Low antiviral uptake of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in adult patients with COVID-19 in Taiwan in 2022
et al., Journal of Global Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.14.05032, Nov 2024
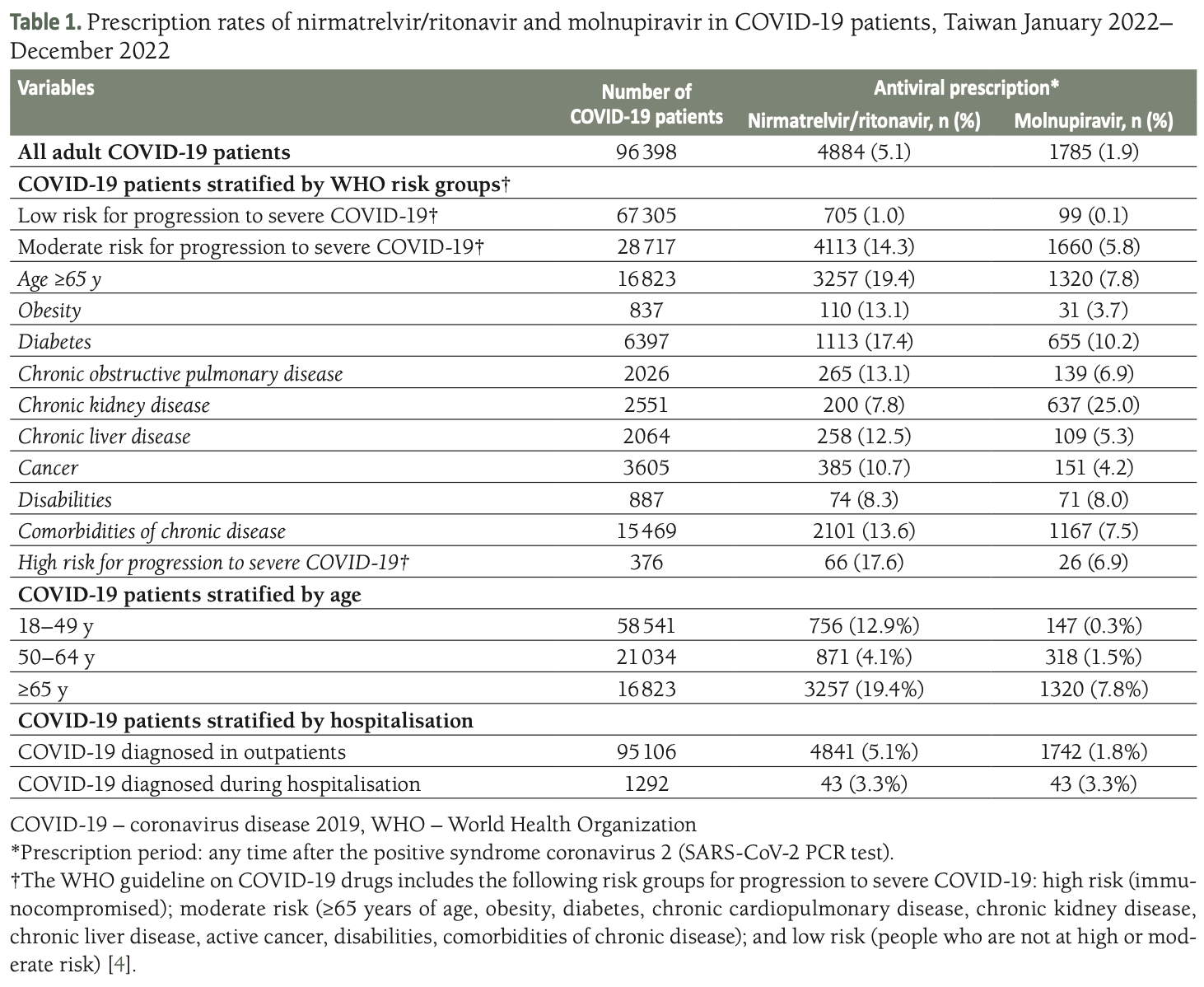
Retrospective 96,398 adult COVID-19 patients in Taiwan showing very low use of approved antivirals nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (5.1%) and molnupiravir (1.9%) in 2022, especially in moderate-to-high risk groups eligible for treatment per WHO guidelines. Barriers to use include the requirement for a prescription, time required for assessing drug interactions, perceived risks/benefits, and lack of awareness.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
Study covers molnupiravir and paxlovid.
