Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID-19: A randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
et al., Food Science and Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2226, Jun 2021
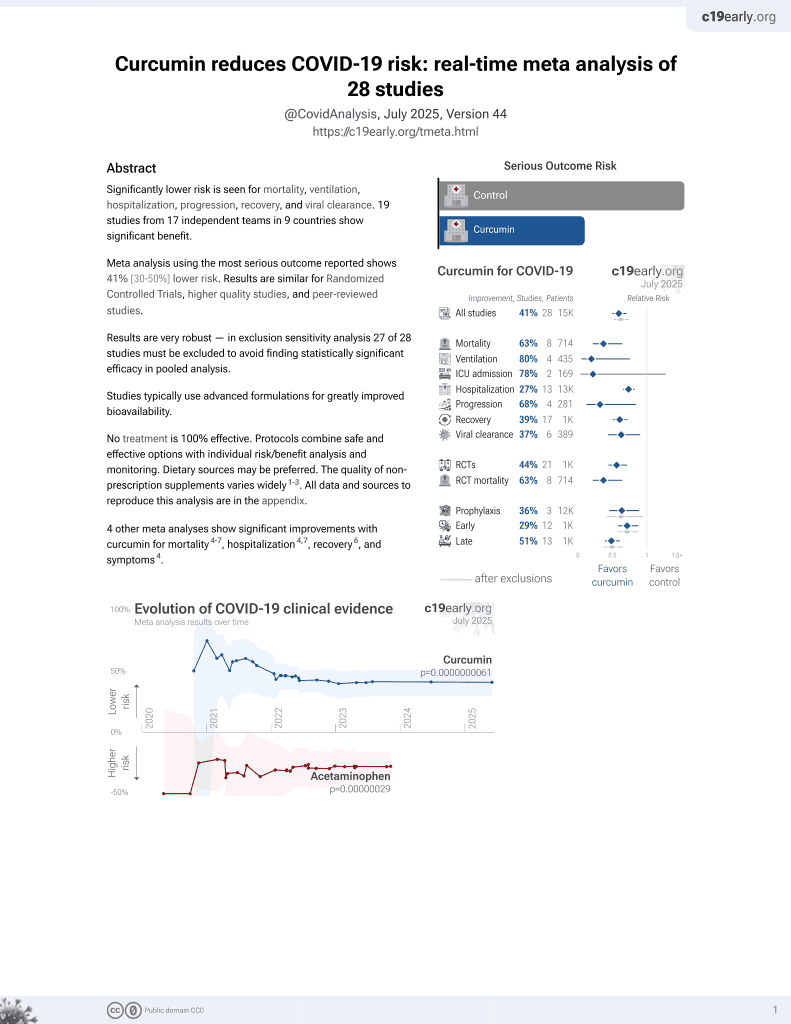
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 60 outpatients in Iran, 30 treated with nano-curcumin showing lower hospitalization and faster recovery with treatment.
This is the 4th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 7th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
risk of hospitalization, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.24, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 3 of 30 (10.0%), NNT 10.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
recovery time, 20.6% lower, relative time 0.79, p = 0.37, treatment 30, control 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ahmadi et al., 19 Jun 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period April 2020 - July 2020.
