The adjuvant therapy of edible herbal product including colchicum bulb, olive leaf, black cumin seeds, lavender flower, and ginger rhizome on the outcome of patients with severe and critical COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial
et al., Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine, doi:10.22038/ajp.2024.24633, Jul 2024
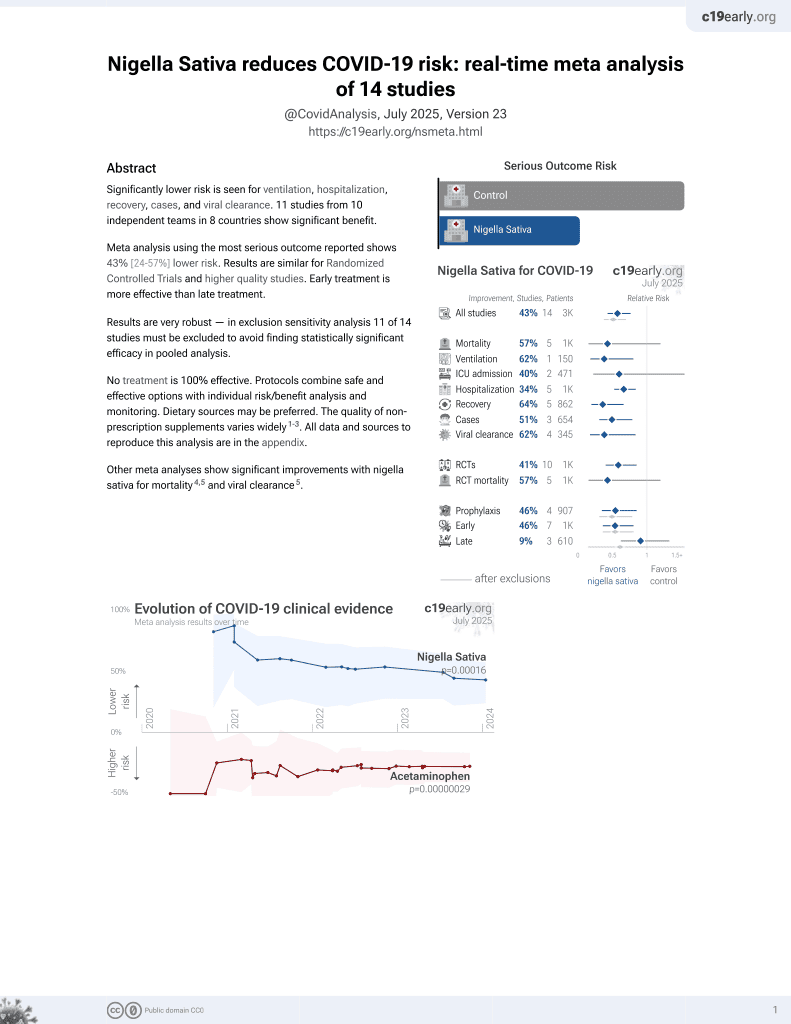
14th treatment shown to reduce risk in
January 2021, now with p = 0.00016 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 150 severe and critical COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality, lower ICU admission, and improved recovery with a treatment including nigella sativa, colchicum autumnal, olea europaea, lavandula angustifolia, and zingiber officinale roscoe.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
many combined treatments which may significantly contribute to the effect seen.
|
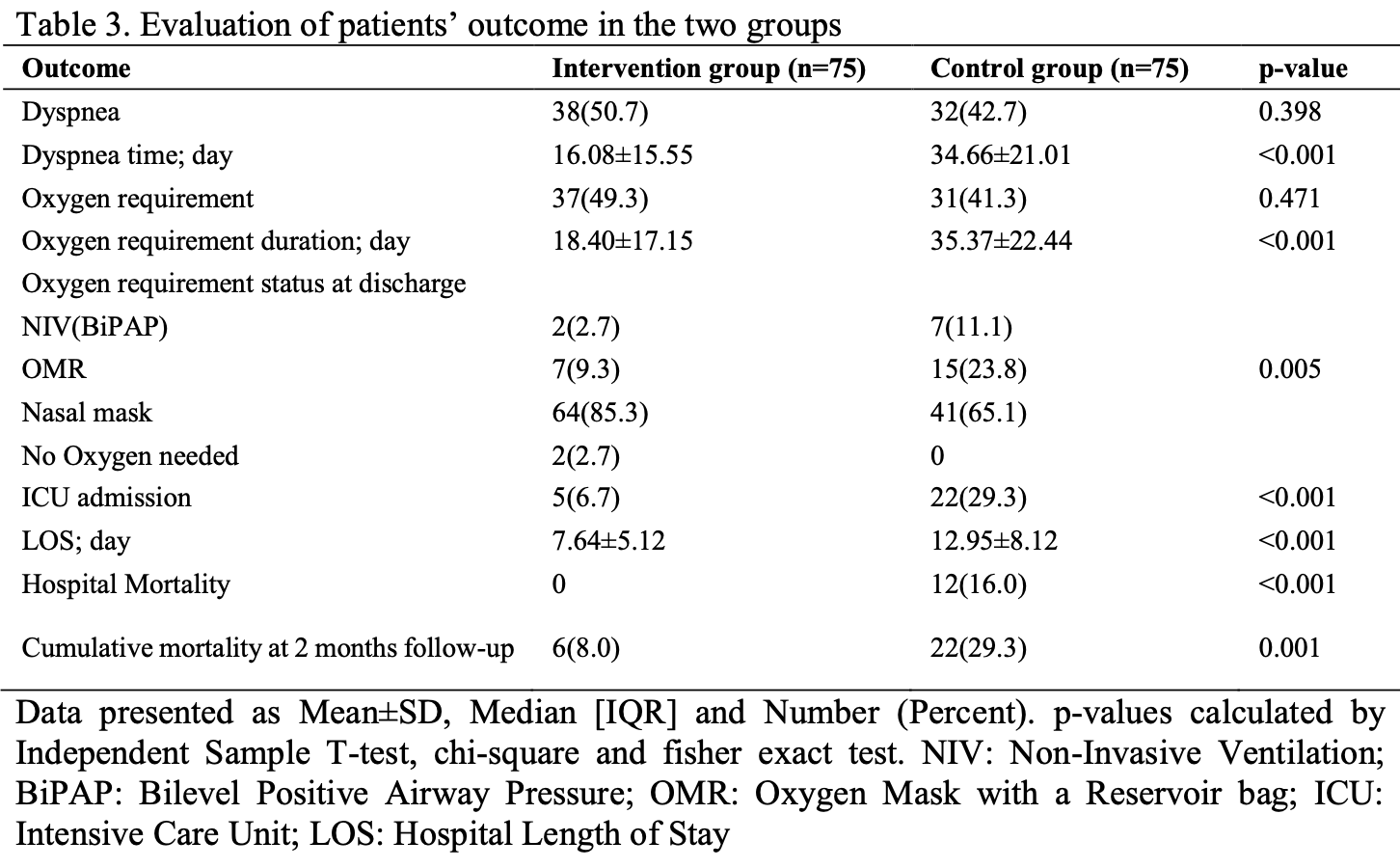
risk of death, 72.7% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.001, treatment 6 of 75 (8.0%), control 22 of 75 (29.3%), NNT 4.7, day 60.
|
|
risk of death, 96.0% lower, RR 0.04, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 75 (0.0%), control 12 of 75 (16.0%), NNT 6.2, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), in hospital.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 77.3% lower, RR 0.23, p < 0.001, treatment 5 of 75 (6.7%), control 22 of 75 (29.3%), NNT 4.4, day 60.
|
|