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Wang et al., 8 Nov 2024, retrospective, Taiwan, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period January 2022 - December 2022.
Contact: jasonhsu@tmu.edu.tw.
Abstract: Cite as: Wang FD, Nguyen PA, Lee D, Taysi B, Lefebvre d‘Hellencourt F, Spinardi J, Phuc PT,
Burton W, Chang YH, Hien NTK, Lin SM, Chieh Y, Kyaw MH, Hsu JC. Low antiviral uptake
of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in adult patients with COVID-19 in Taiwan in
2022. J Glob Health 2024;14:05032.
Low antiviral uptake of nirmatrelvir/
ritonavir and molnupiravir in adult patients
with COVID-19 in Taiwan in 2022
Fu-Der Wang1,2, Phung-Anh Nguyen3,4,5,6 ,
David Lee7, Bulent Taysi8, Florence Lefebvre
d’Hellencourt9 , Julia Spinardi9, Phan Thanh
Phuc10 , Whitney Burton10, Yu-Hui Chang11,
Nguyen Thi Kim Hien12,13, Shiue-Ming Lin6, Yang
Chieh6, Moe H Kyaw9 , Jason C Hsu4,5,6,10
Background Antivirals are effective in reducing hospitalisation and death in mild-to-moderate coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) patients. We estimated the antiviral uptake of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir
in adult patients with a syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2) infection during the Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) period in Taiwan.
Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal
Medicine, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
2
National Yang-Ming Chiao-Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan
3
Graduate Institute of Data Science, College of Management,
Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
4
Clinical Data Center, Office of Data Science, Taipei Medical
University, Taipei, Taiwan
5
Clinical Big Data Research Center, Taipei Medical University
Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
6
Research Center of Health Care Industry Data Science, College
of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
7
Pfizer, Taipei, Taiwan
8
Pfizer, Singapore
9
Pfizer, New York, USA
10
International PhD Program in Biotech and Healthcare
Management, College of Management, Taipei Medical
University, Taipei, Taiwan
11
School of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Taipei Medical
University, Taipei, Taiwan
12
Master Program in Global Health and Development, College
of Public Health, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan
13
College of Nutrition, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City,
Taiwan
Methods A retrospective cohort study was conducted in
Taiwan between January 2022 and December 2022. Patients aged ≥18 years with a SARS-CoV-2 infection were
included from the Taipei Medical University Clinical Research Database (TMUCRD) and stratified in three risk
groups according to World Health Organization criteria.
1
Results In total, 96 398 COVID-19 patients (mean age
46.7 ± 17.7 years, 45.8% male) were included. Of these
patients 69.8% were classified as low risk, 29.8% as moderate risk, and 0.4% as high risk for progression to severe COVID-19. Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was prescribed
in 5.1% of the COVID-19 patients (low risk = 1.0%,
moderate risk = 14.3%, high risk = 17.6%). Molnupiravir
was prescribed in 1.9% of the COVID-19 patients (low
risk = 0.1%, moderate risk = 5.8%, high risk = 6.9%).
Conclusions Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir
were poorly used in the treatment of adult COVID-19
patients in Taiwan during the pandemic in 2022, especially in moderate-to-high risk groups for progression to
severe COVID-19.
Since its emergence in December 2019, coronavirus disease
2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), led to significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. As of April 2024, Taiwan
had nearly 10 million confirmed cases and 18 thousand
deaths due to COVID-19 [1].
