A triple-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin-containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7294, Sep 2021
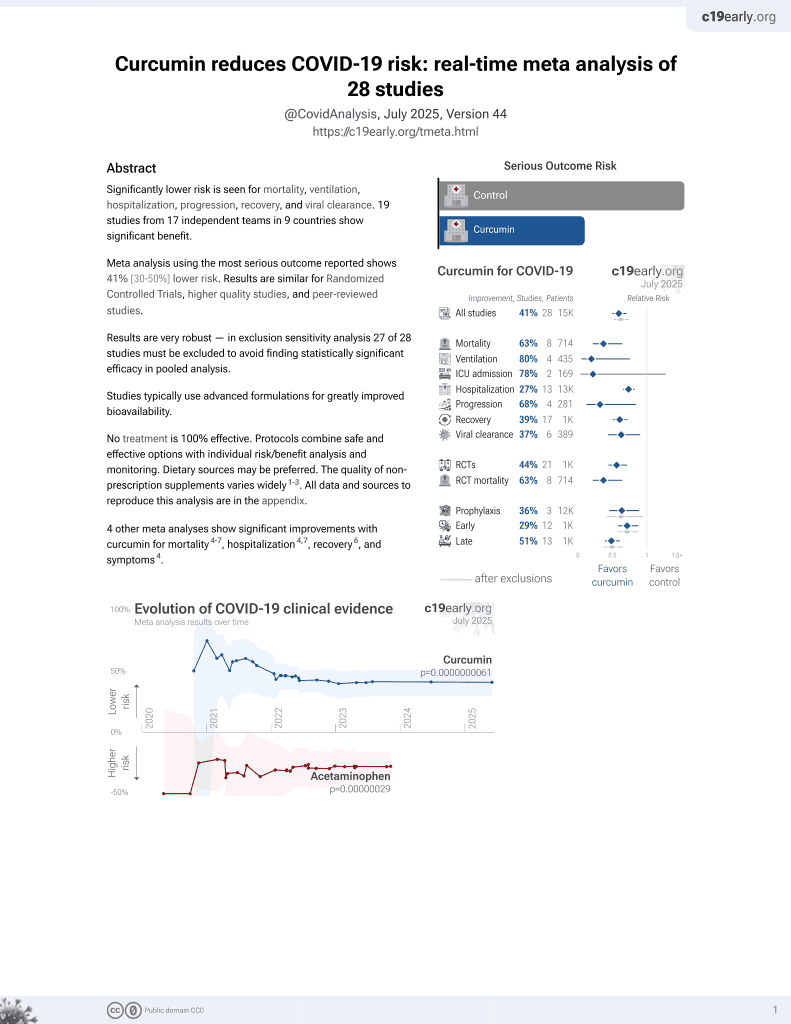
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
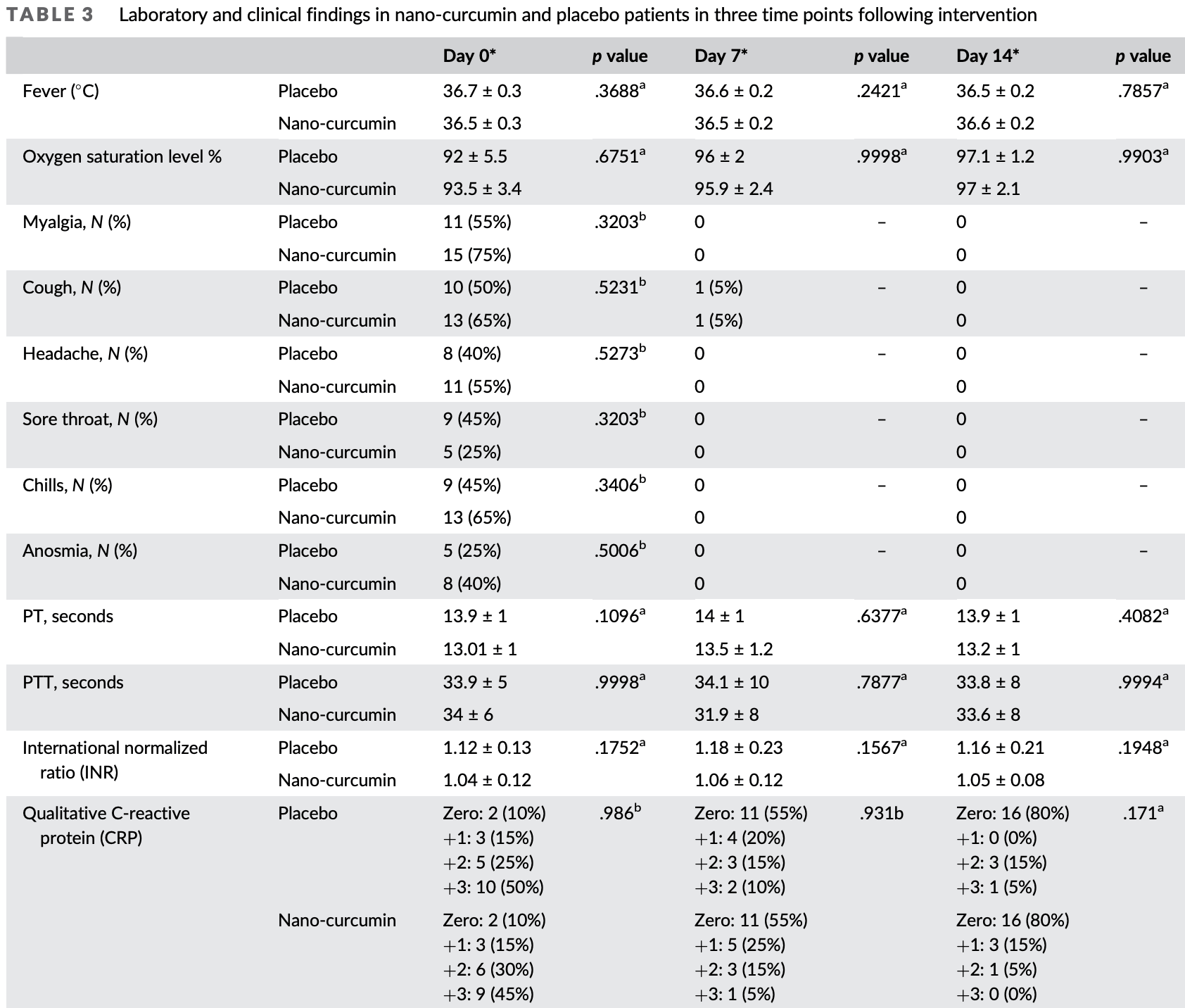
Small RCT with 40 low risk patients in Iran, 20 treated with nano-curcumin, showing no significant difference in outcomes with treatment. Authors note that treatment can improve peripheral blood inflammatory indices and modulate immune response by decreasing Th1 and Th17 responses, increasing T regulatory responses, further reducing IL-17 and IFN-γ, and increasing suppressive cytokines TGF-β and IL-4.
This is the 6th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 9th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
relative improvement in SpO2, 45.7% worse, RR 1.46, p = 0.90, treatment 20, control 20.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hassaniazad et al., 19 Sep 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
A triple‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin‐containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome inCOVID‐19 patients
Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7294
Iran (grant no. 990126) is acknowledged. The Exir Nano Sina company had no role in funding or dedication of SinaCurcumin and placebo capsules, data collection, analysis, and interpretation of data.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST Prof. Mahmoud Reza Jaafari, one of the co-authors, founded Exir Nano Sina Company, a Nano pharmaceutical company. The other coauthors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Adibian, Hodaei, Nikpayam, Sohrab, Hekmatdoost et al., The effects of curcumin supplementation on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, serum adiponectin, and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial, Phytotherapy Research
Avasarala, Zhang, Liu, Wang, London et al., Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, PLoS One
Banez, Geluz, Chandra, Hamdan, Biswas et al., A systemic review on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol, curcumin, and dietary nitric oxide supplementation on human cardiovascular health, Nutrition Research
Berhane, Melku, Amsalu, Enawgaw, Getaneh et al., The role of neutrophil to lymphocyte count ratio in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis and bacterial communityacquired pneumonia: A cross-sectional study at Ayder and Mekelle Hospitals, Ethiopia, Clinical Laboratory
Biswas, Mcclure, Jimenez, Megson, Rahman, Curcumin induces glutathione biosynthesis and inhibits NF-κB activation and interleukin-8 release in alveolar epithelial cells: Mechanism of free radical scavenging activity, Antioxidants & Redox Signaling
Bruder, Srikiatkhachorn, Enelow, Cellular immunity and lung injury in respiratory virus infection, Viral Immunology
Cohen, Veena, Srivatsan, Wang, Suppression of interleukin 6 and 8 production in head and neck cancer cells with curcumin via inhibition of Iκβ kinase, Archives of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies, Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents
Dai, Gu, Su, Wang, Zhao et al., Inhibition of curcumin on influenza A virus infection and influenzal pneumonia via oxidative stress, TLR2/4, p38/JNK MAPK and NF-κB pathways, International Immunopharmacology
Dei Cas, Ghidoni, Dietary curcumin: Correlation between bioavailability and health potential, Nutrients
Djalali, Abdolahi, Hosseini, Miraghajani, Mohammadi et al., The effects of nano-curcumin supplementation on Th1/Th17 balance in migraine patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial, Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice
Farhood, Mortezaee, Goradel, Khanlarkhani, Salehi et al., Curcumin as an antiinflammatory agent: Implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, Journal of Cellular Physiology
Farrar, Schreiber, The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor, Annual Review of Immunology
Garg, Ahuja, Sankar, Kumar, Moss, Curcumin for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Gera, Sharma, Ghosh, Huynh, Lee et al., Nanoformulations of curcumin: An emerging paradigm for improved remedial application, Oncotarget
