A Retinol Derivative Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Interrupting Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry
et al., mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01485-22, Jul 2022
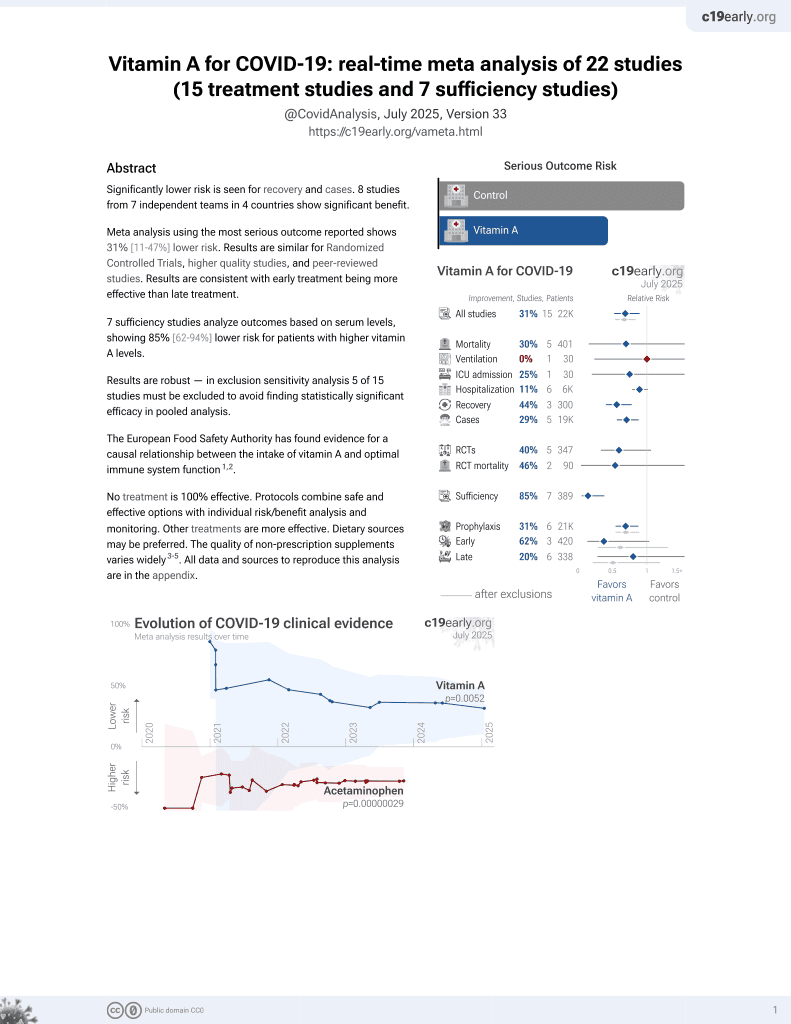
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
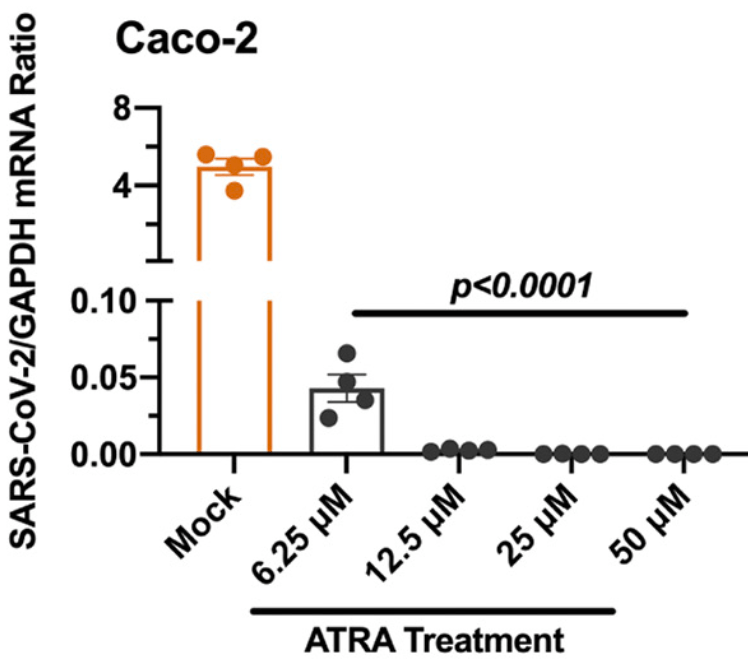
In vitro study showing all-trans retinoic acid, a vitamin A derivative, has potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in both human cell lines and human organoids of the lower respiratory tract.