Oral nano‐curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID‐19: A randomized triple‐blind placebo‐controlled clinical trial
Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2226
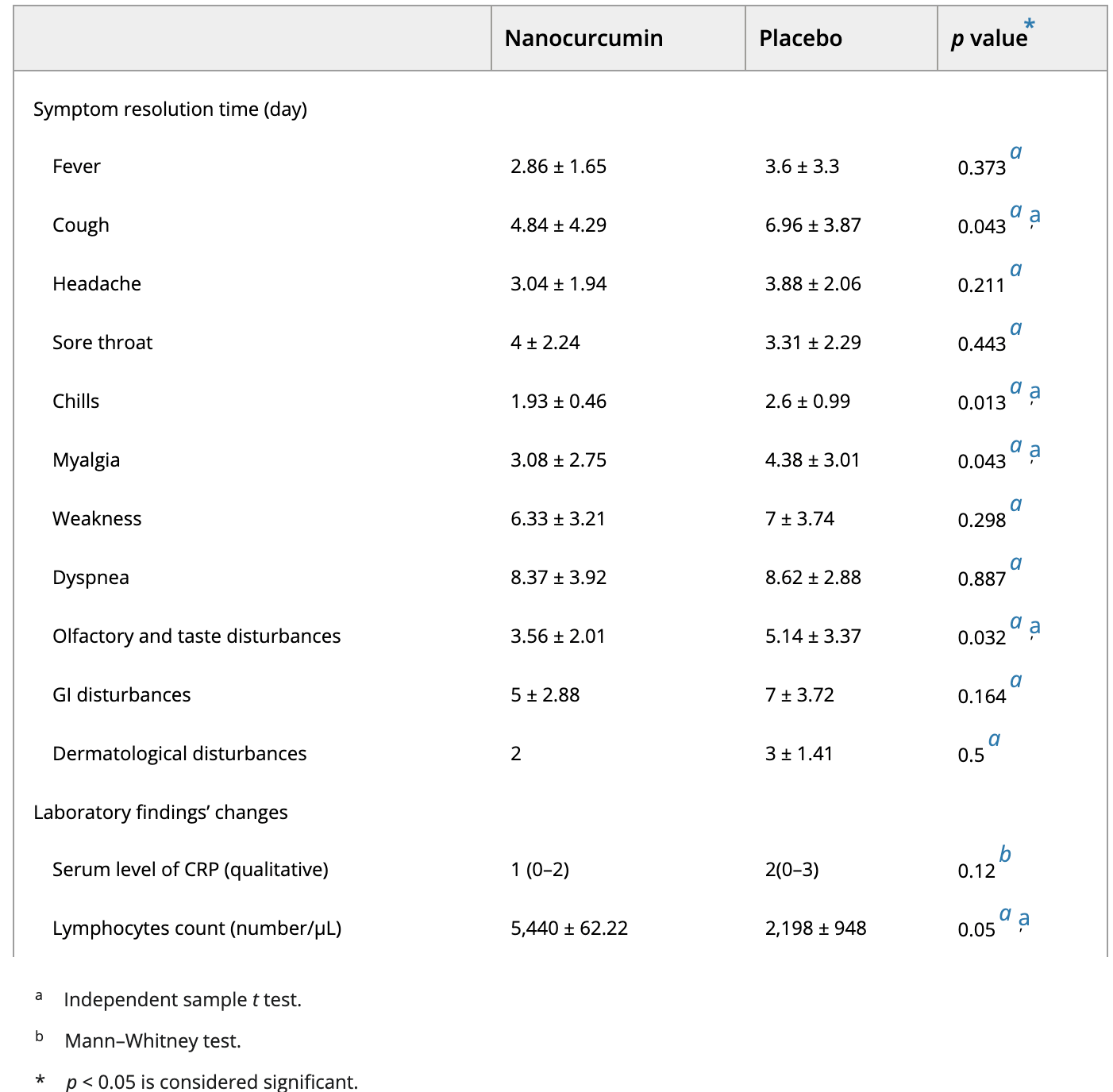
Background: Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound, is proposed as a potential treatment option for patients with coronavirus disease by inhibiting the entry of virus to the cell, encapsulation of the virus and viral protease, as well as modulating various cellular signaling pathways. In this study, the efficacy and safety of nanocurcumin oral formulation has been evaluated in patients with mild-moderate Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in outpatient setting.