Ghaebi, Osali, Valizadeh, Roshangar, Ahmadi, Vaccine development and therapeutic design for 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2: Challenges and chances, Journal of Cellular Physiology
Han, Xu, Guo, Huang, Curcumin ameliorates severe influenza pneumonia via attenuating lung injury and regulating macrophage cytokines production, Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
Hassaniazad, Inchehsablagh, Kamali, Tousi, Eftekhar et al., The clinical effect of Nano micelles containing curcumin as a therapeutic supplement in patients with COVID-19 and the immune responses balance changes following treatment: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials
Hatamipour, Sahebkar, Alavizadeh, Dorri, Jaafari, Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids, Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
He, Yue, Zheng, Zhang, Chen et al., Curcumin, inflammation, and chronic diseases: How are they linked?, Molecules
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The Lancet
Jobin, Bradham, Russo, Juma, Narula et al., Curcumin blocks cytokinemediated NF-κB activation and proinflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-κB kinase activity, The Journal of Immunology
Kahkhaie, Mirhosseini, Aliabadi, Mohammadi, Mousavi et al., Curcumin: A modulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the immune system, Inflammopharmacology
Kannan, Kolandaivel, Antiviral potential of natural compounds against influenza virus hemagglutinin, Computational Biology and Chemistry
Khan, Khan, Nano-gold displayed anti-inflammatory property via NF-kB pathways by suppressing COX-2 activity, Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology
Lafleur, Oderda, Methods to measure patient compliance with medication regimens, Journal of Pain & Palliative Care Pharmacotherapy
Liu, Liu, Xiang, Pu, Xiong et al., Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts critical illness patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in the early stage, Journal of Translational Medicine
Liu, Zhao, Liu, Xu, Wong et al., T-cell immunity of SARS-CoV: Implications for vaccine development against MERS-CoV, Antiviral Research
Mcmichael, Rowland-Jones, Cellular immune responses to HIV, Nature
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Villamizar-Peña, Holguin-Rivera et al., Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Roy, Sarkar, Celik, Ghosh, Basu et al., Can concomitant use of zinc and curcumin with other immunity-boosting nutraceuticals be the arsenal against COVID-19?, Phytotherapy Research
Saadati, Sadeghi, Mansour, Yari, Poustchi et al., Curcumin and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial, BMC Gastroenterology
Saber-Moghaddam, Salari, Hejazi, Amini, Taherzadeh et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research
Sakpal, Sample size estimation in clinical trial, Perspectives in Clinical Research
Shimizu, Funamoto, Sunagawa, Shimizu, Katanasaka et al., Anti-inflammatory action of curcumin and its use in the treatment of lifestyle-related diseases, European Cardiology Review
Sordillo, Helson, Curcumin suppression of cytokine release and cytokine storm. A potential therapy for patients with Ebola and other severe viral infections, Vivo
Valizadeh, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Danshina, Gencer, Ammari et al., Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, International Immunopharmacology
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama
Wen, Kuo, Jan, Liang, Wang et al., Specific plant terpenoids and lignoids possess potent antiviral activities against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Xu, Liu, Curcumin alleviates macrophage activation and lung inflammation induced by influenza virus infection through inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses
Yang, Li, Li, Wang, Huang, Synergistic antiviral effect of curcumin functionalized graphene oxide against respiratory syncytial virus infection, Nanoscale
Zhang, Zhou, Zhu, Song, Feng et al., A triple-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin-containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients, Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7294",
"ISSN": [
"0951-418X",