11 preclinical studies support the efficacy of vitamin A for COVID-19:
Vitamin A has been identified by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal relationship between intake and optimal immune system function11-13.
Vitamin A has potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in both human cell lines and human organoids of the lower respiratory tract (active metabolite all-trans retinoic acid, ATRA)8, is predicted to bind critical host and viral proteins for SARS-CoV-2 and may compensate for gene expression changes related to SARS-CoV-22-4, may be beneficial for COVID-19 via antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects according to network pharmacology analysis5, reduces barrier compromise caused by TNF-α in Calu-3 cells7, inhibits mouse coronavirus replication10, may stimulate innate immunity by activating interferon responses in an IRF3-dependent manner (ATRA)10, may reduce excessive inflammation induced by SARS-CoV-22, shows SARS-CoV-2 antiviral activity In Vitro2,6,9 , is effective against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants in Calu-3 cells9, and inhibits the entry and replication of SARS-CoV-2 via binding to ACE2 / 3CLpro / RdRp / helicase / 3'-to-5' exonuclease2.
1.
Voloudakis et al., A genetically based computational drug repurposing framework for rapid identification of candidate compounds: application to COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.10.25320348.
2.
Huang et al., All-trans retinoic acid acts as a dual-purpose inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 infection and inflammation, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.107942.
3.
Chakraborty et al., In-silico screening and in-vitro assay show the antiviral effect of Indomethacin against SARS-CoV-2, Computers in Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105788.
4.
Pandya et al., Unravelling Vitamin B12 as a potential inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2: A computational approach, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2022.100951.
5.
Li et al., Revealing the targets and mechanisms of vitamin A in the treatment of COVID-19, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103888.
6.
Moatasim et al., Potent Antiviral Activity of Vitamin B12 against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, and Human Coronavirus 229E, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112777.
7.
DiGuilio et al., The multiphasic TNF-α-induced compromise of Calu-3 airway epithelial barrier function, Experimental Lung Research, doi:10.1080/01902148.2023.2193637.
8.
Tong et al., A Retinol Derivative Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Interrupting Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01485-22.
9.
Morita et al., All-Trans Retinoic Acid Exhibits Antiviral Effect against SARS-CoV-2 by Inhibiting 3CLpro Activity, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13081669.
10.
Franco et al., Retinoic Acid-Mediated Inhibition of Mouse Coronavirus Replication Is Dependent on IRF3 and CaMKK, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v16010140.
11.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
12.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
13.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin A and cell differentiation (ID 14), function of the immune system (ID 14), maintenance of skin and mucous membranes (ID 15, 17), maintenance of vision (ID 16), maintenance of bone (ID 13, 17), maintenance of teeth (ID 13, 17), maintenance of hair (ID 17), maintenance of nails (ID 17), metabolism of iron (ID 206), and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (ID 209) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1221.
