Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2
et al., Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437, Mar 2021
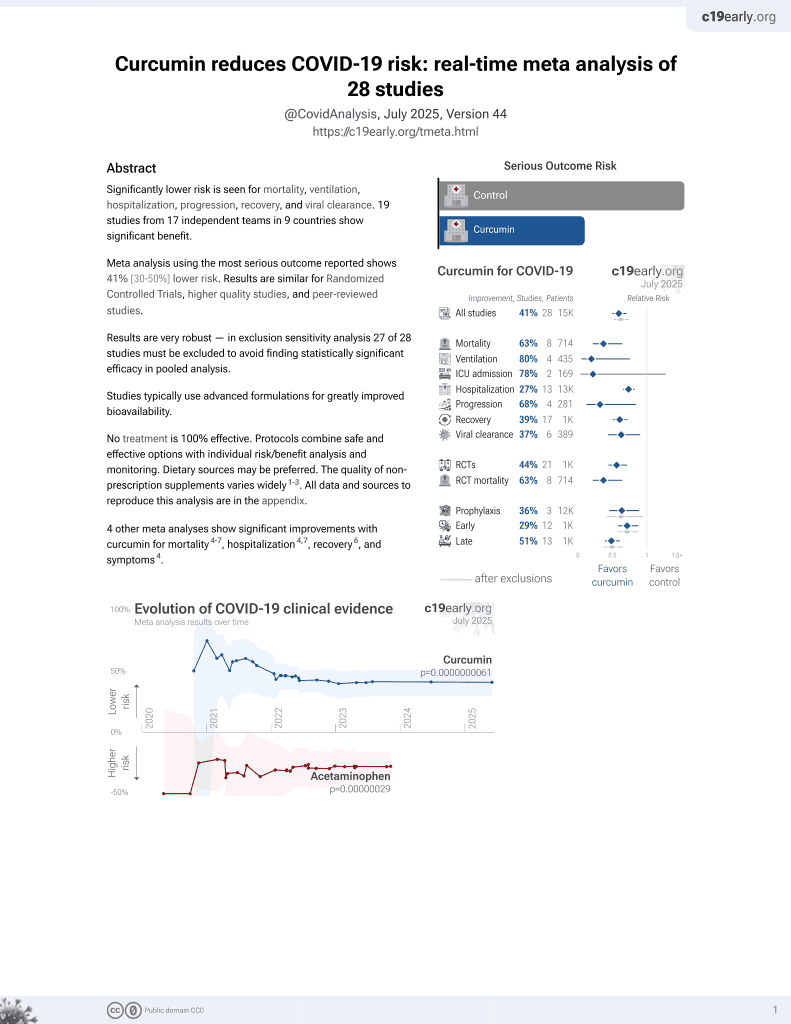
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 40 hospitalized, 40 ICU, and 40 control patients in Iran, showing lower mortality and improved regulatory T cell responses with nanocurcumin treatment (SinaCurcumin).
This is the 2nd of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 4th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
risk of death, 83.3% lower, RR 0.17, p = 0.11, treatment 1 of 40 (2.5%), control 6 of 40 (15.0%), NNT 8.0.
|
|
risk of death, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 20 (0.0%), control 1 of 20 (5.0%), NNT 20, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), non-ICU patients.
