Selective Impact of Selenium Compounds on Two Cytokine Storm Players
et al., Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202308.1168.v1, Aug 2023
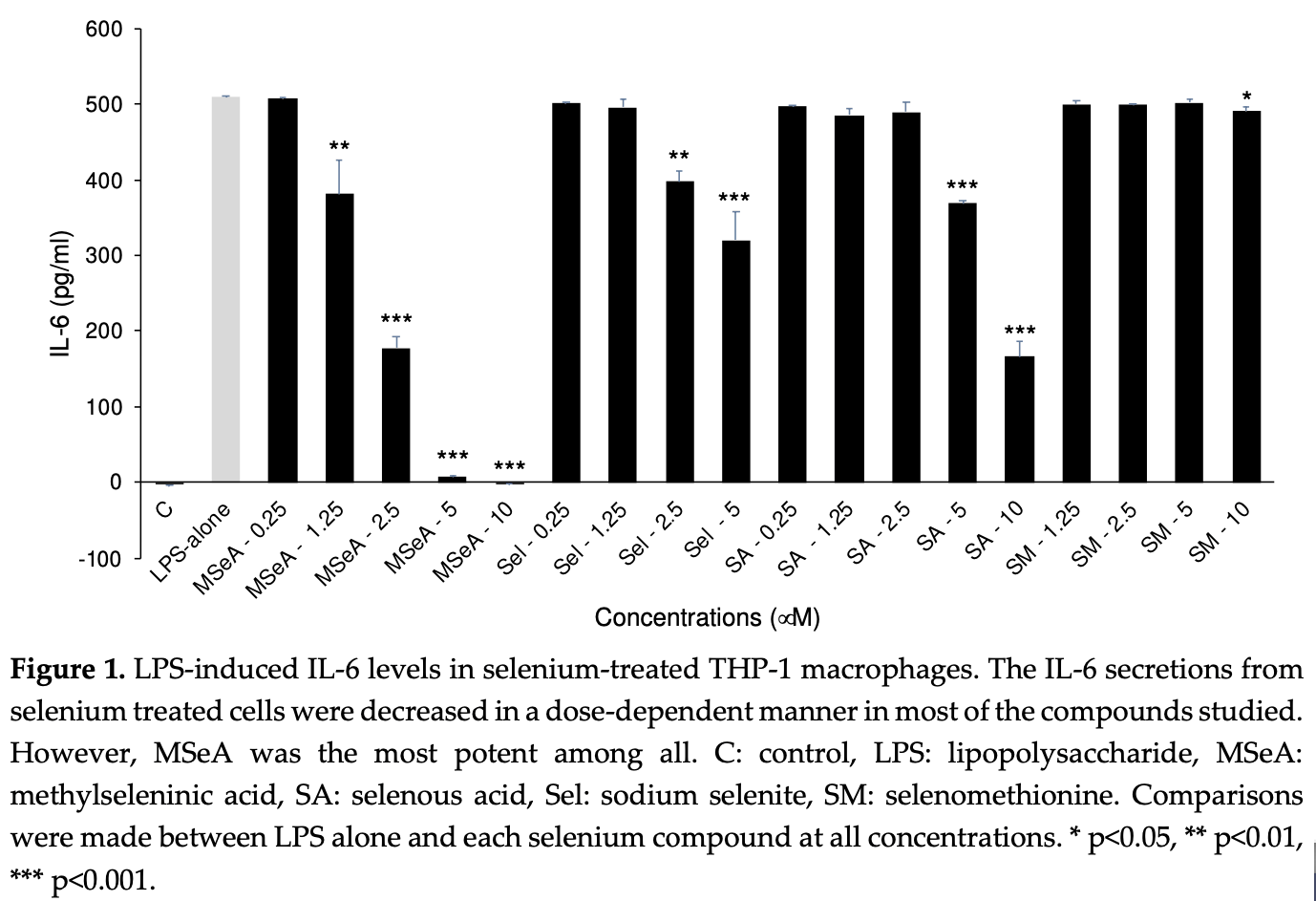
In vitro analysis of selenium for reducing inflammatory cytokine production in a cell model of COVID-19 infection. Methylseleninic acid was the most potent at reducing secretion of the cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, key factors in the cytokine storm in severe COVID-19. Authors also show an increase in Nrf2 and decrease in pIkBa in human macrophages with methylseleninic acid.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of selenium for COVID-19:
Selenium has been identified by the European Food
Safety Authority (EFSA) as having sufficient evidence for a causal
relationship between intake and optimal immune system function4-6.
