Benefits of Treatment With Favipiravir in Hospitalized Patients for COVID-19: a Retrospective Observational Case-control Study
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-175340/v1, Feb 2021
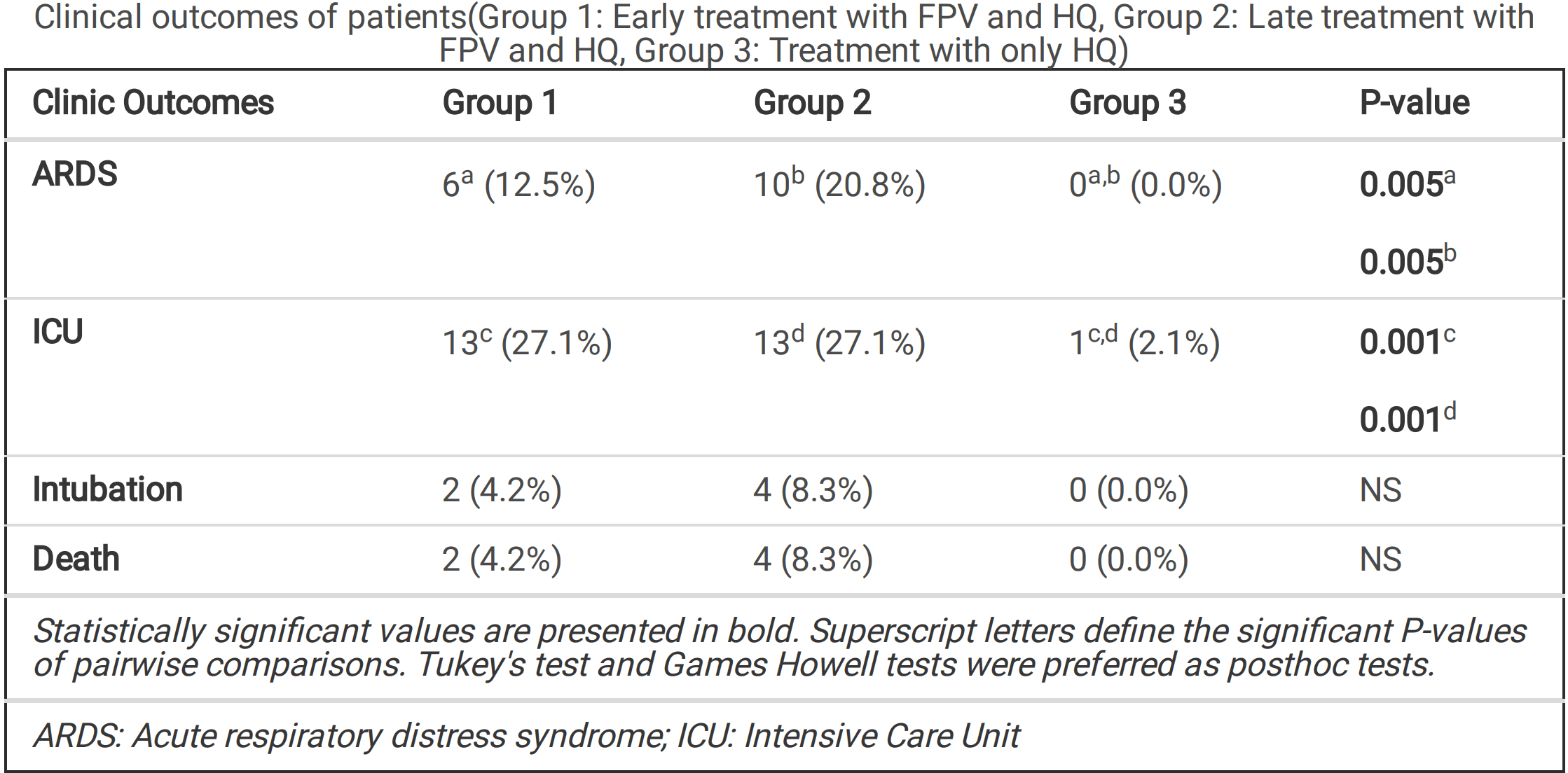
Retrospective 144 COVID-19 patients in Turkey, one group receiving FPV after a mean of 4.7 days, a second group after a mean of 8.6 days, and all groups receiving HCQ. No improvement in clinical outcomes was seen with the addition of FPV, however the groups are not comparable and no adjustments were made. FPV was first used in patients whose clinical condition worsened or whose pneumonia findings progressed, while later patients started FPV treatment early.