|
|
risk of death, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.18, treatment 1 of 20 (5.0%), control 5 of 20 (25.0%), NNT 5.0, ICU patients.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tahmasebi et al., 28 Mar 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2
Life Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be considered as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Ahmadi, Abdolmohamadi-Vahid, Ghaebi, Dolati, Abbaspour-Aghdam et al., Sirolimus as a new drug to treat RIF patients with elevated Th17/Treg ratio: a double-blind, phase II randomized clinical trial, Int. Immunopharmacol
Ahmadi, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Ghaebi, Aghebati-Maleki, Dolati et al., Regulatory T cells improve pregnancy rate in RIF patients after additional IVIG treatment, Syst Biol Reprod Med
Ahmadi, Hajialilo, Dolati, Eghbal-Fard, Heydarlou et al., The effects of nanocurcumin on Treg cell responses and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, J. Cell. Biochem
Ahmadi, Yousefi, Abbaspour-Aghdam, Dolati, Aghebati-Maleki et al., Disturbed Th17/Treg balance, cytokines, and miRNAs in peripheral blood of patients with Behcet's disease, J. Cell. Physiol
Chai, Chen, -H. Lin, Xie, Wang et al., Curcumin regulates the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells and activates IL-10 immune modulation against acute lung injury in mice, Biomed. Pharmacother
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J. Clin. Invest
Da Silva Antonio, Wiedemann, Veiga-Junior, Natural products' role against COVID-19, RSC Adv
Das, Sarmah, Lyndem, Roy, An investigation into the identification of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease using molecular docking study, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn
Dolati, Ahmadi, Rikhtegar, Babaloo, Ayromlou et al., Changes in Th17 cells function after nanocurcumin use to treat multiple sclerosis, Int. Immunopharmacol
Dolati, Babaloo, Ayromlou, Ahmadi, Rikhtegar et al., Nanocurcumin improves regulatory T-cell frequency and function in patients with multiple sclerosis, J. Neuroimmunol
Eghbal-Fard, Yousefi, Heydarlou, Ahmadi, Taghavi et al., The imbalance of Th17/Treg axis involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia, J. Cell. Physiol
Esmaeilzadeh, Tahmasebi, Athari, Chimeric antigen receptor -T cell therapy: applications and challenges in treatment of allergy and asthma, Biomed. Pharmacother
Flora, Gupta, Tiwari, Nanocurcumin: a promising therapeutic advancement over native curcumin, Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst
Gera, Sharma, Ghosh, Huynh, Lee et al., Nanoformulations of curcumin: an emerging paradigm for improved remedial application, Oncotarget
Ghaebi, Osali, Valizadeh, Roshangar, Ahmadi, Vaccine development and therapeutic design for 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2: Challenges and chances, J. Cell. Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.29771
Giamarellos-Bourboulis, Netea, Rovina, Akinosoglou, Antoniadou et al., Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure, Cell Host & Microbe
Gupta, Patchva, Aggarwal, Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials, AAPS J
Hajialilo, Dolati, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Ahmadi, Kamrani et al., Nanocurcumin: a novel strategy in treating ankylosing spondylitis by modulating Th17 cells frequency and function, J. Cell. Biochem
Hanna, Saad, Nanocurcumin: preparation, characterization and cytotoxic effects towards human laryngeal cancer cells, RSC Adv
Hatamipour, Sahebkar, Alavizadeh, Dorri, Jaafari, Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids, Iranian journal of basic medical sciences
Heger, Van Golen, Broekgaarden, Michel, The molecular basis for the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of curcumin and its metabolites in relation to cancer, Pharmacol. Rev
Imran, Ullah, Saeed, Nadeem, Arshad et al., Cucurmin, anticancer, & antitumor perspectives: a comprehensive review, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr
Izadi, Tahmasebi, Pustokhina, Yumashev, Lakzaei et al., Changes in Th17 cells frequency and function after ozone therapy used to treat multiple sclerosis patients, Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders
Lelli, Sahebkar, Johnston, Pedone, Curcumin use in pulmonary diseases: state of the art and future perspectives, Pharmacol. Res
Liu, Ying, The inhibitory effect of curcumin on virus-induced cytokine storm and its potential use in the associated severe pneumonia, Frontiers in cell and developmental biology
Manoharan, Haridas, Vasanthakumar, Muthu, Thavoorullah et al., Curcumin: a wonder drug as a preventive measure for COVID19 management, Indian journal of clinical biochemistry
Mathew, Hsu, Antiviral potential of curcumin, J. Funct. Foods
Mccreary, Pogue, Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options
Moghadamtousi, Kadir, Hassandarvish, Tajik, Abubakar et al., A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin, Biomed. Res. Int
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infec. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19), Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America
Rahimi, Kazemi Oskuee, Curcumin from traditional Iranian medicine to molecular medicine, Razavi Int J Med
Rahimi, Mohammadpour, Dastani, Jaafari, Abnous et al., The effect of nano-curcumin on HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile in diabetic subjects: a randomized clinical trial, Avicenna journal of phytomedicine
Rahimi, Nedaeinia, Shamloo, Nikdoust, Oskuee, Novel delivery system for natural products: nano-curcumin formulations, Avicenna journal of phytomedicine
Rana, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: potential therapeutics for immunomodulation, Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine
Rizk, Kalantar-Zadeh, Mehra, Lavie, Rizk, Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19, Drugs
Sadeghi, Tahmasebi, Mahmood, Kuznetsova, Valizadeh et al., Th17 and Treg cells function in SARS-CoV2 patients compared with healthy controls, J. Cell. Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.30047
Suravajhala, Parashar, Malik, Nagaraj, Padmanaban et al., Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin With COVID-19 Proteins
Suravajhala, Parashar, Malik, Nagaraj, Padmanaban et al., Comparative docking studies on curcumin with COVID-19 proteins, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202005.0439.v2
Tahmasebi, El-Esawi, Mahmoud, Timoshin, Valizadeh et al., Immunomodulatory Effects of Nanocurcumin on Th17 Cell Responses in Mild and Severe COVID-19 Patients
Tahmasebi, Elahi, Khosh, Esmaeilzadeh, Programmable and multitargeted CARs: a new breakthrough in cancer CAR-T cell therapy, Clin. Transl. Oncol
Tahmasebi, Khosh, Esmaeilzadeh, The outlook for diagnostic purposes of the 2019-novel coronavirus disease, J. Cell. Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.29804
Tan, Liu, Zhou, Deng, Li et al., Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13223
Wang, Hou, Luo, Tang, Wu et al., The laboratory tests and host immunity of COVID-19 patients with different severity of illness, JCI insight
Wang, Su, Pang, Qiao, Feng et al., High-dimensional immune profiling by mass cytometry revealed immunosuppression and dysfunction of immunity in COVID-19 patients
Willenbacher, Khan, Curcumin: New Insights Into an Ancient Ingredient Against Cancer
Yang, Liu, Liu, Zhang, Wan et al., COVID-19: immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics, Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