"1099-1573"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7294",
"abstract": "<jats:p>In COVID‐19 patients, cytokine storm due to excessive immune responses can cause severe complications. In this study, we investigated the effect of curcumin nanomicelles on clinical outcome and cellular immune responses subtypes changes in COVID‐19 patients. A randomized, triple‐blinded, placebo‐controlled study was done. Forty COVID‐19 patients were included into two groups of nano‐curcumin and placebo. The nano‐curcumin group received 40 mg of nano‐curcumin capsule, four times per day for 2 weeks. Clinical signs and gene expression of TBX21, GATA3, RORC and FOXP3 genes and IFN‐γ, IL‐4, IL‐17 and TGF‐β cytokines serum levels were measured at time points of 0, 7 and 14 days. Serum levels of IFN‐γ (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .52) and IL‐17 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .11) decreased, while IL‐4 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .12) and TGF‐β (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .14) increased in the nano‐curcumin group compared with placebo on day 14. Moreover, gene expressions of TBX21 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .02) and FOXP3 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .005) genes were significantly decreased and increased between nano‐curcumin and placebo groups on day 7, respectively. It can be concluded that administration of nano‐curcumin in inflammatory phase of COVID‐19 can accelerate recovering of the acute inflammatory phase by modulating inflammatory immune responses. Therefore, it is suggested that this supplement in inflammatory diseases, including COVID‐19, can be effective in controlling the inflammatory responses.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ptr.7294"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-03-07"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-09-04"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-09-19"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Center, Hormozgan Health Institute Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Hassaniazad",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Eftekhar",
"given": "Ebrahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Inchehsablagh",
"given": "Behnaz Rahnama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Kamali",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Tousi",
"given": "Abdolali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nanotechnology Research Center, Pharmaceutical Technology Institute Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology, School of Pharmacy Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
},
{
"name": "Biotechnology Research Center, Pharmaceutical Technology Institute Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Mashhad Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jaafari",
"given": "Mahmoud Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, Faculty of Medicine Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rafat",
"given": "Milad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Faculty of Pharmacy Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Fathalipour",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Nikoofal‐Sahlabadi",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Center, Hormozgan Health Institute Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Gouklani",
"given": "Hamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Center, Hormozgan Health Institute Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"family": "Alizade",
"given": "Hesam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5619-8771",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Research Center, Hormozgan Health Institute Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences Bandar Abbas Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nikpoor",
"given": "Amin Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"container-title-short": "Phytotherapy Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-20T00:39:36Z",
"timestamp": 1632098376000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-23T23:52:46Z",
"timestamp": 1692834766000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100011917",
"award": [