Methods: In this triple-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, sixty mild to moderate COVID-19 patients in outpatient setting who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were randomly allocated to treatment (n = 30) group to receive oral nanocurcumin formulation (Sinacurcumin soft gel which contains 40 mg curcuminoids as nanomicelles), two soft gels twice a day after food for 2 weeks or placebo (n = 30) group. Patients' symptoms and laboratory data were assessed at baseline and during followup period and compared between two groups. Results: All symptoms except sore throat resolved faster in the treatment group and the difference was significant for chills, cough and smell and taste disturbances. The CRP serum level was lower in the treatment group at the end of two weeks and the lymphocyte count was significantly higher in treatment group. No significant adverse reaction reported in the treatment group.
References
Al-Shamlan, El-Hashim, Bradykinin sensitizes the cough reflex via a B(2) receptor dependent activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 channels through metabolites of cyclooxygenase and 12-lipoxygenase, Respiratory Research
Babaei, Nassiri-Asl, Hosseinzadeh, Curcumin (a constituent of turmeric): New treatment option against COVID-19, Food Science & Nutrition
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARSCoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies, J Biol Regul Homeost
Davoudi-Monfared, Rahmani, Khalili, Hajiabdolbaghi, Salehi et al., Efficacy and safety of interferon β-1a in treatment of severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy, JAMA
Hashemzadeh, Davoudian, Jaafari, Mirfeizi, The effect of nanocurcumin on the improvement symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial, Current Rheumatology Reviews
Hatamipour, Sahebkar, Alavizadeh, Dorri, Jaafari, Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids, Iran J Basic Med Sci, doi:10.22038/ijbms.2019.32873.7852
Hewitt, Adams, Mazzone, Mori, Yu et al., Pharmacology of bradykinin-evoked coughing in guinea pigs, Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
Ho, Bryson, Rumsfeld, Medication adherence: Its importance in cardiovascular outcomes, Circulation
Kunnumakkara, Harsha, Banik, Vikkurthi, Sailo et al., Is curcumin bioavailability a problem in humans: Lessons from clinical trials, Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Moballegh Nasery, Abadi, Poormoghadam, Zarrabi, Keyhanvar et al., Curcumin delivery mediated by bio-based nanoparticles: A review, Molecules
Moghadamtousi, Abdul Kadir, Hassandarvish, Tajik, Abubakar et al., A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin, BioMed Research International, doi:10.1155/2014/186864
Pandaran Sudheeran, Jacob, Natinga Mulakal, Gopinathan Nair, Maliakel et al., Safety, tolerance, and enhanced efficacy of a bioavailable formulation of curcumin with fenugreek dietary fiber on occupational stress: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study, Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology
Rahimi, Mohammadpour, Dastani, Jafari, Abnous et al., The effect of nanocurcumin on HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile in diabetic subjects: A randomized clinical trial, Avicenna J Phytomed
Rao, Regulation of COX and LOX by curcumin, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology
Richardson, Griffin, Tucker, Smith, Oechsle et al., Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease, Lancet
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Villamizar-Peña, Holguin-Rivera et al., Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Roy, Sarkar, Celik, Ghosh, Basu et al., Can concomitant use of zinc and curcumin with other immunity-boosting nutraceuticals be the arsenal against COVID-19?, Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.6766
Sabermoghaddam, Salari, Hejazi, Amini, Taherzadeh et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research
Scotton, Chambers, Molecular targets in pulmonary fibrosis: The myofibroblast in focus, Chest
Singh, Aggarwal, Activation of transcription factor NFkappa B is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane) [corrected, Journal of Biological Chemistry
Tahmasebi, El-Esawi, Mahmoud, Immunomodulatory effects of Nanocurcumin on Th17 cell responses in mild and severe COVID-19 patients, Journal of Cellular Physiology
Valizadeh, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Danshina, Gencer, Ammari et al., Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, International Immunopharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088
Whitehead, Julious, Cooper, Campbell, Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable, Statistical Methods in Medical Research
Wu, Chen, Cai, Zhou, Xu et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Internal Medicine
Zahedipour, Hosseini, Sathyapalan, Majeed, Jamialahmadi, Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytotherapy Research
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"ISSN": [
"2048-7177",
"2048-7177"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound, is proposed as a potential treatment option for patients with coronavirus disease by inhibiting the entry of virus to the cell, encapsulation of the virus and viral protease, as well as modulating various cellular signaling pathways. In this study, the efficacy and safety of nanocurcumin oral formulation has been evaluated in patients with mild‐moderate Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) in outpatient setting.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In this triple‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled clinical trial, sixty mild to moderate COVID‐19 patients in outpatient setting who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were randomly allocated to treatment (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 30) group to receive oral nanocurcumin formulation (Sinacurcumin soft gel which contains 40 mg curcuminoids as nanomicelles), two soft gels twice a day after food for 2 weeks or placebo (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 30) group. Patients’ symptoms and laboratory data were assessed at baseline and during follow‐up period and compared between two groups.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>All symptoms except sore throat resolved faster in the treatment group and the difference was significant for chills, cough and smell and taste disturbances. The CRP serum level was lower in the treatment group at the end of two weeks and the lymphocyte count was significantly higher in treatment group. No significant adverse reaction reported in the treatment group.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Oral nanoformulation of curcumin can significantly improve recovery time in patients with mild to moderate COVID‐19 in outpatient setting. Further studies with larger sample size are recommended.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/fsn3.2226"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-01-03"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-02-21"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-06-19"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine School of Medicine Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ahmadi",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy School of Pharmacy Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Salari",