Selenium may be beneficial for COVID-19 by inhibiting
ferroptosis, an oxidative stress-induced cell death pathway implicated
in COVID-19 pathogenesis7.
Selenium enhances immune response, inhibits ROS
production, and protects against ferroptosis via GPX4 induction8.
1.
Sinha et al., Selective Impact of Selenium Compounds on Two Cytokine Storm Players, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202308.1168.v1.
2.
Hajdrik et al., In Vitro Determination of Inhibitory Effects of Humic Substances Complexing Zn and Se on SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replication, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods11050694.
3.
Zhou et al., Metal-coding assisted serological multi-omics profiling deciphers the role of selenium in COVID-19 immunity, Chemical Science, doi:10.1039/d3sc03345g.
4.
Galmés et al., Suboptimal Consumption of Relevant Immune System Micronutrients Is Associated with a Worse Impact of COVID-19 in Spanish Populations, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14112254.
5.
Galmés (B) et al., Current State of Evidence: Influence of Nutritional and Nutrigenetic Factors on Immunity in the COVID-19 Pandemic Framework, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092738.
6.
EFSA, Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to selenium and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage (ID 277, 283, 286, 1289, 1290, 1291, 1293, 1751), function of the immune system (ID 278), thyroid function (ID 279, 282, 286, 1289, 1290, 1291, 1293), function of the heart and blood vessels (ID 280), prostate function (ID 284), cognitive function (ID 285) and spermatogenesis (ID 396) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006, EFSA Journal, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1220.
Sinha et al., 16 Aug 2023, preprint, 3 authors.
Contact: rsinha@pennstatehealth.psu.edu (corresponding author), isinha@pennstatehealth.psu.edu, jzhu2@pennstatehealth.psu.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Selective Impact of Selenium Compounds on Two Cytokine Storm Players
doi:10.20944/preprints202308.1168.v1
COVID-19 patients suffer from detrimental effects of cytokine storm and not much success has been achieved to overcome this issue. We sought to test the ability of selenium in reducing the impact of two important cytokine storm players; IL-6 and TNF-. The effects of four selenium compounds were evaluated on the secretion of these cytokines from THP-1 macrophages in vitro following LPS challenge. Also, potential impact of methylseleninic acid (MSeA) on Nrf2 and IB was determined following short treatment of THP-1 macrophages. MSeA was observed to be the most potent selenium form to reduce IL-6 and TNF- levels among the four selenium compounds tested. In addition, an increase in Nrf2 and decrease in pIB in human macrophages was observed following MSeA treatment. Our data indicate that COVID-19 patients might benefit by suppressing their cytokine storm with addition of MSeA to the standard therapy.
Supplementary Materials: Not applicable Author Contributions: Conceptualization, I.S. and R.S.; methodology, I.S.; validation, I.S. and R.S.; formal analysis, I.S., J.Z. and R.S.; investigation, I.S.; writing-original draft preparation, R.S.; writing-review and editing, I.S., J.Z. and R.S.; visualization, I.S. and R.S.; supervision, R.S.; project administration, R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Alfthan, Eurola, Ekholm, Venäläinen, Root et al., Effects of nationwide addition of selenium to fertilizers on foods, and animal and human health in Finland: From deficiency to optimal selenium status of the population, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.04.009
Alshammari, Fatima, Alraya, Khuzaim Alzahrani, Kamal et al., Selenium and COVID-19: A spotlight on the clinical trials, inventive compositions, and patent literature, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2022.09.011
Amaral, Cantor, Silverman, Malats, Selenium and bladder cancer risk: a meta-analysis, Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev, doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0544
Angstwurm, Engelmann, Zimmermann, Lehmann, Spes et al., Selenium in Intensive Care (SIC): Results of a prospective randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-center study in patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, and septic shock, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000251124.83436.0E
Angstwurm, Schottdorf, Schopohl, Gaertner, Selenium replacement in patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome improves clinical outcome, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/00003246-199909000-00017
Balboni, Zagnoli, Filippini, Fairweather-Tait, Vinceti, Zinc and selenium supplementation in COVID-19 prevention and treatment: a systematic review of the experimental studies, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.126956
Bermano, Meplan, Mercer, Hesketh, Selenium and viral infection: are there lessons for COVID-19?, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114520003128
