Non-effectiveness of Ivermectin on Inpatients and Outpatients With COVID-19; Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.919708, IRCT20111224008507N5, Jun 2022
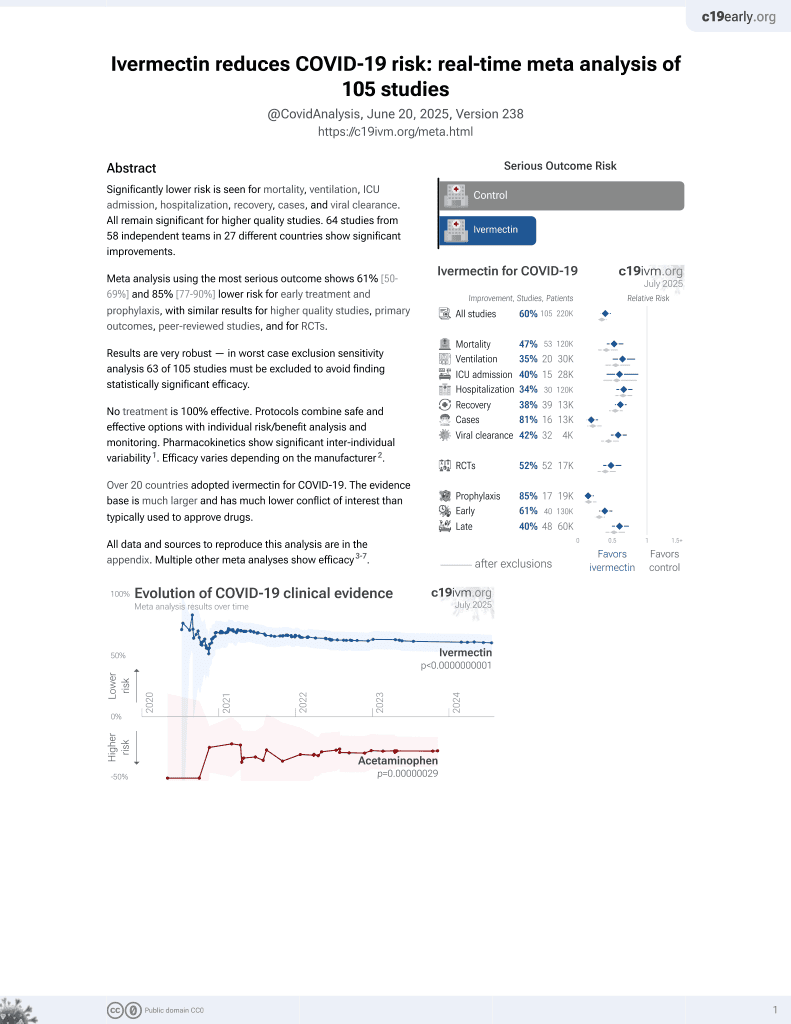
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 609 inpatients in Iran. Reported outcomes are very different from the pre-specified outcomes1. The outpatient trial is listed separately.
From the pre-specified outcomes, all are either positive or not reported. Pre-specified outcomes:
- Reduction in persistent cough - RR 0.36 p = 0.06
- Negative RT-PCR - not reported
- Main complaints recovery time - not reported
- Mortality - RR 0.69 p = 0.36
- Side effects - reported as none (anomalous)
- Reduction in tachypnea - RR 0.24 p = 0.38
- Oxygen saturation >94% - not reported
- Negative RT-PCR - not reported
- Main complaints recovery time - not reported
- Mortality - RR 0.69 p = 0.36
- Side effects - reported as none (anomalous)
- Reduction in tachypnea - RR 0.24 p = 0.38
- Oxygen saturation >94% - not reported
All negative outcomes are protocol violations and are not listed in the protocol, including the novel "relative recovery" outcome.
Authors include a researcher caught on video admitting that conclusions on ivermectin research were influenced by a funder2.
