Comparative Analysis of Serum Zinc, Copper and Magnesium Level and Their Relations in Association with Severity and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Patients
et al., Biological Trace Element Research, doi:10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7, Jan 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
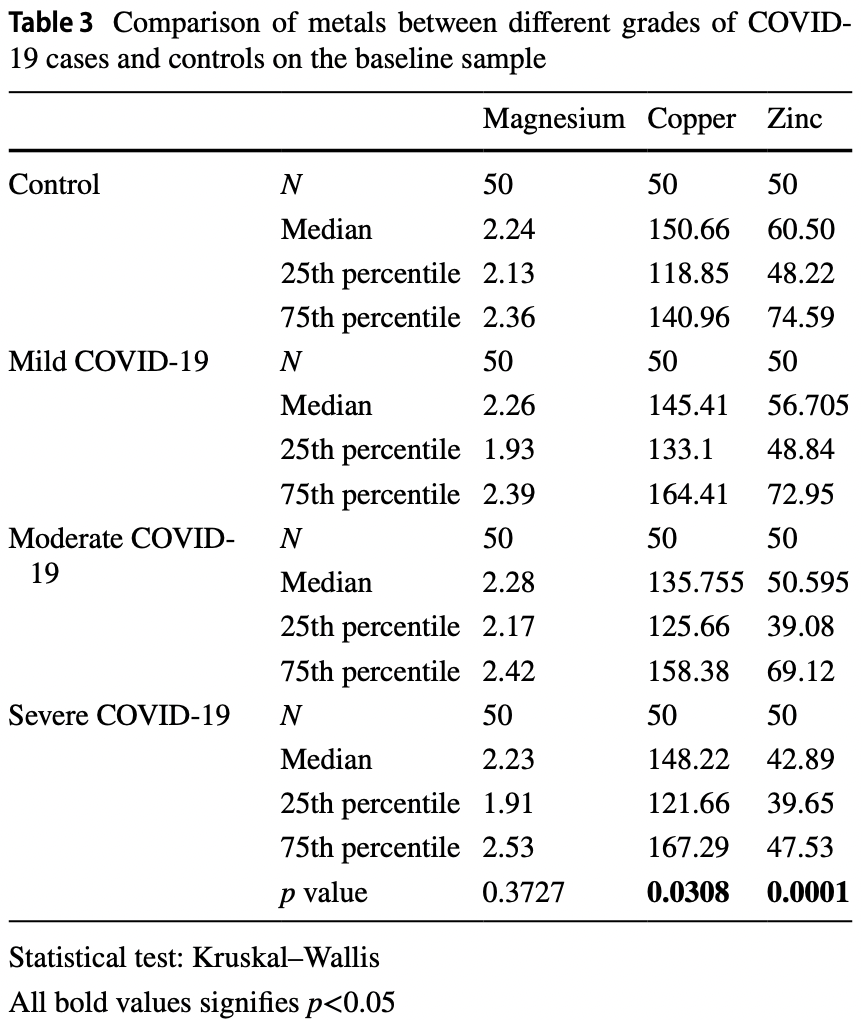
Analysis of 150 COVID+ hospitalized patients in India, showing lower zinc levels associated with higher severity.
PVSN et al., 22 Jan 2022, India, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Comparative Analysis of Serum Zinc, Copper and Magnesium Level and Their Relations in Association with Severity and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Patients
Biological Trace Element Research, doi:10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7
The deficiencies of trace elements and infectious diseases often coexist and exhibit complex interactions. Several trace elements such as zinc (Zn), copper (Cu) and magnesium (Mg) have immunomodulatory functions and thus influence the susceptibility to the course and outcome of a variety of viral infections. So, this present study was aimed to study relations of trace metals in association with severity and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 patients. A total of 150 individuals infected with COVID-19 and 50 healthy individuals were recruited. Cases were divided based on severity (mild, moderate and severe) and outcome (discharged or deceased). Serum Zn, Mg and Cu levels were analysed by direct colourimetric method. Both serum Cu and Zn levels were significantly decreased in cases when compared to those in controls (p < 0.005 and p < 0.0001). Serum magnesium levels although not significant were found to be slightly decreased in controls. On comparing the trace elements between the deceased and discharged cases, a significant difference was found between serum copper and zinc levels, but for magnesium, both groups have similar levels. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve results indicate that a serum Cu/Zn ratio along with the age of patient provides some reliable information on COVID-19 course and survival odds by yielding an AUC of 95.1% with a sensitivity of 93.8% and specificity of 89.8%. Therefore, we would like to emphasize that measuring the serum copper and zinc along with their ratio can be used as routine investigations for COVID-19 patients in proper identification and management of severe cases in upcoming new waves of COVID-19.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s12011-022-03124-7.