Potential risks of favipiravir include kidney injury1-3, liver injury2-5, cardiovascular events5,6, pulmonary toxicity6,7, and mutagenicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, embryotoxicity, and the creation of dangerous variants8-14.
1.
Abdulaziz et al., Clinical Features and Prognosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospital-Admitted Patients with COVID-19 in Egypt: A Single-Center Experience, Mansoura Medical Journal, doi:10.58775/2735-3990.1433.
2.
Ülger et al., Experimental evaluation of favipiravir (T-705)-induced liver and kidney toxicity in rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115472.
3.
El-Fetouh et al., Experimental Studies on Some Drugs Used in Covid-19 Treatment (Favipiravir and Dexamethasone) in Albino Rats, Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 13:10, www.advetresearch.com/index.php/AVR/article/view/1635.
4.
Almutairi et al., Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed8020129.
5.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
6.
Ozhan et al., Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary effects of repurposed COVID-19 therapeutics in healthy rats, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31048-4.
7.
Ülger (B) et al., Evaluation of the effects of favipiravir (T-705) on the lung tissue of healty rats: An experimental study, Food and Chemical Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2025.115235.
8.
Zhirnov et al., Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action, Journal of microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology, doi:10.36233/0372-9311-114.
9.
Waters et al., Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: the special case of molnupiravir, Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, doi:10.1002/em.22471.
10.
Hadj Hassine et al., Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14040841.
11.
Shum, C., An investigational study into the drug-associated mutational signature in SARS-CoV-2 viruses, The University of Hong Kong, PhD Thesis, hub.hku.hk/handle/10722/344396.
12.
Shiraki et al., Convenient screening of the reproductive toxicity of favipiravir and antiviral drugs in Caenorhabditis elegans, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35331.
Uçan et al., 4 Feb 2021, retrospective, Turkey, preprint, 8 authors, average treatment delay 4.73 days.
Benefits of Treatment With Favipiravir in Hospitalized Patients for COVID-19: a Retrospective Observational Case-control Study
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-175340/v1
Background: Although more than a year past since COVID-19 was de ned, there is no speci c treatment yet. Since COVID-19 management differs over time, it is hard to determine which therapy is more e cacious. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the e cacy of the regimen with Favipiravir (FPV) and determine if the timing of FPV addition offers any improvement. Methods: A retrospective observational case-controlled cohort study was performed between March and Sep-tember 2020, including adults with COVID-19 in a single-center in Turkey. We categorized patients into age-sex matched three groups, group 1 (n=48) and group 2 (n=48) included patients treated with the combination of FPV plus Hydroxychloroquine (HQ) early and late, respectively. Group 3 (n=48) consisted of patients on HQ monot-herapy. In Group 2, if the respiratory or clinic condition had not improved su ciently, FPV was added on or after day 3. Results: We found that starting FPV early had an impact on PCR negativity and the progression of the disease. 'No progression' was de ned as the absence of a new nding in the control radiological examination and the absence of accompanying clinical deterioration. Also, the decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) was greater in Group 1 than Group 3 (p <0.001). However, we found that early initiation of FPV treatment did not have a posi-tive effect on the estimated survival time. Conclusions: According to this retrospective study results, we believe that for better clinical outcomes, FPV treatment should be started promptly to enhance antiviral effects and improve clinical outcomes.
Declarations Authors' contributions AU and PC contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection, material preparation, and analysis were performed by SE, AY, HA, and AO. All authors commented on the latest version of the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the nal manuscript.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing Interests The authors declare that they have no competing inte rests.
