Finasteride in hospitalized adult males with COVID-19: A risk factor for severity of the disease or an adjunct treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial
et al., Medical Journal of The Islamic Republic of Iran, doi:10.47176/mjiri.35.30, Apr 2021
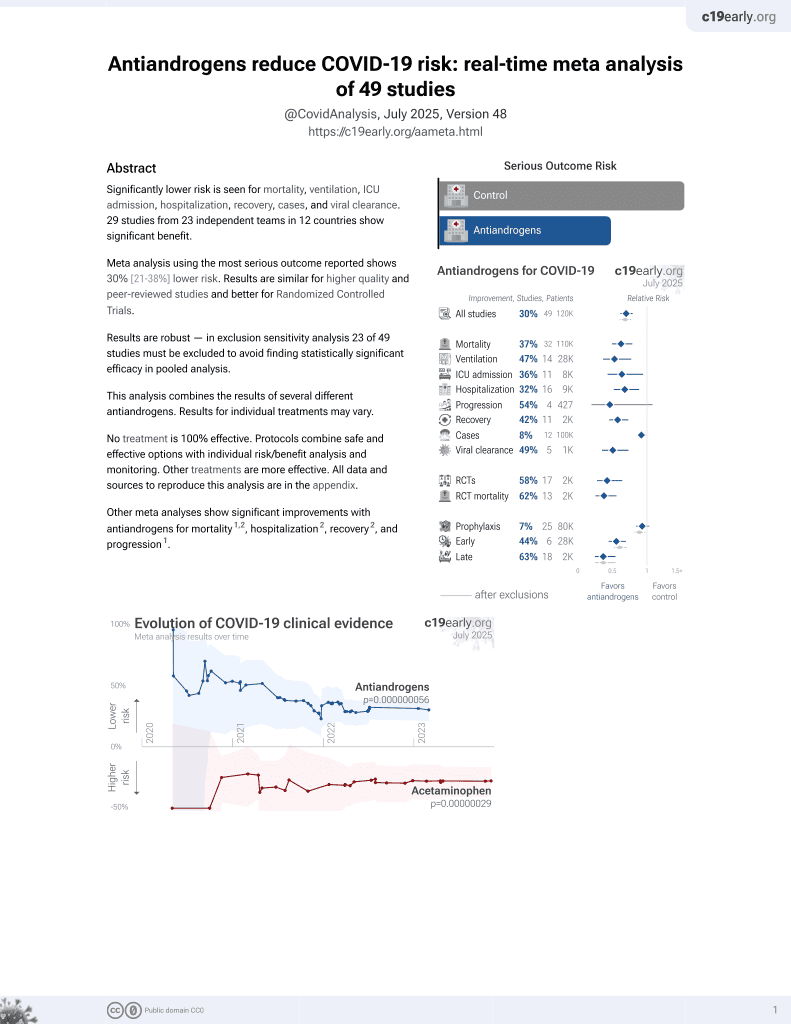
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
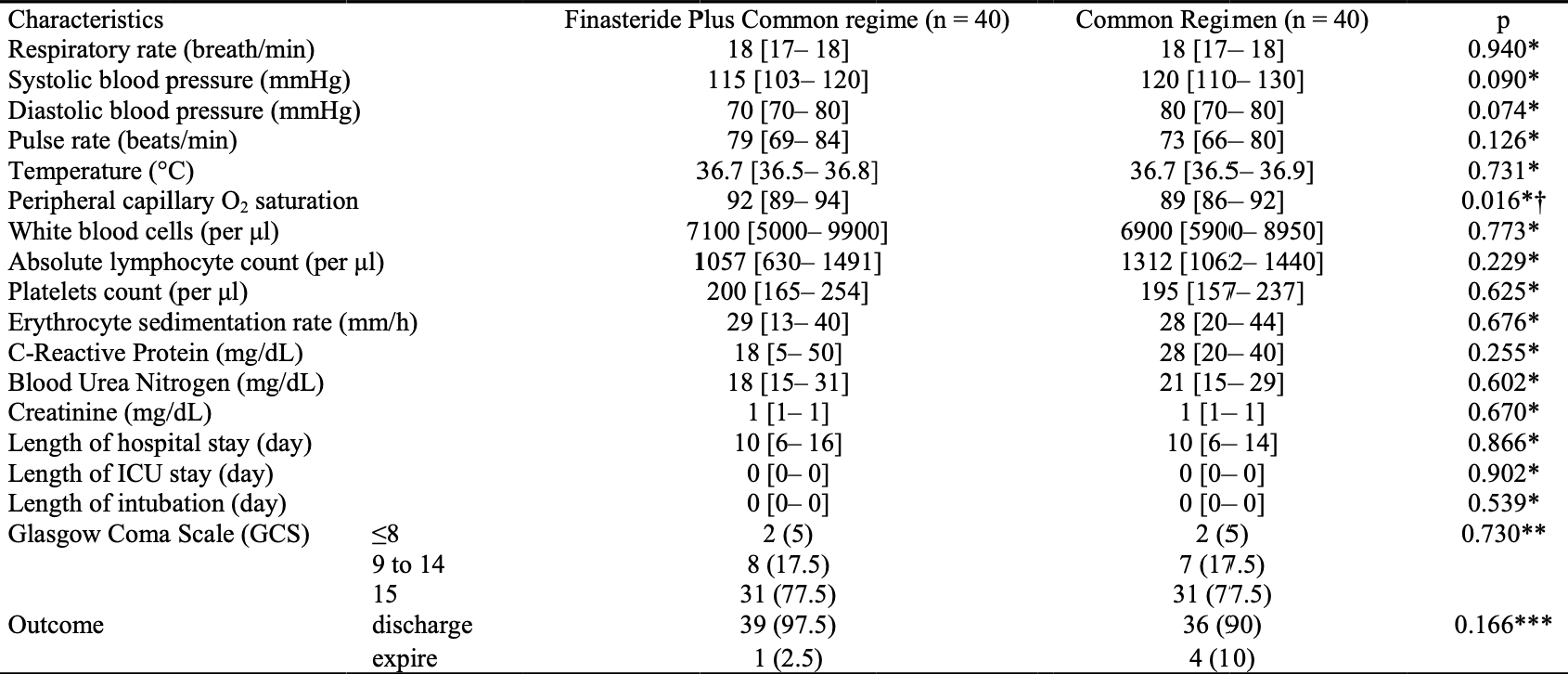
RCT 80 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran, 40 treated with finasteride, showing no significant differences other than improved oxygen saturation on the 5th day with treatment. There was significantly more patients with diabetes in the control group. 5mg finasteride for 7 days. IRCT20200505047318N1.
|
risk of death, 75.0% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.36, treatment 1 of 40 (2.5%), control 4 of 40 (10.0%), NNT 13.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 40 (2.5%), control 1 of 40 (2.5%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zarehoseinzade et al., 30 Apr 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Finasteride in hospitalized adult males with COVID-19: A risk factor for severity of the disease or an adjunct treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Medical Journal of The Islamic Republic of Iran, doi:10.47176/mjiri.35.30
Background finasteride mig COVID-19 infe Methods: W patients aged ≥ patients were r drug therapy an and secondary protocol was IR.QUMS.REC significant. Results: We (p= 0.018). Th patients in the f Conclusion: hospitalized m required to help
staff at the B in the study.
Conflict of I The authors d
References
Adamowicz, reductase inhi Med Hypothes
Chen, Xu inducible fact transition in
Goren, J, C Mesinkovska N with Reduced Androgenetic, Dermatol
Goren, Mcc, What An insight into
Guan, None, Ni characteristics
Hoffmann, Erichsen, None, Cell
Li, Huang, -19 pa rate of meta-an
Mehta, Mca, None, C immunosuppre
Mikkonen, None, Endocrinol
Moran, Jones, Sharafi, S, outcome of co and over. Int J 14. Hayes AF, P Quantification
Temgoua Mn Belobo, Et, screening of Middle-Incom, Med J
Wambier, Nau, None, Drug
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.47176/mjiri.35.30",
"ISSN": [
"1016-1430",
"2251-6840"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.47176/mjiri.35.30",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zarehoseinzade",
"given": "Elham",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Allami",
"given": "Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmadi",
"given": "Mehrnoosh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bijani",
"given": "Behzad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohammadi",
"given": "Navid",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Medical Journal of The Islamic Republic of Iran"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.mjiri.iums.ac.ir"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-06T11:16:01Z",
"timestamp": 1622978161000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-06T11:16:25Z",
"timestamp": 1622978185000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-31T02:29:37Z",
"timestamp": 1648693777420
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1016-1430"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2251-6840"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://mjiri.iums.ac.ir/article-1-7160-en.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "26714",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.47176",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Academic World Research",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://mjiri.iums.ac.ir/article-1-7160-en.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"mjiri"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Finasteride in hospitalized adult males with COVID-19: A risk factor for severity of the disease or an adjunct treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.47176/mjiri/crossmark_policy"
}