Author Contribution
Declarations Ethics Approval This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the institutional ethics committee.
Consent to Participate All participants has freely given informed consent to participate in the study.
Competing Interests The authors declare no competing interests. Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Anuk, Polat, Akdas, The relation between trace element status (zinc, copper, magnesium) and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infection during pregnancy, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02496-y
Arrieta, Martinez-Vaello, Bengoa, Serum zinc and copper in people with COVID-19 and zinc supplementation in parenteral nutrition, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111467
Bahrami, Arabestani, Taheri, Exploring the role of heavy metals and their derivatives on the pathophysiology of COVID-19, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02893-x
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.001250
Chang, Lin, Wei, Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus infections involving 13 patients outside Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1623
Chen, Li, Zhang, Association of serum trace elements with schizophrenia and effects of antipsychotic treatment, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-017-1039-6
Dharmalingam, Birdi, Tomo, Trace elements as immunoregulators in SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections, Indian J Clin Biochem IJCB, doi:10.1007/s12291-021-00961-6
Diao, Han, Pang, HRCT imaging features in representative imported cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia, Precis Clin Med, doi:10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa004
Fakhrolmobasheri, Mazaheri-Tehrani, Kieliszek, COVID-19 and selenium deficiency: a systematic review, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02997-4
Finzi, Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: a report on four patients, Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006
Fooladi, Matin, Mahmoodpoor, Copper as a potential adjunct therapy for critically ill COVID-19 patients, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.022
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A review of micronutrients and the immune system-working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Hackler, Heller, Sun, Relation of serum copper status to survival in COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13061898
Heller, Sun, Hackler, Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764
Iotti, Wolf, Mazur, Maier, The COVID-19 pandemic: is there a role for magnesium? Hypotheses and perspectives, Magnes Res, doi:10.1684/mrh.2020.0465
Ishida, Antiviral activities of Cu2+ ions in viral prevention, replication, RNA degradation, and for antiviral efficacies of lytic virus, ROS-mediated virus, copper chelation, World Sci News
Johnson, Kehl-Fie, Klein, Role of copper efflux in pneumococcal pathogenesis and resistance to macrophage-mediated immune clearance, Infect Immun, doi:10.1128/IAI.03015-14
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Kanellopoulou, George, Masutani, Mg2+ regulation of kinase signaling and immune function, J Exp Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20181970
Laine, Tuomainen, Salonen, Virtanen, Serum copper-to-zinc-ratio and risk of incident infection in men: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study, Eur J Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-020-00644-1
Li, Gleason, Zhang, Candida albicans adapts to host copper during infection by swapping metal cofactors for superoxide dismutase, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.1513447112
Li, Gong, Wang, Clinical features of familial clustering in patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198043
Li, Li, Zhang, Wang, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x
Maggini, Pierre, Calder, Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10101531
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases, Transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007
Maier, Castiglioni, Locatelli, Magnesium and inflammation: advances and perspectives, Semin Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.002
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med, doi:10.1177/2050312121991246
Percival, Copper and immunity, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/67.5.1064S
Prasad, Zinc: role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283312956
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Adv Nutr Bethesda Md, doi:10.1093/advances/nmz013
Sagripanti, Routson, Lytle, Virus inactivation by copper or iron ions alone and in the presence of peroxide, Appl Environ Microbiol
Stanimirovic, Vujovic, Pejin, A contribution to the elemental profile of the leaf samples of newly developed Cabernet Franc varieties, Nat Prod Res, doi:10.1080/14786419.2018.1457671
Taheri, Bahrami, Habibi, Nouri, A review on the serum electrolytes and trace elements role in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02377-4
Tomo, Karli, Dharmalingam, The clinical laboratory: a key player in diagnosis and management of COVID-19, EJIFCC
Tomo, Kumar, Roy, Complement activation and coagulopathy -an ominous duo in COVID19, Expert Rev Hematol, doi:10.1080/17474086.2021.1875813
Van Doremalen, Bushmaker, Morris, Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2004973
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176
Yadav, Birdi, Tomo, Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: a cross-sectional study, Indian J Clin Biochem IJCB, doi:10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1
Yao, Paguio, Dee, The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study, Chest, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082
Yasui, Yasui, Suzuki, Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment -relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008
