al. Liposomes augment biological benefits of curcumin for multitargeted skin therapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019;144:154–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.09.016.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4236/JBM.2018.64003",
"author": "S Rafiq",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "J Biosci Med",
"key": "6375_CR12",
"unstructured": "Rafiq S, Raza MH, Younas M, Naeem F, Adeeb R, Iqbal J, et al. Molecular targets of curcumin and future therapeutic role in leukemia. J Biosci Med. 2018;6(04):33. https://doi.org/10.4236/JBM.2018.64003.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05648.x",
"author": "SC Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "283",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol",
"key": "6375_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gupta SC, Patchva S, Koh W, Aggarwal BB. Discovery of curcumin, a component of golden spice, and its miraculous biological activities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;39(3):283–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05648.x.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.26249",
"author": "F Keihanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4497",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Cell Physiol",
"key": "6375_CR14",
"unstructured": "Keihanian F, Saeidinia A, Bagheri RK, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. Curcumin, hemostasis, thrombosis, and coagulation. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(6):4497–511. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26249.",
"volume": "233",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2008.2140",
"author": "SK Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "241",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Antioxid Redox Signal",
"key": "6375_CR15",
"unstructured": "Jain SK, Rains J, Croad J, Larson B, Jones K. Curcumin supplementation lowers TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1 secretion in high glucose-treated cultured monocytes and blood levels of TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, glucose, and glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetic rats. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(2):241–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2140.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0134982",
"author": "S Avasarala",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e57285",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "6375_CR16",
"unstructured": "Avasarala S, Zhang F, Liu G, Wang R, London SD, London L. Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57285. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134982.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13337-020-00598-8",
"author": "VK Maurya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "179",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Virusdisease",
"key": "6375_CR17",
"unstructured": "Maurya VK, Kumar S, Prasad AK, Bhatt ML, Saxena SK. Structure-based drug designing for potential antiviral activity of selected natural products from Ayurveda against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and its cellular receptor. Virusdisease. 2020;31(2):179–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-020-00598-8.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6745",
"author": "FAC Rocha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2085",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR18",
"unstructured": "Rocha FAC, de Assis MR. Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19. Phytother Res. 2020;34(9):2085–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6745.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06350",
"author": "RK Thimmulappa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e06350",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "6375_CR19",
"unstructured": "Thimmulappa RK, Kumar MNK, Shivamallu C, Subramaniam KT, Radhakrishnan A, Suresh B, et al. Antiviral and immunomodulatory activity of curcumin: a case for prophylactic therapy for COVID-19. Heliyon. 2021;7(2):e06350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06350.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7118",
"author": "M Bagherniya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4804",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR20",
"unstructured": "Bagherniya M, Khedmatgozar H, Fakheran O, Xu S, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A. Medicinal plants and bioactive natural products as inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome. Phytother Res. 2021;35(9):4804–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7118.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6939",
"author": "B Alikiaii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1939",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR21",
"unstructured": "Alikiaii B, Bagherniya M, Askari G, Sathyapalan T, Sahebkar A. Evaluation of the effect of curcumin on pneumonia: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Phytother Res. 2021;35(4):1939–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6939.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/186864",
"author": "S Zorofchian Moghadamtousi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "186864",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "6375_CR22",
"unstructured": "Zorofchian Moghadamtousi S, Abdul Kadir H, Hassandarvish P, Tajik H, Abubakar S, Zandi K. A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:186864. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/186864.",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551",
"author": "VK Soni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "173551",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pharmacol",
"key": "6375_CR23",
"unstructured": "Soni VK, Mehta A, Ratre YK, Tiwari AK, Amit A, Singh RP, et al. Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19? Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;886:173551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551.",
"volume": "886",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.669362",
"author": "KS Pawar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "669362",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "6375_CR24",
"unstructured": "Pawar KS, Mastud RN, Pawar SK, Pawar SS, Bhoite RR, Bhoite RR, et al. Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:669362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.669362.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.1858",
"author": "F Babaei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5215",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "6375_CR25",
"unstructured": "Babaei F, Nassiri-Asl M, Hosseinzadeh H. Curcumin (a constituent of turmeric): New treatment option against COVID-19. Food Sci Nutr. 2020;8(10):5215–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1858.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020256",
"author": "A Vahedian-Azimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "256",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "6375_CR26",
"unstructured": "Vahedian-Azimi A, Abbasifard M, Rahimi-Bashar F, Guest PC, Majeed M, Mohammadi A, et al. Effectiveness of curcumin on outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review of clinical trials. Nutrients. 2022;14(2):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14020256.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_16",
"author": "M Miryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "197",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol",
"key": "6375_CR27",
"unstructured": "Miryan M, Soleimani D, Askari G, Jamialahmadi T, Guest PC, Bagherniya M, et al. Curcumin and piperine in COVID-19: a promising duo to the rescue? Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1327:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_16.",
