Inhaled remdesivir reduces viral burden in a nonhuman primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection
et al., Science Translational Medicine, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8282, Dec 2021
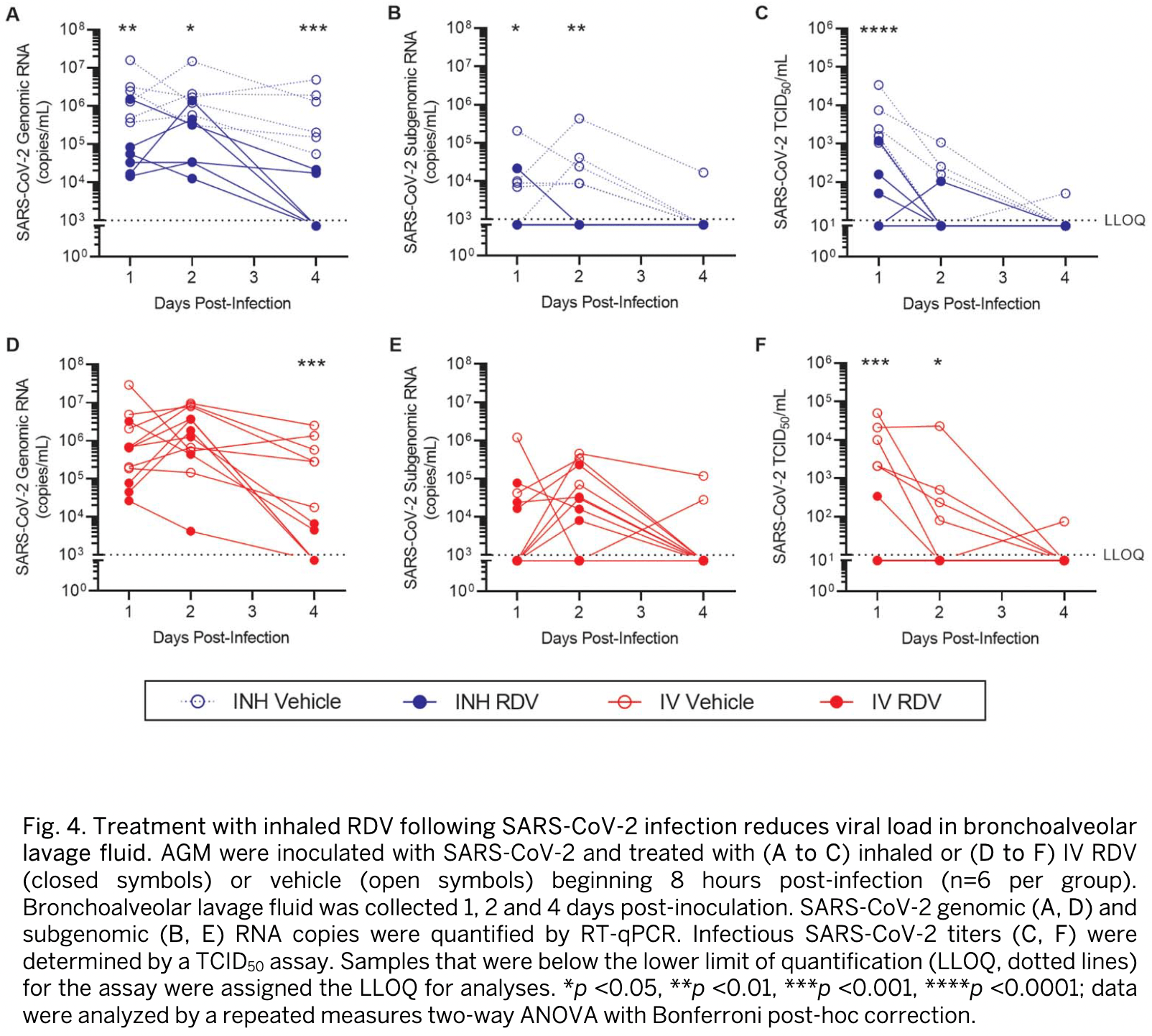
African green monkey study of inhaled versus IV remdesivir, showing similar efficacy with inhalation. Comparable concentrations of the active triphosphate in the lower respiratory tract were found with ~20x lower dose using inhalation, and there was lower systemic exposure to remdesivir and metabolites.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Vermillion et al., 30 Dec 2021, peer-reviewed, 26 authors.