hospitalization time, 41.0% lower, relative time 0.59, p < 0.001, treatment mean 7.64 (±5.12) n=75, control mean 12.95 (±8.12) n=75.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sebghatollahi et al., 22 Jul 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period September 2021 - April 2022, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with colchicum autumnal, olea europaea, lavandula angustifolia, and zingiber officinale roscoe) - results of individual treatments may vary.
The adjuvant therapy of edible herbal product including colchicum bulb, olive leaf, black cumin seeds, lavender flower, and ginger rhizome on the outcome of patients with severe and critical COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial
Objective: The present study aimed at evaluating the effect of combination of medicinal plants, including Colchicum autumnal L., Olea europaea L., Nigella sativa L., Lavandula angustifolia L., and Zingiber officinale Roscoe, on the recovery and outcome of COVID-19 patients. Materials and Methods: This study was conducted on 150 COVID-19 patients. All patients received both pharmaceutical and supportive treatments. In addition to the standard care treatment, intervention group received two capsules of herbal medicine orally every 8 hours, while control group received placebo. Results: Oxygen saturation percentage (SpO2) of the intervention group (median:88.00) was significantly higher than that of the control group (median:86.00), while C-reactive protein (CRP) of the intervention group (median:20.00) was significantly lower than that of the control group (median:28.00) at the time of hospital discharge (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The combination of studied medicinal plants could significantly reduce the oxygen requirement and oxygen therapy.