"volume": "1327",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.37185/LnS.1.1.137",
"author": "F Subhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5",
"issue": "supplement",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "6375_CR28",
"unstructured": "Subhan F, Khalil AAK, Zeeshan M, Haider A, Tauseef I, Haleem SK, et al. Curcumin: from ancient spice to modern anti-viral drug in COVID-19 pandemic. Life Sci. 2020;1(supplement):5.",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"author": "H Valizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107088",
"issue": "Pt B",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "6375_CR29",
"unstructured": "Valizadeh H, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid S, Danshina S, Gencer MZ, Ammari A, Sadeghi A, et al. Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;89(Pt B):107088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088.",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pbb.2008.10.007",
"author": "MK Bhutani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Biochem Behav",
"key": "6375_CR30",
"unstructured": "Bhutani MK, Bishnoi M, Kulkarni SK. Anti-depressant like effect of curcumin and its combination with piperine in unpredictable chronic stress-induced behavioral, biochemical and neurochemical changes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009;92(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.10.007.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00213-008-1300-y",
"author": "SK Kulkarni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "435",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Psychopharmacology",
"key": "6375_CR31",
"unstructured": "Kulkarni SK, Bhutani MK, Bishnoi M. Antidepressant activity of curcumin: involvement of serotonin and dopamine system. Psychopharmacology. 2008;201(3):435–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1300-y.",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_16",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "6375_CR32",
"unstructured": "Miryan M, Soleimani D, Askari G, Jamialahmadi T, Guest PC, Bagherniya M, et al. Curcumin and piperine in COVID-19: a promising duo to the rescue? In: Identification of biomarkers, new treatments, and vaccines for COVID-19. Switzerland: Springer; 2021. p. 197–204."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/mp700113r",
"author": "P Anand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "807",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Mol Pharm",
"key": "6375_CR33",
"unstructured": "Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB. Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm. 2007;4(6):807–18. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp700113r.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04924-9",
"author": "M Miryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "6375_CR34",
"unstructured": "Miryan M, Bagherniya M, Sahebkar A, Soleimani D, Rouhani MH, Iraj B, et al. Effects of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical signs, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in patients with COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-020-04924-9.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.023",
"author": "M Cevik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "842",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "6375_CR35",
"unstructured": "Cevik M, Bamford CGG, Ho A. COVID-19 pandemic-a focused review for clinicians. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(7):842–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.023.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00480",
"author": "MJ Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "480",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "6375_CR36",
"unstructured": "Ali MJ, Hanif M, Haider MA, Ahmed MU, Sundas F, Hirani A, et al. Treatment options for COVID-19: a review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00480.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"author": "R Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4068",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "6375_CR37",
"unstructured": "Ahmadi R, Salari S, Sharifi MD, Reihani H, Rostamiani MB, Behmadi M, et al. Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID-19: a randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;9(8):4068–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2226.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7294",
"author": "M Hassaniazad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6417",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR38",
"unstructured": "Hassaniazad M, Eftekhar E, Inchehsablagh BR, Kamali H, Tousi A, Jaafari MR, et al. A triple-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin-containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients. Phytother Res. 2021;35(11):6417–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7294.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7374",
"author": "E Honarkar Shafie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1013",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "6375_CR39",
"unstructured": "Honarkar Shafie E, Taheri F, Alijani N, Okhovvat AR, Goudarzi R, Borumandnia N, et al. Effect of nanocurcumin supplementation on the severity of symptoms and length of hospital stay in patients with COVID-19: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. 2022;36(2):1013–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7374.",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437",
"author": "S Tahmasebi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119437",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "6375_CR40",
"unstructured": "Tahmasebi S, Saeed BQ, Temirgalieva E, Yumashev AV, El-Esawi MA, Navashenaq JG, et al. Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2. Life Sci. 2021;276:119437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437.",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.675287",
"author": "BAC Rattis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "675287",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "6375_CR41",
"unstructured": "Rattis BAC, Ramos SG, Celes MRN. Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:675287. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.675287.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fncel.2021.673217",
"author": "A Sfera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "673217",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Neurosci",
"key": "6375_CR42",
"unstructured": "Sfera A, Osorio C, Del Campo CMZM, Pereida S, Maurer S, Maldonado JC, et al. Endothelial senescence and chronic fatigue syndrome, a COVID-19 based hypothesis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:673217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.673217.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30746-6",
"author": "C Wilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10",
"issue": "3278",
"journal-title": "New Sci (1971)",
"key": "6375_CR43",
"unstructured": "Wilson C. Concern coronavirus may trigger post-viral fatigue syndromes. New Sci (1971). 2020;246(3278):10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30746-6.",
"volume": "246",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2021.1924397",
"author": "SJ Yong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis",
"key": "6375_CR44",
"unstructured": "Yong SJ. Long COVID or post-COVID-19 syndrome: putative pathophysiology, risk factors, and treatments. Infect Dis. 2021;53(10):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2021.1924397.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.14.20212993",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6375_CR45",
"unstructured": "Sun Y, Zhou J, Ye K. White blood cells and severe COVID-19: a Mendelian randomization study. medRxiv. 2020:2020.10.14.20212993. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.14.20212993."