"990126"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T09:55:35Z",
"timestamp": 1712570135561
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 51,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632009600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7294",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/ptr.7294",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7294",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "6417-6427",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
19
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6328",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0057285",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2020.03.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of neutrophil to lymphocyte count ratio in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis and bacterial community‐acquired pneumonia: A cross‐sectional study at Ayder and Mekelle Hospitals, Ethiopia",
"author": "Berhane M.",
"first-page": "527",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clinical Laboratory",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2005.7.32",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2006.19.147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archotol.135.2.190",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Induction of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐1 and IL‐6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus‐19 (COVI‐19 or SARS‐CoV‐2): Anti‐inflammatory strategies",
"author": "Conti P.",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2017.11.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.27442",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Curcumin for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis",
"author": "Garg S. K.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.19164",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcp.29771",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1440-1681.12848",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04824-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel nanomicelle formulation to enhance bioavailability and stability of curcuminoids",
"author": "Hatamipour M.",
"first-page": "282",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules20059183",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.163.6.3474",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-019-00607-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2017.11.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21691401.2018.1446968",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/J354v18n03_09",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02374-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/35073658",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6766",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12876-019-1055-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_34_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Sample size estimation in clinical trial",
"author": "Sakpal T.",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Perspectives in Clinical Research",
"key": "e_1_2_8_35_1",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15420/ecr.2019.17.2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_36_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Curcumin suppression of cytokine release and cytokine storm. A potential therapy for patients with Ebola and other severe viral infections",
"author": "Sordillo P. P.",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "In Vivo",
"key": "e_1_2_8_37_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm070295s",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12459",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C7NR06520E",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2020.00157",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_43_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ptr.7294"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A triple‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of curcumin‐containing nanomicelles on cellular immune responses subtypes and clinical outcome in <scp>COVID</scp>‐19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "35"
}