Inhaled remdesivir reduces viral burden in a nonhuman primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Science Translational Medicine, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8282
Remdesivir (RDV) is a nucleotide analog prodrug with demonstrated clinical benefit in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . In October 2020, the US FDA approved intravenous (IV) RDV as the first treatment for hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Furthermore, RDV has been approved or authorized for emergency use in more than 50 countries. To make RDV more convenient for non-hospitalized patients earlier in disease, alternative routes of administration are being evaluated. Here, we investigated the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of RDV administered by head dome inhalation in African green monkeys (AGM). Relative to an IV administration of RDV at 10 mg/kg, an approximately 20-fold lower dose administered by inhalation produced comparable concentrations of the pharmacologically active triphosphate in lower respiratory tract tissues. Distribution of the active triphosphate into the upper respiratory tract was also observed following inhaled RDV exposure. Inhalation RDV dosing resulted in lower systemic exposures to RDV and its metabolites as compared with IV RDV dosing. An efficacy study with repeated dosing of inhaled RDV in an AGM model of SARS-CoV-2 infection demonstrated reductions in viral replication in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and respiratory tract tissues compared with placebo. Efficacy was observed with inhaled RDV administered once daily at a pulmonary deposited dose of 0.35 mg/kg beginning approximately 8 hours post-infection. Moreover, the efficacy of inhaled RDV was similar to that of IV RDV administered once at 10 mg/kg followed by 5 mg/kg daily in the same study. Together, these findings support further clinical development of inhalation RDV.
References
Alexander, Collins, Coombs, Gilkison, Hardy et al., Association of Inhalation Toxicologists (AIT) working party recommendation for standard delivered dose calculation and expression in non-clinical aerosol inhalation toxicology studies with pharmaceuticals, Inhal. Toxicol, doi:10.1080/08958370802207318
Assiri, Al-Tawfiq, Al-Rabeeah, Al-Rabiah, Al-Hajjar et al., Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: A descriptive study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70204-4
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., ACTT-1 Study Group Members, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19 -Final Report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Benech, Théodoro, Herbet, Page, Schlemmer et al., Peripheral blood mononuclear cell counting using a DNA-detectionbased method, Anal. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.03.015
Blair, Vaccari, Doyle-Meyers, Roy, Russell-Lodrigue et al., Acute Respiratory Distress in Aged, SARS-CoV-2-Infected African Green Monkeys but Not Rhesus Macaques, Am. J. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.016
Choi, Kang, Kim, Choi, Joh et al., Korean Society of Infectious Diseases, Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome in the Republic of Korea, Infect. Chemother, doi:10.3947/ic.2016.48.2.118
Hartman, Nambulli, Mcmillen, White, Tilston-Lunel et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of African green monkeys results in mild respiratory disease discernible by PET/CT imaging and shedding of infectious virus from both respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, PLOS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008903
Hill, Paredes Deiros, Vaca, Mera, Webb et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of high-risk non-hospitalized individuals with COVID-19: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Humeniuk, Mathias, Cao, Osinusi, Shen et al., Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Remdesivir, An Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19, in Healthy Subjects, Clin. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12840
Ksiazek, Erdman, Goldsmith, Zaki, Peret et al., SARS Working Group, A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030781
Li, Liclican, Xu, Pitts, Niu et al., Key Metabolic Enzymes Involved in Remdesivir Activation in Human Lung Cells, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00602-21
Mackman, Hui, Perron, Murakami, Palmiotti et al., Prodrugs of a 1′-CN-4-Aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-Nucleoside Leading to the Discovery of Remdesivir (GS-5734) as a Potent Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus with Efficacy in the African Green Monkey Model of RSV, J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00071
Mers, Group, State of Knowledge and Data Gaps of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in Humans, PLOS Curr
Munster, Feldmann, Williamson, Van Doremalen, Pérez-Pérez et al., Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2324-7
Pitts, Lu, Du Pont, Riola, Li et al., Delta Variant and Other Variants of Concern
Speranza, Williamson, Feldmann, Sturdevant, Pérez-Pérez et al., Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals SARS-CoV-2 infection dynamics in lungs of African green monkeys, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abe8146
Tepper, Kuehl, Cracknell, Nikula, Pei et al., Symposium Summary: "Breathe In, Breathe Out, Its Easy: What You Need to Know About Developing Inhaled Drugs, Int. J. Toxicol, doi:10.1177/1091581815624080
Warren, Jordan, Lo, Ray, Mackman et al., Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature17180
Williamson, Feldmann, Schwarz, Meade-White, Porter et al., Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5
Woolsey, Borisevich, Prasad, Agans, Deer et al., Establishment of an African green monkey model for COVID-19 and protection against re-infection, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-00835-8
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Wölfel, Corman, Guggemos, Seilmaier, Zange et al., Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8282",
"ISSN": [
"1946-6234",
"1946-6242"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8282",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8282"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1602-7027",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lovelace Biomedical; 2425 Ridgecrest Drive, SE, Albuquerque, NM 87108, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Vermillion",
"given": "Meghan S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2315-2819",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Murakami",
"given": "Eisuke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7549-2658",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4080-4321",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Pitts",