Correspondence..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.14.05032",
"ISSN": [
"2047-2978",
"2047-2986"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7189/jogh.14.05032",
"article-number": "05032",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "National Yang-Ming Chiao-Tung University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Fu-Der",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Graduate Institute of Data Science, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Data Center, Office of Data Science, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Big Data Research Center, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "Research Center of Health Care Industry Data Science, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Phung-Anh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer, Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Taysi",
"given": "Bulent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer, New York, USA"
}
],
"family": "Lefebvre d'Hellencourt",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer, New York, USA"
}
],
"family": "Spinardi",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International PhD Program in Biotech and Healthcare Management, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Phuc",
"given": "Phan Thanh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "International PhD Program in Biotech and Healthcare Management, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Burton",
"given": "Whitney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Chang",
"given": "Yu-Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Master Program in Global Health and Development, College of Public Health, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "College of Nutrition, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Hien",
"given": "Nguyen Thi Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center of Health Care Industry Data Science, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Shiue-Ming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Center of Health Care Industry Data Science, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Chieh",
"given": "Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer, New York, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kyaw",
"given": "Moe H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Data Center, Office of Data Science, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "Clinical Big Data Research Center, Taipei Medical University Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "Research Center of Health Care Industry Data Science, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
},
{
"name": "International PhD Program in Biotech and Healthcare Management, College of Management, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan"
}
],
"family": "Hsu",
"given": "Jason C",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Global Health",
"container-title-short": "J Glob Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T10:04:31Z",
"timestamp": 1731060271000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T10:04:36Z",
"timestamp": 1731060276000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-09T05:10:13Z",
"timestamp": 1731129013545,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jogh.org/2024/jogh-14-05032",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4223",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7189",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "International Society of Global Health",
"reference": [
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R1",
"unstructured": "Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19). 2024. Available: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/en/Disease/SubIndex/. Accessed: 25 April 2024."
},
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R2",
"unstructured": "Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Taiwan Food and Drug Administration of the approved the import of Paxlovid. 2022. Available: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-5264-65592-1.html. Accessed: 10 December 2022."
},
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R3",
"unstructured": "Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. First batch of oral antiviral Molnupiravir drug for COVID-19 purchased by Taiwan arrives; Molnupiravir can be used to treat patients at risk of severe illness and diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms to reduce medical care burden. 2022. Available: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/En/Category/ListContent/tov1jahKUv8RGSbvmzLwFg?uaid=kgJmpGaAZ-iYWkIsRP-ozQ. Accessed: 10 December 2022."
},
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R4",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ 2020;370:m3379. 2024. Available: https://www.bmj.com/content/370/bmj.m3379. Accessed: 27 March 2024."
},
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R5",
"unstructured": "Taipei Medical University. Taipei Medical University Clinical Research Database (TMUCRD). 2024. Available: https://ods.tmu.edu.tw/portal_c3_cnt.php?owner_num=c3_75328&button_num=c3&folder_id=4354. Accessed: 27 March 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad796",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Prescribing Gaps Among Non-Hospitalized High-Risk Adults.",
"author": "Levy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1531",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R6",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad674",
"article-title": "Oral COVID-19 antiviral uptake among a highly vaccinated US cohort of adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection between December 2021 and October 2022.",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofad674",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R7",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02398-4",
"article-title": "Uptake of monoclonal antibodies and antiviral therapies for COVID-19 in Scotland.",
"author": "Tibble",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R8",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7303a2",
"article-title": "Underuse of Antiviral Drugs to Prevent Progression to Severe COVID-19—Veterans Health Administration, March–September 2022.",
"author": "Monach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R9",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs.",
"author": "Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R10",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2023.11.003",
"article-title": "Cost-effectiveness of oral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in patients at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 in the United States.",
"author": "Carlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Value Health",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R11",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40273-022-01168-0",
"article-title": "Cost-effectiveness analysis of molnupiravir versus best supportive care for the treatment of outpatient COVID-19 in adults in the US.",
"author": "Goswami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "PharmacoEconomics",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R12",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19.",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R13",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients.",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R14",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00118-4",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in preventing hospital admissions and deaths in people with COVID-19: a cohort study in a large US health-care system.",
"author": "Lewnard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "806",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R15",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-023-01204-1",
"article-title": "Long COVID and possible preventive options.",
"author": "Sebők",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2807",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R16",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.0743",
"article-title": "Association of treatment with nirmatrelvir and the risk of post–COVID-19 condition.",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "554",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R17",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.16666",
"article-title": "Outpatient treatment for COVID-19.",
"author": "Raglow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1295",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R18",
"volume": "330",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "key-10.7189/jogh.14.05032-202411080923-R19",
"unstructured": "Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Cumulative number of vaccinations for various COVID-19 vaccine recipients and COVID-19 vaccination rates by county and city. Available: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/Category/Page/9jFXNbCe-sFK9EImRRi2Og. Accessed: 27 March 2024."
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jogh.org/2024/jogh-14-05032"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Low antiviral uptake of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir and molnupiravir in adult patients with COVID-19 in Taiwan in 2022",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
wang40