Retreatment With Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Following Return of COVID-19 Symptoms and SARS-CoV-2 Positivity
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaf548 (results released 10/8/2024), NCT05567952, Oct 2024
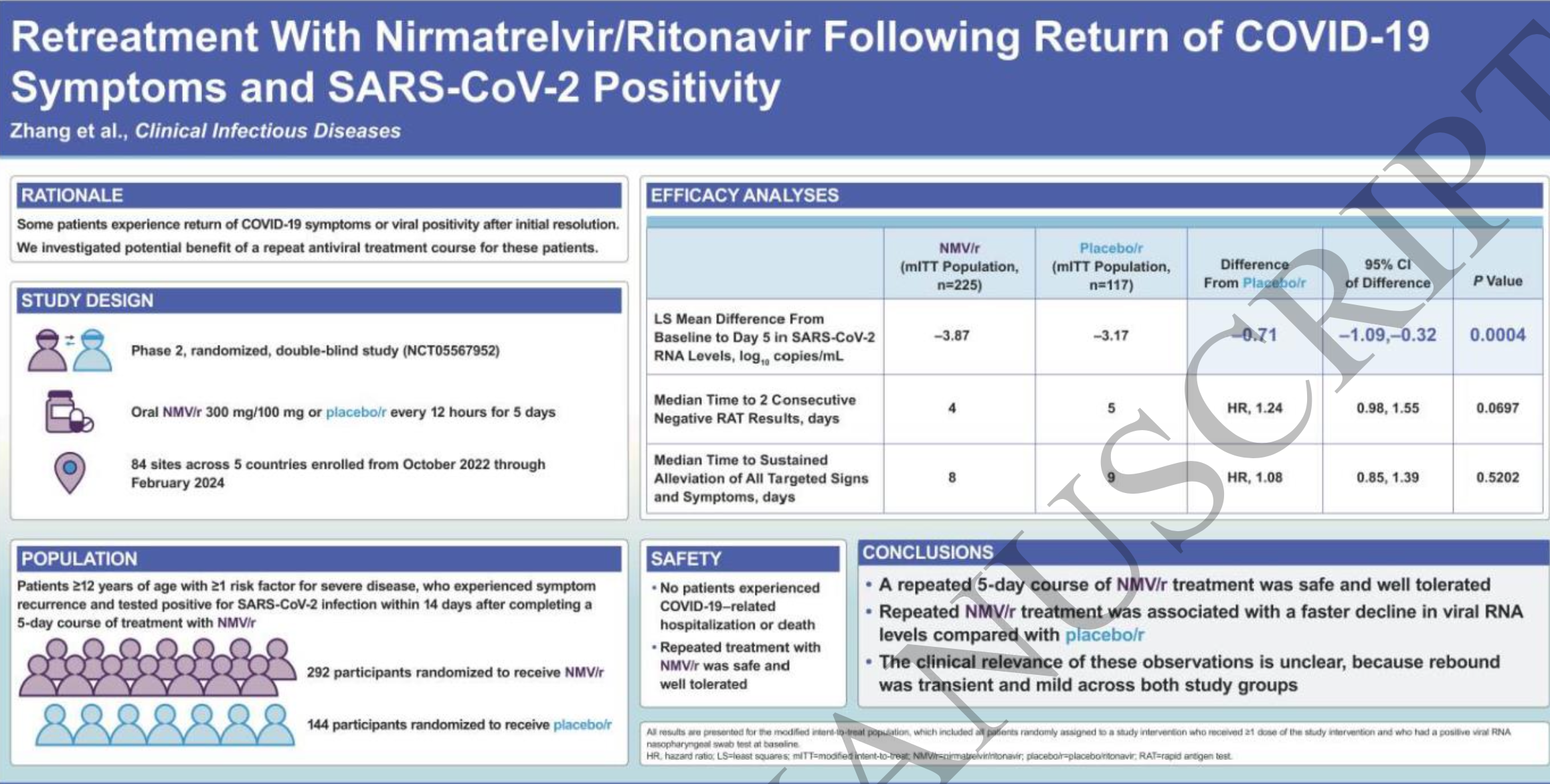
RCT 436 patients with post-paxlovid rebound showing improved viral load at day 5 but no significant difference in recovery time or viral clearance with repeated paxlovid treatment vs. placebo/ritonavir.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of no recovery, 7.9% lower, HR 0.92, p = 0.52, treatment 186, control 99, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
|
relative reduction in viral load, 18.2% better, RR 0.82, p < 0.001, treatment 218, control 113, day 5.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 19.0% lower, HR 0.81, p = 0.07, treatment 223, control 115, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, time to two consecutive negative RAT results at least 24 hours apart, Cox proportional hazards, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zhang et al., 8 Oct 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, trial NCT05567952 (history).
Contact: jennifer.hammond@pfizer.com.
Retreatment With Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Following Return of COVID-19 Symptoms and SARS-CoV-2 Positivity
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaf548
Background: Rebound of COVID-19 is defined as return of symptoms and/or viral positivity after resolution of the initial infection. While rebound is typically mildly symptomatic and rarely associated with progression to severe disease, the benefit of repeated antiviral treatment has not been investigated.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a second 5-day treatment course of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir versus placebo/ritonavir in participants with symptomatic mild to moderate COVID-19 with a positive SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test within 14 days of initial nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment. The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA level from baseline to Day 5.
Author contributions Jennifer Hammond, Candace Bramson, Mary Lynn Baniecki, Shunjie Guan, Wuyan Zhang, and Wayne Wisemandle designed the research, analyzed the data, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final draft. Steve Terra designed the research, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final draft. Edward Alan Weinstein, Alex Agyemang, and Simone Antonucci analyzed the data, critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content, and approved the final draft. Heidi Leister-Tebbe critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the final draft.