Zahedipour, Hosseini, Sathyapalan, Majeed, Jamialahmadi et al., Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytother. Res
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437",
"ISSN": [
"0024-3205"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437",
"alternative-id": [
"S0024320521004227"
],
"article-number": "119437",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Life Sciences"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tahmasebi",
"given": "Safa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saeed",
"given": "Balsam Qubais",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Temirgalieva",
"given": "Elmira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yumashev",
"given": "Alexei Valerievich",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Esawi",
"given": "Mohamed A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navashenaq",
"given": "Jamshid Gholizadeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valizadeh",
"given": "Hamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadeghi",
"given": "Armin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslani",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yousefi",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jadidi-Niaragh",
"given": "Farhad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adigozalou",
"given": "Javad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmadi",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roshangar",
"given": "Leila",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Life Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Life Sciences",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-28T21:24:53Z",
"timestamp": 1616966693000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-24T06:50:10Z",
"timestamp": 1698130210000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004366",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tabriz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T10:00:15Z",
"timestamp": 1712570415196
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 45,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625097600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0024320521004227?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0024320521004227?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "119437",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.29804",
"article-title": "The outlook for diagnostic purposes of the 2019-novel coronavirus disease",
"author": "Tahmasebi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9211",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0005",
"volume": "235",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0010",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.009",
"article-title": "Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure",
"author": "Giamarellos-Bourboulis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "992",
"journal-title": "Cell Host & Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0015",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109685",
"article-title": "Chimeric antigen receptor -T cell therapy: applications and challenges in treatment of allergy and asthma",
"author": "Esmaeilzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0020",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Programmable and multi-targeted CARs: a new breakthrough in cancer CAR-T cell therapy",
"author": "Tahmasebi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Oncol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0025",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13223",
"article-title": "Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0030",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-00243-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19: immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0035",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0040",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infec. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0045",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.29771",
"article-title": "Vaccine development and therapeutic design for 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2: Challenges and chances",
"author": "Ghaebi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9098",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0050",
"volume": "235",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options",
"author": "McCreary",
"first-page": "ofaa105",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0055",
"series-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5812/rijm.19982",
"article-title": "Curcumin from traditional Iranian medicine to molecular medicine",
"author": "Rahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Razavi Int J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0060",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1208/s12248-012-9432-8",
"article-title": "Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "AAPS J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0065",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.017",
"article-title": "Curcumin use in pulmonary diseases: state of the art and future perspectives",
"author": "Lelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0070",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.017",
"article-title": "Antiviral potential of curcumin",
"author": "Mathew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "J. Funct. Foods",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0075",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids",
"author": "Hatamipour",
"first-page": "282",
"journal-title": "Iranian journal of basic medical sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0080",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of nano-curcumin on HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, and lipid profile in diabetic subjects: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Rahimi",
"first-page": "567",
"journal-title": "Avicenna journal of phytomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0085",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/pr.110.004044",
"article-title": "The molecular basis for the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of curcumin and its metabolites in relation to cancer",
"author": "Heger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0090",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2016.1252711",
"article-title": "Cucurmin, anticancer, & antitumor perspectives: a comprehensive review",
"author": "Imran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1271",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0095",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"author": "Willenbacher",
"first-page": "20",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0100",
"series-title": "Curcumin: New Insights Into an Ancient Ingredient Against Cancer",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2013007236",
"article-title": "Nanocurcumin: a promising therapeutic advancement over native curcumin",
"author": "Flora",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "331",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0105",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.19164",
"article-title": "Nanoformulations of curcumin: an emerging paradigm for improved remedial application",
"author": "Gera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0110",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0RA03719B",
"article-title": "Nanocurcumin: preparation, characterization and cytotoxic effects towards human laryngeal cancer cells",