Tong et al., 13 Jul 2022, China, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Contact: gongcheng@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn, yxiang@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn, renlizhangszcdc@aliyun.com, lil@sustech.edu.cn.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
A Retinol Derivative Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Interrupting Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry
mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01485-22
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the etiological agent of the global pandemic and life-threatening coronavirus disease 2019 . Although vaccines and therapeutic antibodies are available, their efficacy is continuously undermined by rapidly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we found that all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a vitamin A (retinol) derivative, showed potent antiviral activity against all SARS-CoV-2 variants in both human cell lines and human organoids of the lower respiratory tract. Mechanistically, ATRA directly binds in a deep hydrophobic pocket of the receptor binding domain (RBD) located on the top of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S) trimer. The bound ATRA mediates strong interactions between the "down" RBDs and locks most of the S trimers in an RBD "all-down" and ACE2-inaccessible inhibitory conformation. In summary, our results reveal the pharmacological biotargets and structural mechanism of ATRA and other retinoids in SARS-CoV-2 infection and suggest that ATRA and its derivatives could be potential hit compounds against a broad spectrum of coronaviruses. IMPORTANCE Retinoids, a group of compounds including vitamin A and its active metabolite all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), regulate serial physiological activity in multiple organ systems, such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. The ATRA analogues reported to date include more than 4,000 natural and synthetic molecules that are structurally and/or functionally related to ATRA. Here, we found that ATRA showed potent antiviral activity against all SARS-CoV-2 variants by directly binding in a deep hydrophobic pocket of the receptor binding domain (RBD) located on top of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S) trimer. The bound ATRA mediates strong interactions between the "down" RBDs and locks most of the S trimers in an RBD "all-down" and ACE2-inaccessible inhibitory conformation, suggesting the pharmacological feasibility of using ATRA or its derivatives as a remedy for and prevention of COVID-19 disease.
References
Altmann, Boyton, Beale, Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abg7404
Aluisio, Perera, Yam, Garbern, Peters et al., Vitamin A supplementation was associated with reduced mortality in patients with Ebola virus disease during the West African outbreak, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxz142
Ao, Lan, He, Liu, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: immune escape and vaccine development, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.126
Baden, Buxman, Weinstein, Yoder, Treatment of ichthyosis with isotretinoin, J Am Acad Dermatol, doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70062-3
Bangaru, Ozorowski, Turner, Antanasijevic, Huang et al., Structural analysis of full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from an advanced vaccine candidate, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abe1502
Bapna, Nair, Tapan, Nair, Kadam et al., All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA): pediatric acute promyelocytic leukemia, Pediatr Hematol Oncol, doi:10.3109/08880019809028791
Bates, Vitamin A, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91157-x
Bojkova, Klann, Koch, Widera, Krause et al., Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2332-7
Böcher, Wallasch, Höhler, Galle, All-trans retinoic acid for treatment of chronic hepatitis C, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01666.x
Chen, Yang, Xu, Su, Effect of all-trans-retinoic acid on enterovirus 71 infection in vitro, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114513004133
Clark, Jit, Warren-Gash, Guthrie, Wang et al., Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe COVID-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30264-3
Coombs, Tavakkoli, Tallman, Acute promyelocytic leukemia: where did we start, where are we now, and the future, Blood Cancer J, doi:10.1038/bcj.2015.25
Degos, All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) therapeutical effect in acute promyelocytic leukemia, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/0753-3322(92)90083-j
Degos, Wang, All trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia, Oncogene, doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204763
Dou, Huang, Zeng, Zhou, Jiang et al., Alltrans retinoic acid enhances the effect of Fra-1 to inhibit cell proliferation and metabolism in cervical cancer, Biotechnol Lett, doi:10.1007/s10529-020-02847-8
Emsley, Lohkamp, Scott, Cowtan, Features and development of Coot, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444910007493
Geria, Scheinfeld, Talarozole, a selective inhibitor of P450-mediated all-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of psoriasis and acne, Curr Opin Invest Drugs
Goddard, Huang, Ferrin, Visualizing density maps with UCSF Chimera, J Struct Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2006.06.010
Gui, Song, Zhou, Xu, Chen et al., Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein reveal a prerequisite conformational state for receptor binding, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/cr.2016.152
Hoffmann, Arora, Groß, Seidel, Hörnich et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and P.1 escape from neutralizing antibodies, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.036
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Hussey, Klein, A randomized, controlled trial of vitamin A in children with severe measles, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM199007193230304
Kawaguchi, Yu, Honda, Hu, Whitelegge et al., A membrane receptor for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1136244
Li, Si, Lou, Wang, Guo et al., All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits mink hair follicle growth via inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis of dermal papilla cells through TGF-b2/Smad2/3 pathway, Acta Histochem, doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151603