References
Bai, Mu, Kargbo, Song Y Bin, Niu et al., Clinical and Virological Characteristics of Ebola Virus Disease Patients Treated with Favipiravir (T-705) -Sierra Leone, Clin Infect Dis
Cai, Yang, Liu, Chen, Shu et al., Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: An Open-Label Control Study, Eng
Casas-Rojo, Santos, Millán-Núñez-Cortés, Lumbreras-Bermejo, Ramos-Rincón et al., Clinical characteristics of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Spain: results from the SEMI-COVID-19 Registry, Rev Clínica Española (English Ed
Chen, Huang, Yin, Zhang, Cheng et al., Favipiravir versus Arbidol for COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial, doi:10.1101/2020.03.17.20037432
Chen, Wang, Lin, Chronic hydroxychloroquine use associated with QT prolongation and refractory ventricular arrhythmia, Clin Toxicol
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Wong, Chan et al., Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: Initial virological and clinical ndings, Thorax
Du, Chen, Favipiravir: Pharmacokinetics and Concerns About Clinical Trials for 2019-nCoV Infection, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.1844
Furuta, Komeno, Nakamura, Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase, Proceedings of the Japan Academy Series B: Physical and Biological Sciences
Grasselli, Pesenti, Cecconi, Critical Care Utilization for the COVID-19 Outbreak in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA
Guan, Liang, Zhao, Liang, Chen et al., Comorbidity and its impact on 1,590 patients with Covid-19 in China: A nationwide analysis, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00547-2020
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Lagadinou, Salomou, Zareifopoulos, Marangos, Gogos et al., Prognosis of COVID-19: Changes in laboratory parameters, Le Infez Med
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (CoVID-19) from publicly reported con rmed cases: Estimation and application, Ann Intern Med [Internet, doi:10.7326/M20-0504
Li, Clercq, Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus
Organization, Clinical management of COVID-19: interim guidance
Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, Bashash, Fateh, Abolghasemi, Laboratory ndings in COVID-19 diagnosis and prognosis, Clinica Chimica Acta. Elsevier B.V
Prokop, Van Everdingen, Rees Vellinga, Van Ufford, Stöger et al., CO-RADS: A Categorical CT Assessment Scheme for Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19-De nition and Evaluation, Radiology
Shiraki, Daikoku, Favipiravir, an anti-in uenza drug against life-threatening RNA virus infections
Sissoko, Laouenan, Folkesson, Lebing, Beavogui et al., Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for Ebola Virus Disease (the JIKI Trial): A Historically Controlled, Single-Arm Proof-of-Concept Trial in Guinea, PLoS Med
Team, Team, The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19) -China, China CDC Weekly
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-175340/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-175340/v1",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Background: Although more than a year past since COVID-19 was defined, there is no specific treatment yet. Since COVID-19 management differs over time, it is hard to determine which therapy is more efficacious. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy of the regimen with Favipiravir (FPV) and determine if the timing of FPV addition offers any improvement. Methods: A retrospective observational case-controlled cohort study was performed between March and Sep-tember 2020, including adults with COVID-19 in a single-center in Turkey. We categorized patients into age-sex matched three groups, group 1 (n=48) and group 2 (n=48) included patients treated with the combination of FPV plus Hydroxychloroquine (HQ) early and late, respectively. Group 3 (n=48) consisted of patients on HQ monot-herapy. In Group 2, if the respiratory or clinic condition had not improved sufficiently, FPV was added on or after day 3. Results: We found that starting FPV early had an impact on PCR negativity and the progression of the disease. 'No progression' was defined as the absence of a new finding in the control radiological examination and the absence of accompanying clinical deterioration. Also, the decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) was greater in Group 1 than Group 3 (p <0.001). However, we found that early initiation of FPV treatment did not have a posi-tive effect on the estimated survival time. Conclusions: According to this retrospective study results, we believe that for better clinical outcomes, FPV treatment should be started promptly to enhance antiviral effects and improve clinical outcomes.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
28
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8771-6121",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ministry of Health"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uçan",
"given": "Anıl",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eskisehir State Hospital: Eskisehir Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Çerçi",
"given": "Pamir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eskisehir State Hospital: Eskisehir Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Efe",
"given": "Serdar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eskişehir Devlet Hastanesi: Eskisehir Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Akgün",
"given": "Hakan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eskişehir Devlet Hastanesi: Eskisehir Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Özmen",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eskişehir Devlet Hastanesi: Eskisehir Devlet Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Yağmuroğlu",
"given": "Aysel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Osmangazi University: Eskisehir Osmangazi Universitesi"
}
],
"family": "Bilgin",
"given": "Muzaffer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Kayseri City Hospital: TC Saglik Bakanligi Kayseri Sehir Egitim ve Arastirma Hastanesi"
}
],
"family": "Avcı",
"given": "Deniz",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-05T16:24:15Z",
"timestamp": 1612542255000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-05T16:24:15Z",
"timestamp": 1612542255000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T07:55:01Z",
"timestamp": 1683705301078
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
4
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612396800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-175340/v1",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-175340/v1.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
4
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-175340/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Benefits of Treatment With Favipiravir in Hospitalized Patients for COVID-19: a Retrospective Observational Case-control Study",
"type": "posted-content"
}