Severe cases were more frequent in the ivermectin group, 49% vs. 43%.
Dose was limited at a maximum of 30mg for 75+kg, resulting in underdosing for patients at higher risk.
Almost all patients received remdesivir, most patients received famotidine and vitamin C, and many patients received vitamin D, metformin, and zinc, limiting room for improvement.
32% of patients were lost to followup. Authors indicate bottles were identical, but tablets were only similar. Ivermectin was obtained from Alborz Daru Co.
This is the 37th of 53 COVID-19 RCTs for ivermectin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000087.
This is the 86th of 106 COVID-19 controlled studies for ivermectin, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
multiple critical issues, see study page.
|
risk of death, 30.8% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.36, treatment 13 of 311 (4.2%), control 18 of 298 (6.0%), NNT 54.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.07, treatment 311, control 298.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 16.0% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.47, treatment 311, control 298.
|
|
hospitalization time, 11.5% higher, relative time 1.11, p = 0.009, treatment mean 7.98 (±4.4) n=311, control mean 7.16 (±3.2) n=298.
|
|
deterioration, 12.7% higher, RR 1.13, p = 0.74, treatment 20 of 311 (6.4%), control 17 of 298 (5.7%).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 24.2% lower, RR 0.76, p = 0.02, treatment 311, control 298, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, post-hoc primary outcome.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 64.0% lower, RR 0.36, p = 0.06, treatment 5 of 145 (3.4%), control 10 of 105 (9.5%), NNT 16, day 7, cough.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 76.0% lower, RR 0.24, p = 0.38, day 7, tachypnea.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rezai et al., 16 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 53.8, 29 authors, study period 19 February, 2021 - 14 August, 2021, average treatment delay 7.18 days, dosage 400μg/kg days 1-3, trial IRCT20111224008507N5.
Contact: drmsrezaii@yahoo.com.
Non-effectiveness of Ivermectin on Inpatients and Outpatients With COVID-19; Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.919708
Background: Ivermectin which was widely considered as a potential treatment for COVID-19, showed uncertain clinical benefit in many clinical trials. Performing largescale clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness of this drug in the midst of the pandemic, while difficult, has been urgently needed. Methods: We performed two large multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of ivermectin in treating inpatients and outpatients with COVID-19 infection. The intervention group received ivermectin, 0.4mg/kg of body weight per day for 3 days. In the control group, placebo tablets were used for 3 days. Results: Data for 609 inpatients and 549 outpatients were analyzed. In hospitalized patients, complete recovery was significantly higher in the ivermectin group (37%) compared to placebo group (28%; RR, 1.32 [95% CI, 1.04-1.66]; p-value = 0.02). On the other hand, the length of hospital stay was significantly longer in the ivermectin group with a mean of 7.98 ± 4.4 days compared to the placebo receiving group with a mean of 7.16 ± 3.2 days (RR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.15-1.45]; p-value = 0.02). In outpatients, the
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (IR.MAZUMS.REC.1399.915 and IR.MAZUMS.REC.1399.869) and by the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials identifier (IRCT20111224008507N5 and IRCT20111224008507N4). Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants or their legal guardian/next of kin.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS MR contributed to the conception or design of the work. MR, FA, AHi, LE, and MMi contributed to the drafting and statistical analysis of the manuscript. All authors contributed toward the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data, critical revision of the manuscript, review and approval of the final version of the manuscript.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed. 2022.919708/full#supplementary-material
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not..