"author": "Hanna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20724",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0115",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel delivery system for natural products: nano-curcumin formulations",
"author": "Rahimi",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Avicenna journal of phytomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0120",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "Tahmasebi",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0125",
"series-title": "Immunomodulatory Effects of Nanocurcumin on Th17 Cell Responses in Mild and Severe COVID-19 Patients",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0130",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.30047",
"article-title": "Th17 and Treg cells function in SARS-CoV2 patients compared with healthy controls",
"author": "Sadeghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2829",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0135",
"volume": "236",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.28901",
"article-title": "The effects of nanocurcumin on Treg cell responses and treatment of ankylosing spondylitis patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0140",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.137799",
"article-title": "The laboratory tests and host immunity of COVID-19 patients with different severity of illness",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JCI insight",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0145",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "650",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0150",
"series-title": "High-dimensional immune profiling by mass cytometry revealed immunosuppression and dysfunction of immunity in COVID-19 patients",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2018.05.018",
"article-title": "Changes in Th17 cells function after nanocurcumin use to treat multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Dolati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "74",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0155",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.msard.2020.102466",
"article-title": "Changes in Th17 cells frequency and function after ozone therapy used to treat multiple sclerosis patients",
"author": "Izadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0160",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.27207",
"article-title": "Disturbed Th17/Treg balance, cytokines, and miRNAs in peripheral blood of patients with Behcet’s disease",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3985",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0165",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.28488",
"article-title": "Nanocurcumin: a novel strategy in treating ankylosing spondylitis by modulating Th17 cells frequency and function",
"author": "Hajialilo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12027",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Biochem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0170",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.27315",
"article-title": "The imbalance of Th17/Treg axis involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia",
"author": "Eghbal-Fard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5106",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0175",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19396368.2017.1390007",
"article-title": "Regulatory T cells improve pregnancy rate in RIF patients after additional IVIG treatment",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "350",
"journal-title": "Syst Biol Reprod Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0180",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105730",
"article-title": "Sirolimus as a new drug to treat RIF patients with elevated Th17/Treg ratio: a double-blind, phase II randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Ahmadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Int. Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0185",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/jrcm.2020.038",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm in COVID-19: potential therapeutics for immunomodulation",
"author": "Rana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Journal of Research in Clinical Medicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0190",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19",
"author": "Rizk",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0195",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0RA03774E",
"article-title": "Natural products’ role against COVID-19",
"author": "da Silva Antonio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23379",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0200",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.01.007",
"article-title": "Nanocurcumin improves regulatory T-cell frequency and function in patients with multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Dolati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroimmunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0210",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109946",
"article-title": "Curcumin regulates the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells and activates IL-10 immune modulation against acute lung injury in mice",
"author": "Chai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0215",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Suravajhala",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0220",
"series-title": "Comparative Docking Studies on Curcumin With COVID-19 Proteins",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1763201",
"article-title": "An investigation into the identification of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease using molecular docking study",
"author": "Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0225",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin",
"author": "Moghadamtousi",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Res. Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0230",
"volume": "2014",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00479",
"article-title": "The inhibitory effect of curcumin on virus-induced cytokine storm and its potential use in the associated severe pneumonia",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in cell and developmental biology",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0235",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00902-9",
"article-title": "Curcumin: a wonder drug as a preventive measure for COVID19 management",
"author": "Manoharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "Indian journal of clinical biochemistry: IJCB",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0240",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative docking studies on curcumin with COVID-19 proteins",
"author": "Suravajhala",
"journal-title": "Preprints",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0245",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119437_bb0250",
"unstructured": "Zahedipour F, Hosseini SA, Sathyapalan T, Majeed M, Jamialahmadi T, Al-Rasadi K, et al. 2020. Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection. Phytother. Res..(n/a)."
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0024320521004227"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nanocurcumin improves Treg cell responses in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "276"
}