"given": "Soofia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Mashhad University of Medical sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Sharifi",
"given": "Mohammad Davood",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Mashhad University of Medical sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Reihani",
"given": "Hamidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy School of Pharmacy Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rostamiani",
"given": "Mohammad Bagher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Department of Emergency Medicine Mashhad University of Medical sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Behmadi",
"given": "Morteza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Targeted Drug Delivery Research Center School of Pharmacy Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Taherzadeh",
"given": "Zhila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine Department of Medical Informatics Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Eslami",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rezayat",
"given": "Seyed Mahdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nanotechnology Research Center Pharmaceutical Technology Institute Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology School of Pharmacy Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jaafari",
"given": "Mahmoud Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9857-1175",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family Medicine School of Medicine Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Elyasi",
"given": "Sepideh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Food Science & Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Food Science & Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-19T13:57:10Z",
"timestamp": 1624111030000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-29T07:55:19Z",
"timestamp": 1693295719000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004748",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Mashhad University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-18T12:06:42Z",
"timestamp": 1710763602059
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 35,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624060800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/fsn3.2226",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4068-4075",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13311-018-0606-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID‐19",
"author": "Airton Castro Rocha F. A.",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2020.111699",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2008.09.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-019-1060-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.1858",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Induction of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1 and IL‐6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus‐19 (COVI‐19 or SARSCoV‐2): Anti‐inflammatory strategies",
"author": "Conti P.",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biol Regul Homeost",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1",
"volume": "34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01061-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1874471013666191223152658",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids",
"author": "Hatamipour M.",
"first-page": "282",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Iran J Basic Med Sci.",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.115.230383",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.768986",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17425255.2019.1650914",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25030689",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JCP.0000000000000508",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of nano‐curcumin on HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile in diabetic subjects: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Rahimi H. R.",
"first-page": "567",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Avicenna J Phytomed",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30304-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6766",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral nano‐curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease‐19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial",
"author": "SaberMoghaddam N.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.06-2568",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.270.42.24995",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of Nanocurcumin on Th17 cell responses in mild and severe COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Tahmasebi S.",
"journal-title": "Journal of Cellular Physiology",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0962280215588241",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_30_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID‐19 infection",
"author": "Zahedipour F.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "e_1_2_9_31_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/186864",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_32_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/fsn3.2226"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Oral nano‐curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID‐19: A randomized triple‐blind placebo‐controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "9"
}