Ye, Li, Xiao, Zheng, Serum magnesium and fractional exhaled nitric oxide in relation to the severity in asthmachronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap, Biol Trace Elem Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-020-02314-5
Zeng, Yang, Yuan, Associations of essential and toxic metals/metalloids in whole blood with both disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19, FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol, doi:10.1096/fj.202002346RR
Zeng, Zhang, Wang, Urinary trace elements in association with disease severity and outcome in patients with COVID-19, Environ Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110670
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4984",
"1559-0720"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7",
"alternative-id": [
"3124"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "21 December 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "22 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics Approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the institutional ethics committee."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to Participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "All participants has freely given informed consent to participate in the study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing Interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "PVSN",
"given": "Kiran Kumar",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tomo",
"given": "Sojit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purohit",
"given": "Purvi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sankanagoudar",
"given": "Shrimanjunath",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charan",
"given": "Jayakaran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purohit",
"given": "Abhishek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nag",
"given": "Vijaylakshami",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhatia",
"given": "Pradeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Kuldeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dutt",
"given": "Naveen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Garg",
"given": "Mahendra Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Praveen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Misra",
"given": "Sanjeev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yadav",
"given": "Dharamveer",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Biological Trace Element Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T02:02:24Z",
"timestamp": 1642816944000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T06:48:41Z",
"timestamp": 1642834121000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100007338",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "All-India Institute of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T14:10:10Z",
"timestamp": 1642860610006
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0163-4984"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1559-0720"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642809600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642809600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12011-022-03124-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007",
"author": "C Magro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Res",
"key": "3124_CR1",
"unstructured": "Magro C, Mulvey JJ, Berlin D et al (2020) Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res 220:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1623",
"author": "D Chang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1092",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "3124_CR2",
"unstructured": "Chang D, Lin M, Wei L et al (2020) Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus infections involving 13 patients outside Wuhan, China. JAMA 323:1092–1093. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.1623",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198043",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "China Virus Res",
"key": "3124_CR3",
"unstructured": "Li J, Gong X, Wang Z et al (2020) Clinical features of familial clustering in patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Virus Res 286:198043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198043",
"volume": "286",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa004",
"author": "K Diao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Precis Clin Med",
"key": "3124_CR4",
"unstructured": "Diao K, Han P, Pang T et al (2020) HRCT imaging features in representative imported cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia. Precis Clin Med 3:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcmedi/pbaa004",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17474086.2021.1875813",
"author": "S Tomo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Hematol",
"key": "3124_CR5",
"unstructured": "Tomo S, Kumar KP, Roy D et al (2021) Complement activation and coagulopathy - an ominous duo in COVID19. Expert Rev Hematol 14:155–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474086.2021.1875813",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786419.2018.1457671",
"author": "B Stanimirovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1209",
"journal-title": "Nat Prod Res",
"key": "3124_CR6",
"unstructured": "Stanimirovic B, Vujovic D, Pejin B et al (2019) A contribution to the elemental profile of the leaf samples of newly developed Cabernet Franc varieties. Nat Prod Res 33:1209–1213. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1457671",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"author": "AF Gombart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E236",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "3124_CR7",
"unstructured": "Gombart AF, Pierre A, Maggini S (2020) A review of micronutrients and the immune system-working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection. Nutrients 12:E236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010236",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10101531",