},
{
"key": "6375_CR46",
"unstructured": "Sarma P. Chapter 152. Red cell indices. In: Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations. 3rd ed. Boston: Butterworths; 1990."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb01372.x",
"author": "O Strandberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127",
"issue": "S454",
"journal-title": "Acta Med Scand",
"key": "6375_CR47",
"unstructured": "Strandberg O. CHAPTER VII: The influence of corticosteroid therapy on hematological values, bone marrow iron and iron absorption in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Med Scand. 1966;180(S454):127–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb01372.x.",
"volume": "180",
"year": "1966"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106077",
"author": "F Bani-Sadr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106077",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "6375_CR48",
"unstructured": "Bani-Sadr F, Hentzien M, Pascard M, N'Guyen Y, Servettaz A, Andreoletti L, et al. Corticosteroid therapy for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: a before–after study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;56(2):106077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106077.",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5694/mja2.50577",
"author": "L Zha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "416",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Med J Aust",
"key": "6375_CR49",
"unstructured": "Zha L, Li S, Pan L, Tefsen B, Li Y, French N, et al. Corticosteroid treatment of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Med J Aust. 2020;212(9):416–20. https://doi.org/10.5694/mja2.50577.",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.3858",
"author": "TJ Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3858",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "6375_CR50",
"unstructured": "Smith TJ, Ashar BH. Iron deficiency anemia due to high-dose turmeric. Cureus. 2019;11(1):e3858. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.3858.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2014.01.018",
"author": "D Chin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "563",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "6375_CR51",
"unstructured": "Chin D, Huebbe P, Frank J, Rimbach G, Pallauf K. Curcumin may impair iron status when fed to mice for six months. Redox Biol. 2014;2:563–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2014.01.018.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"author": "GS Sultana",
"first-page": "370",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mymensingh Med J",
"key": "6375_CR52",
"unstructured": "Sultana GS, Haque SA, Sultana T, Ahmed AN. Value of red cell distribution width (RDW) and RBC indices in the detection of iron deficiency anemia. Mymensingh Med J. 2013;22(2):370–6.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxab009",
"author": "A Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1591",
"issue": "nxab009",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "6375_CR53",
"unstructured": "Liu A, Cong J, Wang Q, Mei Y, Peng Y, Zhou M, et al. Risk of malnutrition is common in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: a cross-sectional study. J Nutr. 2021;151(nxab009):1591–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxab009.",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00223-018-0470-9",
"author": "N Hong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "26",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Calcif Tissue Int",
"key": "6375_CR54",
"unstructured": "Hong N, Kim CO, Youm Y, Choi JY, Kim HC, Rhee Y. Elevated red blood cell distribution width is associated with morphometric vertebral fracture in community-dwelling older adults, independent of anemia, inflammation, and nutritional status: the Korean Urban Rural Elderly (KURE) study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;104(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-018-0470-9.",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15420/cfr.2019.13.1",
"author": "A García-Escobar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "176",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Card Fail Rev",
"key": "6375_CR55",
"unstructured": "García-Escobar A, Grande Ingelmo JM. Red cell volume distribution width as another biomarker. Card Fail Rev. 2019;5(3):176–9. https://doi.org/10.15420/cfr.2019.13.1.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijlh.12082",
"author": "J Ford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "351",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Lab Hematol",
"key": "6375_CR56",
"unstructured": "Ford J. Red blood cell morphology. Int J Lab Hematol. 2013;35(3):351–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12082.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3544826",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "6375_CR57",
"unstructured": "Hu X, Chen D, Wu L, He G, Ye W. Low serum cholesterol level among patients with COVID-19 infection in Wenzhou, China. SSRN Electron J. 2020. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3544826."