Das, Bortner, Desai, Amin, El-Bayoumy, The selenium analog of the chemopreventive compound S,S'-(1,4-phenylenebis[1,2-ethanediyl])bisisothiourea is a remarkable inducer of apoptosis and Preprints (www.preprints.org) | NOT PEER-REVIEWED | Posted: 16 August
Deng, Liu, Yang, Bao, Lin et al., Progress of Selenium Deficiency in the Pathogenesis of Arthropathies and Selenium Supplement for Their Treatment, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-03022-4
Dound, Sehgal, Preclinical Efficacy and Safety Studies of Formulation SSV-003, a Potent Anti-Viral Herbal Formulation, J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, doi:10.2147/JEP.S310452
Emmert, El-Bayoumy, Das, Sun, Amin et al., Induction of lung glutathione and glutamylcysteine ligase by 1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)selenocyanate and its glutathione conjugate: role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2. Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.03.018
Fairweather-Tait, Bao, Broadley, Collings, Ford et al., Selenium in human health and disease, Antioxidants Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3275
Fakhrolmobasheri, Mazaheri-Tehrani, Kieliszek, Zeinalian, Abbasi et al., COVID-19 and Selenium Deficiency: A Systematic Review, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02997-4
Ghanem, Brown, Eat Mohamed, Fuller, A meta-summary and bioinformatic analysis identified interleukin 6 as a master regulator of COVID-19 severity biomarkers, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2022.156011
Gholizadeh, Khalili, Roodi, Saeedy, Najafi et al., Selenium supplementation decreases CRP and IL-6 and increases TNF-alpha: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127199
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, Selenoproteins and Viral Infection, doi:10.3390/nu11092101
Harthill, Review: micronutrient selenium deficiency influences evolution of some viral infectious diseases, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-011-8977-1
Ip, Dong, Methylselenocysteine modulates proliferation and apoptosis biomarkers in premalignant lesions of the rat mammary gland, Anticancer Res
Itoh, Chiba, Takahashi, Ishii, Igarashi et al., An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6943
Jablonska, Li, Reszka, Wieczorek, Tarhonska et al., Therapeutic Potential of Selenium and Selenium Compounds in Cervical Cancer, Cancer Control, doi:10.1177/10732748211001808
Jenkins, Kitts, Giovannucci, Sahye-Pudaruth, Paquette et al., Selenium, antioxidants, cardiovascular disease, and all-cause mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa245
Jones, Droz, Greve, Gottschalk, Poffet et al., Selenium deficiency risk predicted to increase under future climate change, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1611576114
Kwon, Suh, Kim, Jung, Kim et al., Niacin and Selenium Attenuate Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury by Up-Regulating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 Signaling, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000001422
Liu, Xu, Huang, Selenium in the prevention of atherosclerosis and its underlying mechanisms, Metallomics, doi:10.1039/c6mt00195e
Mal'tseva, Goltyaev, Turovsky, Varlamova, Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Selenium-Containing Agents: Their Role in the Regulation of Defense Mechanisms against COVID-19, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23042360
Mangalmurti, Hunter, Cytokine Storms: Understanding COVID-19, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017
Martinez, Huang, Acuna, Laverde, Trujillo et al., Role of Selenium in Viral Infections with a Major Focus on SARS-CoV-2, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23010280
Michot, Albiges, Chaput, Saada, Pommeret et al., Tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, to treat COVID-19-related respiratory failure: a case report, Ann. Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.300
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality Risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Munteanu, Schwartz, The relationship between nutrition and the immune system, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1082500
Notz, Herrmann, Schlesinger, Helmer, Sudowe et al., Clinical Significance of Micronutrient Supplementation in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients with Severe ARDS, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13062113
Prabhu, Zamamiri-Davis, Stewart, Thompson, Sordillo et al., Selenium deficiency increases the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in RAW 264.7 macrophages: role of nuclear factor-kappaB in up-regulation, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/BJ20020256
Preprints, | NOT PEER-REVIEWED | Posted: 16 August
Schomburg, Selenium Deficiency Due to Diet, Pregnancy, Severe Illness, or COVID-19-A Preventable Trigger for Autoimmune Disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms22168532
Schomburg, Selenium Deficiency in COVID-19-A Possible Long-Lasting Toxic Relationship, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020283
Schomburg, Selenium, selenoproteins and the thyroid gland: interactions in health and disease, Nat. Rev. Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/nrendo.2011.174
