Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Nitazoxanide (NTZ) for Pre- and Post Exposure Prophylaxis of COVID-19 and Other Viral Respiratory Illnesses (VRI) in Healthcare Workers and Others at Increased Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
, NCT04359680, NCT04359680, Jun 2024
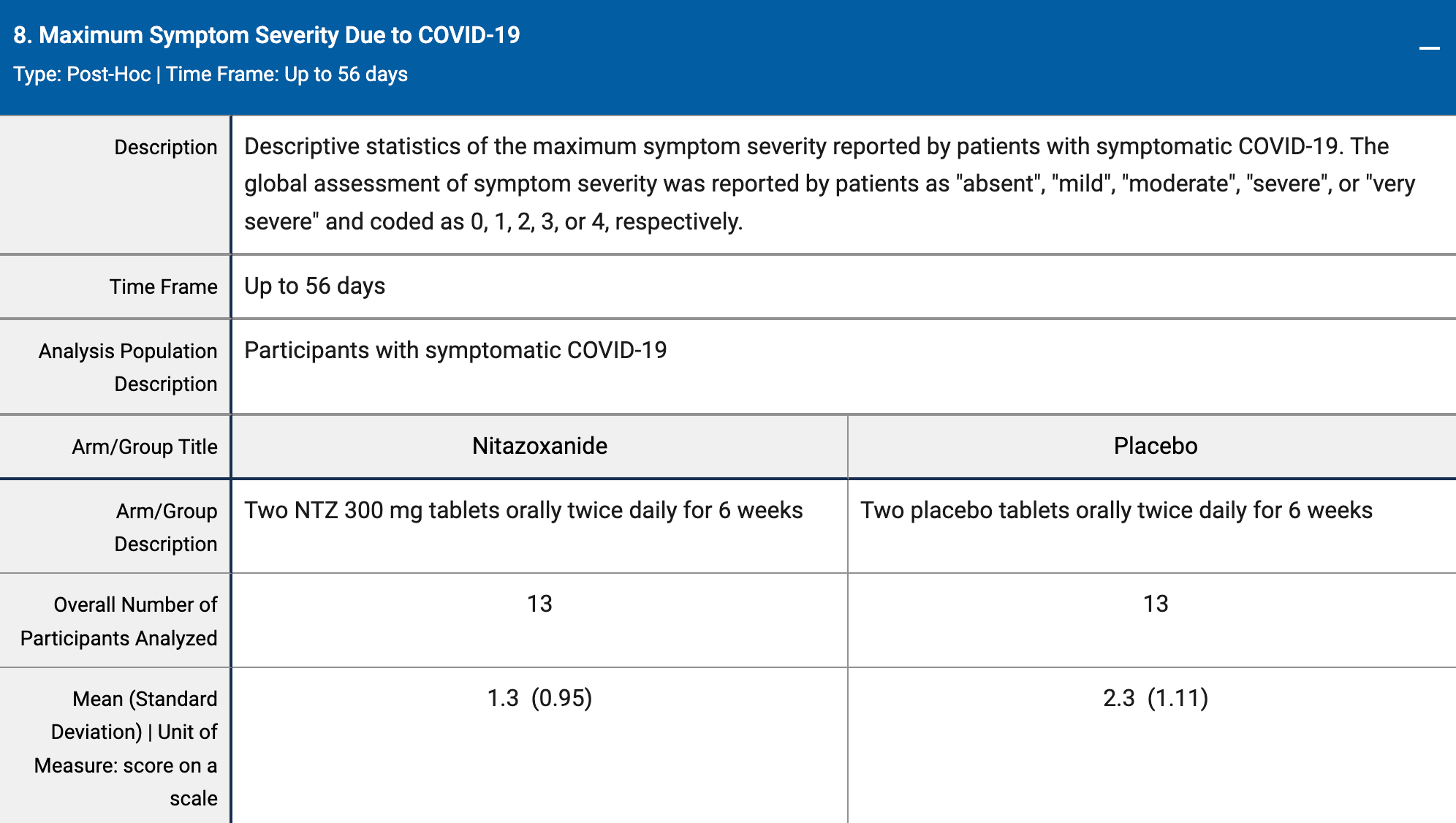
RCT 1,407 healthcare workers and others at high risk of SARS-CoV-2 exposure, showing no difference in COVID-19 cases (13 in each group). There was lower symptom severity for nitazoxanide and a trend towards shorter illness duration. There is no publication, results are only available on clinicaltrials.gov, posted 3 years after completion (FDA pre-notice of noncompliance1).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of progression, 43.5% lower, RR 0.57, p = 0.02, treatment mean 1.3 (±0.95) n=13, control mean 2.3 (±1.11) n=13.
|
|
time to perform usual activities, 50.3% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.10, treatment mean 8.2 (±11.73) n=13, control mean 16.5 (±12.72) n=13.
|
|
time to usual health, 32.3% lower, RR 0.68, p = 0.32, treatment mean 13.2 (±16.88) n=13, control mean 19.5 (±14.58) n=13.
|
|
acute respiratory illness time, 27.5% lower, RR 0.72, p = 0.49, treatment mean 10.0 (±15.52) n=13, control mean 13.8 (±12.05) n=13.
|
|
risk of case, 2.5% lower, RR 0.97, p = 1.00, treatment 13 of 629 (2.1%), control 13 of 613 (2.1%), NNT 1854.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Romark et al., 26 Jun 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, preprint, 1 author, trial NCT04359680 (history).