"given": "Jared",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5855-7472",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Tomkinson",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1472-2739",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Rautiola",
"given": "Davin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5599-1671",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Babusis",
"given": "Darius",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9342-9874",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lovelace Biomedical; 2425 Ridgecrest Drive, SE, Albuquerque, NM 87108, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Irshad",
"given": "Hammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"family": "Siegel",
"given": "Dustin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Cynthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2786-7416",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Xiaofeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0225-5616",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Niu",
"given": "Congrong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6487-1652",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Jesse",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lovelace Biomedical; 2425 Ridgecrest Drive, SE, Albuquerque, NM 87108, USA."
}
],
"family": "Gigliotti",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8744-0997",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Inspired - Pulmonary Solutions; San Carlos, CA 94070, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Kadrichu",
"given": "Nani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4327-1727",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Bilello",
"given": "John P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6850-9741",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6311-1440",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Bannister",
"given": "Roy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"family": "Subramanian",
"given": "Raju",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8713-9889",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Bill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8861-7205",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mackman",
"given": "Richard L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2933-9468",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "William A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7567-3002",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lovelace Biomedical; 2425 Ridgecrest Drive, SE, Albuquerque, NM 87108, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Kuehl",
"given": "Philip J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"family": "Hartke",
"given": "Jim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"family": "Cihlar",
"given": "Tomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8459-2370",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Gilead Sciences; 333 Lakeside Drive, Foster City, CA 94404, USA."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Porter",
"given": "Danielle P.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Science Translational Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-30T18:58:20Z",
"timestamp": 1640890700000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-30T18:58:26Z",
"timestamp": 1640890706000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-31T05:52:58Z",
"timestamp": 1640929978116
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1946-6234"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1946-6242"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "221",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1126",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa030781",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70204-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3947/ic.2016.48.2.118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_5_2"
},
{
"article-title": "State of Knowledge and Data Gaps of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in Humans",
"author": "Who Mers-Cov Research Group",
"first-page": "•••",
"journal-title": "PLOS Curr.",
"key": "e_1_3_2_6_2",
"unstructured": "Who Mers-Cov Research Group, State of Knowledge and Data Gaps of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in Humans. PLOS Curr. 5, ••• (2013). 24270606",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature17180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00602-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpu.30542",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_3_2_12_2",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration News Release: FDA Approves First Treatment for COVID-19. 22 October 2020. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-covid-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1091581815624080",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12840",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2423-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-00835-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab466.1642",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_3_2_19_2",
"unstructured": "J. Hill R. Paredes Deiros C. Carlos Vaca J. Mera B. Webb G. Perez P. Ryan-Murua J. Gerstoft M. Brown G. Oguchi J. Schiffer S. Brown M. Katz A. Ginde G. Camus D. Porter R. Hyland S. Chen K. Juneja A. Osinusi F. Duff R. Gottlieb Remdesivir for the treatment of high-risk non-hospitalized individuals with COVID-19: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Abstract LB1 IDWeek 2021 Virtual Conference 29 Sep – Oct 3 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2324-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abe8146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008903",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_23_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_24_2",
"unstructured": "J. D. Pitts X. Lu V. Du Pont N. C. Riola J. Li S. Manhas R. Martin J. Perry T. Cihlar D. P. Porter J. P. Bilello. Remdesivir Retains Potent Antiviral Activity Against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant and Other Variants of Concern. Poster 135. ISIRV-WHO Virtual Conference 19–21 October (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08958370802207318",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ab.2004.03.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_26_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Sci. Transl. Med."
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Inhaled remdesivir reduces viral burden in a nonhuman primate model of SARS-CoV-2 infection"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}