References
Abdelrahman, Li, Wang, Comparative review of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and influenza a respiratory viruses, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.552909
Andrade, Rangel, Santos, Freitas, Soares et al., Repurposing approved drugs for guiding Covid-19 prophylaxis: a systematic review, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.590598
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Scott et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of Covid-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, Am J Therap, doi:10.1097/mjt.0000000000001402
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antivir Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787
Campbell, Fisher, Stapley, Albers-Schönberg, Jacob, Ivermectin: a potent new antiparasitic agent, Science, doi:10.1126/science.6308762
Chaccour, Casellas, Blanco-Di Matteo, Pineda, Fernandez-Montero et al., The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe Covid-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720
Chowdhury, Shahbaz, Karim, Islam, Guo et al., A comparative study on ivermectin-doxycycline and hydroxychloroquineazithromycin therapy on COVID-19 patients, EJMO, doi:10.14744/ejmo.2021.16263
Clark, Jit, Warren-Gash, Guthrie, Wang et al., Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe Covid-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study, Lancet Glob Health, doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30264-3
Crump, Ômura, Ivermectin, 'wonder drug' from Japan: the human use perspective, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, doi:10.2183/pjab.87.13
Cusinato, Cau, Calvani, Mori, Repurposing drugs for the management of Covid-19, Exp Opin Ther Patents, doi:10.1080/13543776.2021.1861248
Datry, Hilmarsdottir, Mayorga-Sagastume, Lyagoubi, Gaxotte et al., Treatment of strongyloides stercoralis infection with ivermectin compared with albendazole: results of an open study of 60 cases, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.1016/0035-9203(94)90110-4
Edwards, Ivermectin: does P-glycoprotein play a role in neurotoxicity?, Filaria J, doi:10.1186/1475-2883-2-s1-s8
Farne, Kumar, Ritchie, Finney, Johnston et al., Repurposing existing drugs for the treatment of Covid-19, Ann Am Thorac Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-566FR
Hill, Garratt, Levi, Falconer, Ellis et al., Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab358
Juarez, Schcolnik-Cabrera, Dueñas-Gonzalez, The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug, Am J Cancer Res
Karale, Bansal, Makadia, Tayyeb, Khan et al., A meta-analysis of mortality, need for ICU admission, use of mechanical ventilation and adverse effects with ivermectin use in Covid-19 patients, doi:10.1101/2021.04.30.21256415
Khodavirdipour, Asadimanesh, Masoumi, Impact of SARS-CoV-2 genetic blueprints on the oral manifestation of Covid-19: a case report, Glob Med Genet, doi:10.1055/s-0041-1735538
Khodavirdipour, Chamanrokh, Alikhani, Alikhani, Potential of Bacillus Subtilis against SARS-CoV-2 -a sustainable drug development perspective, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.718786
Khodavirdipour, Inclusion of cephalexin in Covid-19 treatment combinations may prevent lung involvement in mild infections: a case report with pharmacological genomics perspective, Glob Med Genet, doi:10.1055/s-0041-1726461
Khodavirdipour, Jabbari, Keramat, Alikhani, Concise update on genomics of Covid-19: approach to its latest mutations, escalated contagiousness, and vaccine resistance, Glob Med Genet, doi:10.1055/s-0041-1725143
Khodavirdipour, Keramat, Hashemi, Alikhani, Sars-Cov-2; from vaccine development to drug discovery and prevention guidelines, AIMS Mol Sci, doi:10.3934/molsci.2020013
Khodavirdipour, Piri, Jabbari, Khalaj-Kondori, Potential of CRISPR/CAS13 system in treatment and diagnosis of Covid-19, Glob Med Genet, doi:10.1055/s-0041-1723086
Krolewiecki, Lifschitz, Moragas, Travacio, Valentini et al., Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with Covid-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959
Low, Yip, Lal, Repositioning ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis
López-Medina, López, Hurtado, Dávalos, Ramirez et al., Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild Covid-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3071
Mohan, Tiwari, Suri, Mittal, Patel et al., Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial, J Infect Chemother, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021
Muñoz, Ballester, Antonijoan, Gich, Rodríguez et al., Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of fixed-dose ivermectin with an innovative 18mg tablet in healthy adult volunteers, PLoS Negl Trop Dis, doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0006020
Ozer, Goksu, Ulker, Balderas, Mahdi, Effectiveness and safety of ivermectin in Covid-19 patients: a prospective study at a safety-net hospital, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27469
Podder, Chowdhury, Sina, Haque, Outcome of ivermectin treated mild to moderate covid-19 cases: a single-centre, open-label, randomised controlled study, IMC J Med Sci
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the ivermectin in Covid Nineteen study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009
Roman, Burela, Pasupuleti, Piscoya, Vidal et al., Ivermectin for the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595
Sajid, Iqbal, Muhammad, Iqbal, Immunomodulatory effect of various anti-parasitics: a review, Parasitology, doi:10.1017/s0031182005009108
Senanayake, Drug repurposing strategies for Covid-19, Future Drug Discov, doi:10.4155/fdd-2020-0010
Shahbaznejad, Davoudi, Eslami, Markowitz, Navaeifar et al., Effects of ivermectin in patients with Covid-19: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial, Clin Therap, doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007
Singh, Parida, Lingaraju, Kesavan, Kumar et al., Drug repurposing approach to fight Covid-19, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00155-6
Singh, Sheth, Dhaneria, Gupta, Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for Covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Asian Pac J Trop Med, doi:10.4103/1995-7645.327070