Conflicts of interest The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
References
Abbasnezhad, Niazmand, Mahmoudabady, Rezaee, Soukhtanloo et al., Nigella sativa L. seed regulated eNOS, VCAM-1 and LOX-1 genes expression and improved vasoreactivity in aorta of diabetic rat, J Ethnopharmacol
Abdelgawad, Hassab, Abourehab, Elkaeed, Eldehna, Olive leaves as a potential phytotherapy in the treatment of COVID-19 disease; a minireview, Front Pharmacol
Ahmad, Rehman, Ahmad, Alkharfy, Covid-19 and thymoquinone: connecting the dots, Phytother Res
Ahmadi, Nasr-Esfahani, Meibody, Ebrahimi, Maghami-Mehr, COVID-19 management in the emergency ward, J Res Med Sci
Ballabeni, Tognolini, Chiavarini, Impicciatore, Bruni et al., Novel antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of essential oil from lavandula hybrida Reverchon "grosso, Phytomedicine
Basch, Foppa, Liebowitz, Nelson, Smith et al., Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia miller), J Herb Pharmacother
Bordoni, Fedeli, Nasuti, Maggi, Papa et al., Antioxidant and antiinflammatory properties of Nigella sativa oil in human pre-adipocytes, antioxidants
Borges, José, Homem, Simões, Comparison of techniques and solvents on the antimicrobial and antioxidant Potential of extracts from acacia dealbata and onnnlea europaea, Antibiotics
Cavanagh, Wilkinson, Biological activities of lavender essential oil, Phytother Res
Hajhashemi, Ghannadi, Jafarabadi, Black cumin seed essential oil, as a potent analgesic and antiinflammatory drug, Phytother Res
Hashem-Dabaghian, Azimi, Bahrami, Latifi, Enayati et al., Effect of lavender (Lavandula angustifolia L.) syrup on olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 infection: A pilot controlled clinical trial, Avicenna J Phytomed
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol
Idm'hand, Msanda, Cherifi, Ethnopharmacological review of medicinal plants used to manage diabetes in morocco, Clinical Phytoscience
Khazdair, Ghafari, Sadeghi, Possible therapeutic effects of Nigella sativa and its thymoquinone on COVID-19, Pharm Biol
Khazdair, The protective effects of nigella sativa and Its constituents on induced neurotoxicity, J Toxicol
Koshak, Koshak, Mobeireek, Badawi, Wali et al., Nigella sativa supplementation to treat symptomatic mild COVID-19: A structured summary of a protocol for a randomised, controlled, clinical trial, Trials
Koshak, Koshak, Nigella sativa L as a potential phytotherapy for coronavirus disease 2019: a mini review of in silico studies, Curr Ther Res Clin Exp
Liao, Leu, Chan, Kuo, Wu, Anti-platelet aggregation and vasorelaxing effects of the constituents of the rhizomes of zingiber officinale, Molecules
Lockyer, Corona, Yaqoob, Spencer, Rowland, Secoiridoids delivered as olive leaf extract induce acute improvements in human vascular function and reduction of an inflammatory cytokine: a randomised, double-blind, placebocontrolled, cross-over trial, Br J Nutr
Mani, Johnson, Steel, Broszczak, Neilsen et al., Natural product-derived phytochemicals as potential agents against coronaviruses: A review, Virus Res
Moghadam Fard, Ketabchi, Farjam, Phytochemical analysis of Essential oil from the seed of nicotiana rustica and its antioxidant and antimicrobial activity, JMPB
Montealegre-Gómez, Garavito, Gómez-López, Rojas-Villarraga, Parra-Medina, Colchicine: a potential therapeutic tool against COVID-19. experience of 5 patients, Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed)
Nadjib, Effective antiviral activity of essential oils and their characteristic terpenes against coronaviruses: an update, J Pharmacol Clin Toxicol
Omar, Oleuropein in olive and its pharmacological effects, Sci Pharm
Papadopoulos, Patoulias, Teperikidis, Mouselimis, Tsarouchas et al., Colchicine as a potential therapeutic agent against cardiovascular complications of COVID-19: an exploratory review, SN Compr Clin Med
Rathinavel, Palanisamy, Palanisamy, Subramanian, Thangaswamy, Phytochemical 6-Gingerol: A promising drug of choice for COVID-19, IJASE
Reichling, Schnitzler, Suschke, Saller, Essential oils of aromatic plants with antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and cytotoxic properties--an overview, Forsch Komplementmed
Reyes, Hu, Teperman, Wampler Muskardin, Tardif et al., Anti-inflammatory therapy for COVID-19 infection: the case for Colchicine, Ann Rheum Dis
Sandhu, Tieng, Chilimuri, Franchin, A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol
Scarsi, Piantoni, Colombo, Airó, Richini et al., Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Rheum Dis
Schlesinger, Firestein, Brunetti, Colchicine in COVID-19: an old drug, new use, Curr Pharmacol Rep
Shahidi, Vahdat, Atapour, Reisizadeh, Soltaninejad et al., The clinical course and risk factors in COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury, J Family Med Prim Care
Tavakoli, Aryaeian, A review of the effect of ginger in inflammation, RSJ
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22038/ajp.2024.24633",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22038/ajp.2024.24633",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1098-2074",
"family": "Sebghatollahi",
"given": "Vahid"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0590-6410",
"family": "Siavash Dastjerdi",
"given": "Mansour"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3202-7043",
"family": "Ghiasi",
"given": "Farzin"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3236-1970",
"family": "Alikiaii",
"given": "Babak"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1946-2953",
"family": "Pourahmad",
"given": "Morteza"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9094-8943",
"family": "Yegdaneh",
"given": "Afsaneh"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5777-9612",
"family": "Akbari",
"given": "Mojtaba"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3090-8365",
"family": "Ghadiri",
"given": "Reza"
}
],
"container-title": "Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine",
"container-title-short": "Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine",
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
},
"journalAbbreviation": "Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine",
"language": "eng",
"publisher": "Mashhad University of Medical Sciences",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "The adjuvant therapy of edible herbal product including colchicum bulb olive leaf black cumin seeds lavender flower and ginger rhizome on the outcome of patients with severe and critical COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial",
"type": "article-journal",
"volume": "14"
}