Li, Zhang, Zhang, Qin, Zhao, All-trans retinoic acid regulates sheep primary myoblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro, Domest Anim Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2019.106394
Liang, Qiao, Liu, Tian, Hui et al., Overview of all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and its analogues: structures, activities, and mechanisms in acute promyelocytic leukaemia, Eur J Med Chem, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113451
Liebschner, Afonine, Baker, Bunkóczi, Chen et al., Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix, Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, doi:10.1107/S2059798319011471
Onnis, Chiaverini, Hickman, Dreyfus, Fischer et al., Alitretinoin reduces erythema in inherited ichthyosis, Orphanet J Rare Dis, doi:10.1186/s13023-018-0783-9
Pan, Wang, Tu, A topical medication of all-trans retinoic acid reduces sebum excretion rate in patients with forehead acne, Am J Ther, doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000000390
Pei, Feng, Zhang, Sun, Li et al., Host metabolism dysregulation and cell tropism identification in human airway and alveolar organoids upon SARS-CoV-2 infection, Protein Cell, doi:10.1007/s13238-020-00811-w
Punjani, Rubinstein, Fleet, Brubaker, cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4169
Roels, Vitamin A physiology, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.1970.03180060075015
Sandell, Sanderson, Moiseyev, Johnson, Mushegian et al., RDH10 is essential for synthesis of embryonic retinoic acid and is required for limb, craniofacial, and organ development, Genes Dev, doi:10.1101/gad.1533407
Scheres, Chen, Prevention of overfitting in cryo-EM structure determination, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.2115
Scheres, RELION: implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination, J Struct Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2012.09.006
Shi, Dong, Rapid global spread of the SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1 .617.2) variant: spatiotemporal variation and public health impact, doi:10.15212/ZOONOSES-2021-0005
Song, Gui, Wang, Xiang, Cryo-EM structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex with its host cell receptor ACE2, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1007236
Sun, Chen, Gu, Yang, Wang et al., A mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.020
Suzuki, Kunisawa, Vitamin-mediated immune regulation in the development of inflammatory diseases, Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/1871530315666150316122128
Tan, Baldwin, Davis, Williamson, Potter et al., Addressing preferred specimen orientation in singleparticle cryo-EM through tilting, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4347
Tepasse, Vollenberg, Fobker, Kabar, Schmidt et al., Vitamin A plasma levels in COVID-19 patients: a ATRA Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry, mBio Month YYYY
Toelzer, Gupta, Yadav, Borucu, Davidson et al., Free fatty acid binding pocket in the locked structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd3255
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9
Webb, Villamor, Update: effects of antioxidant and non-antioxidant vitamin supplementation on immune function, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.tb00298.x
Weisblum, Schmidt, Zhang, Dasilva, Poston et al., Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.61312
Who, WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2507
Wrobel, Benton, Xu, Roustan, Martin et al., SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-020-0468-7
Xia, Liu, Wang, Xu, Lan et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x
Yan, Folic acid-induced animal model of kidney disease, Animal Model Exp Med, doi:10.1002/ame2.12194
Yang, Liu, Zhang, Du, Zhou et al., Characteristic analysis of Omicron-included SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.129
Zhang, Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction, J Struct Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003
Zhang, Qiao, Yu, Zeng, Shan et al., Bat and pangolin coronavirus spike glycoprotein structures provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 evolution, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21767-3
Zheng, Palovcak, Armache, Verba, Cheng et al., MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4193
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01485-22",
"ISSN": [
"2150-7511"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01485-22",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n Retinoids, a group of compounds including vitamin A and its active metabolite all-\n <jats:italic>trans</jats:italic>\n retinoic acid (ATRA), regulate serial physiological activity in multiple organ systems, such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. The ATRA analogues reported to date include more than 4,000 natural and synthetic molecules that are structurally and/or functionally related to ATRA.\n </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/mbio.01485-22"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-06-01"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-06-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-07-13"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Infectious Diseases, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Liangqin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Lin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Otolaryngology, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Thoracic Surgery, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen, China"
}
],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Shumin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiao",
"given": "Xiaoping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Pathogenic Organisms, Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Pathogenic Organisms, Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Chunli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Yibin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Infectious Diseases, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Tai",
"given": "Wanbo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China"
},
{