Temple, Hoang, Hendrickson, Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmc2114907
Vallejos, Zoni, Bangher, Villamandos, Bobadilla et al., Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with Covid-19 (Ivercor-Covid19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5
Venkatesan, Repurposing drugs for treatment of Covid-19, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00270-8
Wouters, Shadlen, Salcher-Konrad, Pollard, Larson et al., Challenges in ensuring global access to Covid-19 vaccines: production, affordability, allocation, and deployment, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00306-8
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Ômura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in Covid-19, Jpn J Antibiot
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2-an extensive review, J Antibiot, doi:10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6
Zhang, Song, Xiong, Ci, Li et al., Inhibitory effects of ivermectin on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-stimulated raw 264.7 macrophages, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.016
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2022.919708",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.919708",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Ivermectin which was widely considered as a potential treatment for COVID-19, showed uncertain clinical benefit in many clinical trials. Performing large-scale clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness of this drug in the midst of the pandemic, while difficult, has been urgently needed.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We performed two large multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of ivermectin in treating inpatients and outpatients with COVID-19 infection. The intervention group received ivermectin, 0.4mg/kg of body weight per day for 3 days. In the control group, placebo tablets were used for 3 days.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Data for 609 inpatients and 549 outpatients were analyzed. In hospitalized patients, complete recovery was significantly higher in the ivermectin group (37%) compared to placebo group (28%; RR, 1.32 [95% CI, 1.04–1.66]; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.02). On the other hand, the length of hospital stay was significantly longer in the ivermectin group with a mean of 7.98 ± 4.4 days compared to the placebo receiving group with a mean of 7.16 ± 3.2 days (RR, 0.80 [95% CI, 0.15–1.45]; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.02). In outpatients, the mean duration of fever was significantly shorter (2.02 ± 0.11 days) in the ivermectin group versus (2.41 ± 0.13 days) placebo group with <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> value = 0.020. On the day seventh of treatment, fever (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.040), cough (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.019), and weakness (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.002) were significantly higher in the placebo group compared to the ivermectin group. Among all outpatients, 7% in ivermectin group and 5% in placebo group needed to be hospitalized (RR, 1.36 [95% CI, 0.65–2.84]; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.41). Also, the result of RT-PCR on day five after treatment was negative for 26% of patients in the ivermectin group versus 32% in the placebo group (RR, 0.81 [95% CI, 0.60–1.09]; <jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value = 0.16).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Our data showed, ivermectin, compared with placebo, did not have a significant potential effect on clinical improvement, reduced admission in ICU, need for invasive ventilation, and death in hospitalized patients; likewise, no evidence was found to support the prescription of ivermectin on recovery, reduced hospitalization and increased negative RT-PCR assay for SARS-CoV-2 5 days after treatment in outpatients. Our findings do not support the use of ivermectin to treat mild to severe forms of COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Clinical Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link>www.irct.ir</jats:ext-link> IRCT20111224008507N5 and IRCT20111224008507N4.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2022.919708"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rezai",
"given": "Mohammad Sadegh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahangarkani",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Leah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirchandani",
"given": "Manya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davoudi",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eslami",
"given": "Gohar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roozbeh",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babamahmoodi",
"given": "Farhang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rouhani",
"given": "Nima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alikhani",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Najafi",
"given": "Narges",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghasemian",
"given": "Roya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehravaran",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajialibeig",
"given": "Azin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Navaeifar",
"given": "Mohammad Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahbaznejad",
"given": "Leila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimzadeh",
"given": "Golnar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saeedi",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh-Navai",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moosazadeh",
"given": "Mahmood",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saeedi",
"given": "Shahab",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Razavi-Amoli",
"given": "Seyedeh-Kiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rezai",
"given": "Shaghayegh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rostami-Maskopaee",