Sharif, Bolshakov, Raines, Newham, Perkins, Transcriptional profiling of the LPS induced NF-kappaB response in macrophages, BMC Immunol, doi:10.1186/1471-2172-8-1
Shirato, Kizaki, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit induces pro-inflammatory responses via tolllike receptor 4 signaling in murine and human macrophages, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06187
Sinha, Allen, Pinto, Sinha, Methylseleninic acid elevates REDD1 and inhibits prostate cancer cell growth despite AKT activation and mTOR dysregulation in hypoxia, Cancer Med, doi:10.1002/cam4.198
Sinha, Goel, Bitzer, Trushin, Liao et al., Evaluating electronic cigarette cytotoxicity and inflammatory responses in vitro, Tob. Induc. Dis, doi:10.18332/tid/147200
Sinha, Karagoz, Fogle, Hollenbeak, Zea et al., Omics" of Selenium Biology: A Prospective Study of Plasma Proteome Network Before and After Selenized-Yeast Supplementation in Healthy Men, Omics, doi:10.1089/omi.2015.0187
Solovyev, Drobyshev, Bjorklund, Dubrovskii, Lysiuk et al., Selenium, selenoprotein P, and Alzheimer's disease: is there a link? Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.02.030
Steinbrenner, Al-Quraishy, Dkhil, Wunderlich, Sies, Dietary selenium in adjuvant therapy of viral and bacterial infections, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.3945/an.114.007575
Unni, Koul, Yung, Sinha, Se-methylselenocysteine inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity of mouse mammary epithelial tumor cells in vitro, Breast Cancer Res, doi:10.1186/bcr1276
Wang, Bi, Wang, Sun, Meng et al., Selenium ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced inflammation in bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting activation of TLR2, NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, BMC Vet. Res, doi:10.1186/s12917-018-1508-y
Wang, Bonorden, Li, Lee, Hu et al., Methylselenium compounds inhibit prostate carcinogenesis in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model with survival benefit, Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila), doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0173
Wolfram, Weidenbach, Adolf, Schwarz, Schädel et al., The Trace Element Selenium Is Important for Redox Signaling in Phorbol Ester-Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms222011060
Wooten, Sinha, Sinha, Selenium Induces Pancreatic Cancer Cell Death Alone and in Combination with Gemcitabine, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10010149
Wu, Rayman, Lv, Schomburg, Cui et al., Low Population Selenium Status Is Associated with Increased Prevalence of Thyroid Disease, J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2015-2222
Zhang, Saad, Taylor, Rayman, Selenium and selenoproteins in viral infection with potential relevance to COVID-19, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101715
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa095
Zhang, Zhang, Lu, Zhang, Zhang et al., Association between fatality rate of COVID-19 and selenium deficiency in China, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06167-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202308.1168.v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.20944/preprints202308.1168.v1",
"abstract": "<jats:p>COVID-19 patients suffer from detrimental effects of cytokine storm and not much success has been achieved to overcome this issue. We sought to test the ability of selenium in reducing the impact of two important cytokine storm players; IL-6 and TNF-a. The effects of four selenium compounds were evaluated on the secretion of these cytokines from THP-1 macrophages in vitro following LPS challenge. Also, potential impact of methylseleninic acid (MSeA) on Nrf2 and IkBa was determined following short treatment of THP-1 macrophages. MSeA was observed to be the most potent selenium form to reduce IL-6 and TNF-a levels among the four selenium compounds tested. In addition, an increase in Nrf2 and decrease in pIkBa in human macrophages was observed following MSeA treatment. Our data indicate that COVID-19 patients might benefit by suppressing their cytokine storm with addition of MSeA to the standard therapy.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
14
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "Indu",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Junjia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9083-8533",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "Raghu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-17T01:59:11Z",
"timestamp": 1692237551000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-17T02:00:28Z",
"timestamp": 1692237628000
},
"group-title": "Biology and Life Sciences",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-17T05:05:58Z",
"timestamp": 1692248758541
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
16
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1692144000000
}
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
16
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.20944",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202308.1168/v1"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Selective Impact of Selenium Compounds on Two Cytokine Storm Players",
"type": "posted-content"
}