"name": "Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Yanhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine, the University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Connecticut, USA"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Penghua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China"
},
{
"name": "Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Pathogenic Organisms, Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Renli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiang",
"given": "Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7447-5488",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, Beijing Frontier Research Center for Biological Structure and Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Infectious Diseases, Shenzhen Bay Laboratory, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Gong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "mBio",
"container-title-short": "mBio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T13:00:50Z",
"timestamp": 1657717250000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T13:01:21Z",
"timestamp": 1657717281000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diamond",
"given": "Michael S.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012166",
"award": [
"2021YFC2300200",
"2020YFC1200104 2019YFC1200201 and 2018YFA0507202"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"32188101 31825001 81730063 81961160737 31925023 21827810 82102389 and 31861143027"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"2020Z99CFG017"
],
"name": "Tsinghua University Spring Breeze Fund"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100010877",
"award": [
"JSGG20191129144225464"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Shenzhen Science and Technology Project"
},
{
"award": [
"SZSM201611064"
],
"name": "Shenzhen San-Ming Project for Prevention and Research on Vector-borne Disease"
},
{
"award": [
"202105AE160020"
],
"name": "Innovation Team Project of Yunnan Science and Technology Department"
},
{
"award": [
"202005AF150034"
],
"name": "Yunnan Cheng gong expert workstation"
},
{
"award": [
"2021B1212030009"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China"
},
{
"award": [
"20201080514"
],
"name": "Tsinghua University Spring Breeze Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T13:41:44Z",
"timestamp": 1657719704878
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1657670400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1657670400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01485-22",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01485-22",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30264-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_4_2"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_2_5_2",
"unstructured": "WHO. 2022. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.61312",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15212/ZOONOSES-2021-0005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.126",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.129",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cr.2016.152",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1007236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871530315666150316122128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2007.tb00298.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ame2.12194",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91157-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.1970.03180060075015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxz142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199007193230304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072173",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1136244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gad.1533407",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01666.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114513004133",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2332-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13238-020-00811-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abg7404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0305-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-0468-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4169",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd3255",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21767-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe1502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10529-020-02847-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.domaniend.2019.106394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151603",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0753-3322(92)90083-j",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/08880019809028791",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.onc.1204763",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/bcj.2015.25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_43_2"
},
{
"article-title": "Talarozole, a selective inhibitor of P450-mediated all-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of psoriasis and acne",
"author": "Geria AN",
"first-page": "1228",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Invest Drugs",
"key": "e_1_3_2_44_2",
"unstructured": "Geria AN, Scheinfeld NS. 2008. Talarozole, a selective inhibitor of P450-mediated all-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of psoriasis and acne. Curr Opin Invest Drugs 9:1228–1237.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000000390",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13023-018-0783-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70062-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113451",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4193",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2012.09.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.2115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2006.06.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444910007493",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S2059798319011471",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_2_56_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.01485-22"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A Retinol Derivative Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Interrupting Spike-Mediated Cellular Entry",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page"
}