"given": "Fereshteh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosseinzadeh",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Movahedi",
"given": "Faezeh Sadat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Markowitz",
"given": "John S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valadan",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-16T10:22:55Z",
"timestamp": 1655374975000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-16T10:23:06Z",
"timestamp": 1655374986000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-16T10:43:09Z",
"timestamp": 1655376189005
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655337600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.919708/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2214-109x(20)30264-3",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national estimates of the population at increased risk of severe Covid-19 due to underlying health conditions in 2020: a modelling study.",
"author": "Clark",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1003",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.552909",
"article-title": "Comparative review of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and influenza a respiratory viruses.",
"author": "Abdelrahman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "552909",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3934/molsci.2020013",
"article-title": "Sars-Cov-2; from vaccine development to drug discovery and prevention guidelines.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "AIMS Mol Sci.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00306-8",
"article-title": "Challenges in ensuring global access to Covid-19 vaccines: production, affordability, allocation, and deployment.",
"author": "Wouters",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1023",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England).",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0041-1725143",
"article-title": "Concise update on genomics of Covid-19: approach to its latest mutations, escalated contagiousness, and vaccine resistance.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Glob Med Genet.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(21)00270-8",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for treatment of Covid-19.",
"author": "Venkatesan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e63",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.590598",
"article-title": "Repurposing approved drugs for guiding Covid-19 prophylaxis: a systematic review.",
"author": "Andrade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "590598",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-566FR",
"article-title": "Repurposing existing drugs for the treatment of Covid-19.",
"author": "Farne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"journal-title": "Ann Am Thorac Soc.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0041-1723086",
"article-title": "Potential of CRISPR/CAS13 system in treatment and diagnosis of Covid-19.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Glob Med Genet.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4155/fdd-2020-0010",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing strategies for Covid-19.",
"author": "Senanayake",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Future Drug Discov.",
"key": "B10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00155-6",
"article-title": "Drug repurposing approach to fight Covid-19.",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1479",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.718786",
"article-title": "Potential of Bacillus Subtilis against SARS-CoV-2 – a sustainable drug development perspective.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "718786",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13543776.2021.1861248",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for the management of Covid-19.",
"author": "Cusinato",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Exp Opin Ther Patents.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0041-1726461",
"article-title": "Inclusion of cephalexin in Covid-19 treatment combinations may prevent lung involvement in mild infections: a case report with pharmacological genomics perspective.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "78",
"journal-title": "Glob Med Genet.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0041-1735538",
"article-title": "Impact of SARS-CoV-2 genetic blueprints on the oral manifestation of Covid-19: a case report.",
"author": "Khodavirdipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Glob Med Genet.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294",
"article-title": "Repositioning ivermectin for Covid-19 treatment: molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication.",
"author": "Low",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166294",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "1868",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug.",
"author": "Juarez",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Am J Cancer Res.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.6308762",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: a potent new antiparasitic agent.",
"author": "Campbell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "Science (New York, NY).",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "221",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0035-9203(94)90110-4",
"article-title": "Treatment of strongyloides stercoralis infection with ivermectin compared with albendazole: results of an open study of 60 cases.",
"author": "Datry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "88",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104787",
"article-title": "The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro.",
"author": "Caly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104787",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100720",