Data sharing statement Upon request and subject to review, Pfizer will provide the data that support the findings of this study. Subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Pfizer may also provide access to the related individual de-identified participant data. See https://www.pfizer.com/science/clinical- trials/trial-data-and-results for more information. (-1.09, -0.32) (-1.07, -0.33) P value 0.0004 0.0002 LLOQ=lower limit of quantification; LS=least s quares; mITT(1)=modified intention to treat (1); MMRM=mixed model for repeated measures; n=number of participants with nonmissing data in the analysis set and the covariates in the statistical model. a Baseline is defined as the latest measurement between Day -1 and Day 1, but postdose samples that were collected within 1 hour..
References
Anderson, Caubel, Rusnak, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and viral load rebound in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Baniecki, Guan, Rai, Integrated clinical virologic analysis of resistance to nirmatrelvir/ritonavir across the EPIC randomised controlled trials
Camp, Caputo, Echevarria, Achenbach, Clinical rebound after treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19, BMC Infect Dis
Deo, Choudhary, Moser, Symptom and viral rebound in untreated SARS-CoV-2 infection, Ann Intern Med
Edelstein, Boucau, Uddin, SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvirritonavir therapy: an observational study, Ann Intern Med
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Yunis, Fountaine, Oral nirmatrelvir-ritonavir as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Harrington, Cong, Troy, Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA rebound after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment in randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials -United States and international sites, 2021-2022, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Kelly, Mcewen, Isaksson, Viral SARS-CoV-2 rebound rates in linked commercial pharmacy-based testing and health care claims, Open Forum Infect Dis
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Pandit, Radin, Chiang, The coronavirus disease 2019 rebound study: a prospective cohort study to evaluate viral and symptom rebound differences in participants treated with nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir versus untreated controls, Clin Infect Dis
Phan, Ribeiro, Edelstein, Modeling suggests SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment is driven by target cell preservation coupled with incomplete viral clearance, J Virol
Ranganath, Horo, Challener, Rebound phenomenon after nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in high-risk persons, Clin Infect Dis
Se, Biddle, Talbot, Symptoms, viral loads, and rebound among COVID-19 outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir compared with propensity score-matched untreated individuals, Clin Infect Dis
Singh, Toussi, Hackman, Innovative randomized phase I study and dosing regimen selection to accelerate and inform pivotal COVID-19 trial of nirmatrelvir, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Smith, Lambrou, Patel, SARS-CoV-2 rebound with and without use of COVID-19 oral antivirals, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Weinstein, Paredes, Gardner, Extended nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment durations for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19 (EPIC-IC): a randomized, double-blind, phase 2 trial, Lancet Inf Dis
Wong, Lau, Au, Viral burden rebound in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 receiving oral antivirals in Hong Kong: a population-wide retrospective cohort study, Lancet Infect Dis
Zhu, Yurgelonis, Noell, In vitro selection and analysis of SARS-CoV-2 nirmatrelvir resistance mutations contributing to clinical virus resistance surveillance, Sci Adv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaf548",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaf548",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Rebound of COVID-19 is defined as return of symptoms and/or viral positivity after resolution of the initial infection. While rebound is typically mildly symptomatic and rarely associated with progression to severe disease, the benefit of repeated antiviral treatment has not been investigated.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of a second 5-day treatment course of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir versus placebo/ritonavir in participants with symptomatic mild to moderate COVID-19 with a positive SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test within 14 days of initial nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment. The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA level from baseline to Day 5.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The full analysis set included 436 participants assigned to treatment (292, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir; 144, placebo/ritonavir). A second 5-day course of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir resulted in a significant reduction in viral RNA levels at Day 5 compared with placebo/ritonavir (P=0.0004; 95% CI, −1.09, −0.32). The median time to 2 consecutive negative RAT results was 4 versus 5 days, and the median time to sustained alleviation of all targeted signs/symptoms was 8 versus 9 days in the nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and placebo/ritonavir groups, respectively. Retreatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was safe and well tolerated, and there were no occurrences of COVID-19−related hospitalizations or deaths.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A repeated 5-day course of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was safe and well tolerated and was associated with a faster decline in viral RNA levels. In this study, there was no clear benefit of retreatment because rebound was transient, mild, and did not lead to severe COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trial Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>NCT05567952; https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05567952</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"article-number": "ciaf548",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , Lake Forest, IL ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Wuyan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , Groton, CT ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Terra",
"given": "Steven G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , New York, NY ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Weinstein",
"given": "Edward Alan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc, Collegeville , PA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Bramson",
"given": "Candace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc, Collegeville , PA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Leister-Tebbe",
"given": "Heidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, MA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Baniecki",
"given": "Mary Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, MA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Guan",
"given": "Shunjie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Ltd , Tadworth ,",
"place": [
"UK"
]
}
],
"family": "Agyemang",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Italia s.r.l. , Milan ,",
"place": [
"Italy"
]
}
],
"family": "Antonucci",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc , Lake Forest, IL ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Wisemandle",
"given": "Wayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4810-8558",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Research and Development, Pfizer Inc, Collegeville , PA ,",
"place": [
"USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hammond",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-30T20:23:07Z",
"timestamp": 1759263787000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-30T20:23:07Z",
"timestamp": 1759263787000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-01T00:14:53Z",
"timestamp": 1759277693853,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1759190400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf548/64455663/ciaf548.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf548/64455663/ciaf548.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaf548/8269311"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Retreatment With Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Following Return of COVID-19 Symptoms and SARS-CoV-2 Positivity",
"type": "journal-article"
}