},
{
"key": "6375_CR58",
"unstructured": "Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. The Effect of Inflammation and Infection on Lipids and Lipoproteins. 2022 Mar 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2017.12.009",
"author": "JJA Ferguson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "6375_CR59",
"unstructured": "Ferguson JJA, Stojanovski E, MacDonald-Wicks L, Garg ML. Curcumin potentiates cholesterol-lowering effects of phytosterols in hypercholesterolaemic individuals. A randomised controlled trial. Metabolism. 2018;82:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.12.009.",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "I Alwi",
"first-page": "201",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Acta Med Indones",
"key": "6375_CR60",
"unstructured": "Alwi I, Santoso T, Suyono S, Sutrisna B, Suyatna FD, Kresno SB, et al. The effect of curcumin on lipid level in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Acta Med Indones. 2008;40(4):201–10.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0240784",
"author": "L Townsend",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0240784",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "6375_CR61",
"unstructured": "Townsend L, Dyer AH, Jones K, Dunne J, Mooney A, Gaffney F, et al. Persistent fatigue following SARS-CoV-2 infection is common and independent of severity of initial infection. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0240784. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240784.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0036933020949253",
"author": "A Çalıca Utku",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Scott Med J",
"key": "6375_CR62",
"unstructured": "Çalıca Utku A, Budak G, Karabay O, Güçlü E, Okan HD, Vatan A. Main symptoms in patients presenting in the COVID-19 period. Scott Med J. 2020;65(4):127–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0036933020949253.",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "JH Holbrook",
"key": "6375_CR63",
"unstructured": "Holbrook JH. Weakness and fatigue; 2011.",
"volume-title": "Weakness and fatigue",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111104",
"author": "P-Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111104",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "6375_CR64",
"unstructured": "Wang P-Y, Li Y, Wang Q. Sarcopenia: an underlying treatment target during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nutrition. 2021;84:111104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2020.111104.",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2008.09.002",
"author": "N Alamdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "6375_CR65",
"unstructured": "Alamdari N, O'Neal P, Hasselgren P-O. Curcumin and muscle wasting: a new role for an old drug? Nutrition. 2009;25(2):125–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2008.09.002.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/bbrc.2001.4497",
"author": "CG Penner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1331",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "6375_CR66",
"unstructured": "Penner CG, Gang G, Wray C, Fischer JE, Hasselgren P-O. The transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1 are differentially regulated in skeletal muscle during sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;281(5):1331–6. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2001.4497.",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpregu.2000.279.4.R1165",
"author": "Y-P Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R1165",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys",
"key": "6375_CR67",
"unstructured": "Li Y-P, Reid MB. NF-κB mediates the protein loss induced by TNF-α in differentiated skeletal muscle myotubes. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys. 2000;279(4):R1165–R70. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.2000.279.4.R1165.",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M207129200",
"author": "KJ Ladner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2294",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "6375_CR68",
"unstructured": "Ladner KJ, Caligiuri MA, Guttridge DC. Tumor necrosis factor-regulated biphasic activation of NF-κB is required for cytokine-induced loss of skeletal muscle gene products. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(4):2294–303. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207129200.",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.027",
"author": "D Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "285",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "6375_CR69",
"unstructured": "Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE Jr, Melendez PA, Oh B-C, Lidov HG, et al. IKKβ/NF-κB activation causes severe muscle wasting in mice. Cell. 2004;119(2):285–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.027.",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjc.6602165",
"author": "S Wyke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1742",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Br J Cancer",
"key": "6375_CR70",
"unstructured": "Wyke S, Russell ST, Tisdale MJ. Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-κ B activation. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(9):1742–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602165.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.669362",
"author": "KS Pawar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1056",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "6375_CR71",
"unstructured": "Pawar KS, Mastud RN, Pawar SK, Pawar SS, Bhoite RR, Bhoite RR, et al. Oral curcumin with piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:1056. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.669362.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 71,
"references-count": 71,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The efficacy of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "23"
}