"article-title": "The effect of early treatment with ivermectin on viral load, symptoms and humoral response in patients with non-severe Covid-19: a pilot, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Chaccour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100720",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2008.12.016",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of ivermectin on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-stimulated raw 264.7 macrophages.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "354",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0031182005009108",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effect of various anti-parasitics: a review.",
"author": "Sajid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "301",
"journal-title": "Parasitology.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.87.13",
"article-title": "Ivermectin, ‘wonder drug’ from Japan: the human use perspective.",
"author": "Crump",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in Covid-19.",
"author": "Yagisawa",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Jpn J Antibiot.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/mjt.0000000000001402",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of Covid-19 infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines.",
"author": "Bryant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e434",
"journal-title": "Am J Therap.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1995-7645.327070",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of ivermectin for Covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "440",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Trop Med.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.04.007",
"article-title": "Effects of ivermectin in patients with Covid-19: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial.",
"author": "Shahbaznejad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1007",
"journal-title": "Clin Therap.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41429-021-00491-6",
"article-title": "The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2-an extensive review.",
"author": "Zaidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "60",
"journal-title": "J Antibiot.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab358",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of randomized trials of ivermectin to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Hill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofab358",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.10.009",
"article-title": "Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019: the ivermectin in Covid Nineteen study.",
"author": "Rajter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Chest.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.04.30.21256415",
"article-title": "A meta-analysis of mortality, need for ICU admission, use of mechanical ventilation and adverse effects with ivermectin use in Covid-19 patients.",
"author": "Karale",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "B32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27469",
"article-title": "Effectiveness and safety of ivermectin in Covid-19 patients: a prospective study at a safety-net hospital.",
"author": "Ozer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.3071",
"article-title": "Effect of ivermectin on time to resolution of symptoms among adults with mild Covid-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "López-Medina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1426",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.21.21257595",
"article-title": "Ivermectin for the treatment of Covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.",
"author": "Roman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "B35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100959",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of high-dose ivermectin in adults with Covid-19: a proof-of-concept randomized trial.",
"author": "Krolewiecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100959",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pntd.0006020",
"article-title": "Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of fixed-dose ivermectin with an innovative 18mg tablet in healthy adult volunteers.",
"author": "Muñoz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0006020",
"journal-title": "PLoS Negl Trop Dis.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3329/imcjms.v14i2.52826",
"article-title": "Outcome of ivermectin treated mild to moderate covid-19 cases: a single-centre, open-label, randomised controlled study.",
"author": "Podder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "IMC J Med Sci.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14744/ejmo.2021.16263",
"article-title": "A comparative study on ivermectin-doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine-azithromycin therapy on COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Chowdhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "63",
"journal-title": "EJMO",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06348-5",
"article-title": "Ivermectin to prevent hospitalizations in patients with Covid-19 (Ivercor-Covid19) a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Vallejos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "635",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1475-2883-2-s1-s8",
"article-title": "Ivermectin: does P-glycoprotein play a role in neurotoxicity?",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Filaria J.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmc2114907",
"article-title": "Toxic effects from ivermectin use associated with prevention and treatment of Covid-19.",
"author": "Temple",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2197",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.021",
"article-title": "Single-dose oral ivermectin in mild and moderate COVID-19 (RIVET-COV): A single-centre randomized, placebo-controlled trial.",
"author": "Mohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1743",
"journal-title": "J Infect Chemother.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2022.919708/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Non-effectiveness of Ivermectin on Inpatients and Outpatients With COVID-19; Results of Two Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "9"
}