"author": "S Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E1531",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "3124_CR8",
"unstructured": "Maggini S, Pierre A, Calder PC (2018) Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course. Nutrients 10:E1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101531",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1513447112",
"author": "CX Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E5336",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "3124_CR9",
"unstructured": "Li CX, Gleason JE, Zhang SX et al (2015) Candida albicans adapts to host copper during infection by swapping metal cofactors for superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E5336-5342. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1513447112",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/67.5.1064S",
"author": "SS Percival",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1064S",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "3124_CR10",
"unstructured": "Percival SS (1998) Copper and immunity. Am J Clin Nutr 67:1064S-1068S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/67.5.1064S",
"volume": "67",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aem.59.12.4374-4376.1993",
"author": "JL Sagripanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4374",
"journal-title": "Appl Environ Microbiol",
"key": "3124_CR11",
"unstructured": "Sagripanti JL, Routson LB, Lytle CD (1993) Virus inactivation by copper or iron ions alone and in the presence of peroxide. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:4374–4376",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"author": "T Ishida",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "World Sci News",
"key": "3124_CR12",
"unstructured": "Ishida T (2018) Antiviral activities of Cu2+ ions in viral prevention, replication, RNA degradation, and for antiviral efficacies of lytic virus, ROS-mediated virus, copper chelation. World Sci News 99:148–168",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2004973",
"author": "N van Doremalen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1564",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "3124_CR13",
"unstructured": "van Doremalen N, Bushmaker T, Morris DH et al (2020) Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med 382:1564–1567. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2004973",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283312956",
"author": "AS Prasad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "646",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care",
"key": "3124_CR14",
"unstructured": "Prasad AS (2009) Zinc: role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 12:646–652. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283312956",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"author": "SA Read",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "696",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr Bethesda Md",
"key": "3124_CR15",
"unstructured": "Read SA, Obeid S, Ahlenstiel C, Ahlenstiel G (2019) The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv Nutr Bethesda Md 10:696–710. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"author": "JS Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "3124_CR16",
"unstructured": "Yao JS, Paguio JA, Dee EC et al (2021) The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study. Chest 159:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"author": "AJW te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "3124_CR17",
"unstructured": "te Velthuis AJW, van den Worm SHE, Sims AC et al (2010) Zn(2+) inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture. PLoS Pathog 6:e1001176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"author": "E Finzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis",
"key": "3124_CR18",
"unstructured": "Finzi E (2020) Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 with high dose oral zinc salts: a report on four patients. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis 99:307–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.006",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20181970",
"author": "C Kanellopoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1828",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "3124_CR19",
"unstructured": "Kanellopoulou C, George AB, Masutani E et al (2019) Mg2+ regulation of kinase signaling and immune function. J Exp Med 216:1828–1842. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20181970",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02314-5",
"author": "M Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1771",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "3124_CR20",
"unstructured": "Ye M, Li Q, Xiao L, Zheng Z (2021) Serum magnesium and fractional exhaled nitric oxide in relation to the severity in asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:1771–1777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02314-5",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "S Tomo",
"first-page": "326",
"journal-title": "EJIFCC",
"key": "3124_CR21",
"unstructured": "Tomo S, Karli S, Dharmalingam K et al (2020) The clinical laboratory: a key player in diagnosis and management of COVID-19. EJIFCC 31:326–346",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02893-x",
"author": "A Bahrami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "3124_CR22",
"unstructured": "Bahrami A, Arabestani MR, Taheri M et al (2021) Exploring the role of heavy metals and their derivatives on the pathophysiology of COVID-19. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02893-x",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02997-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3124_CR23",
"unstructured": "Fakhrolmobasheri M, Mazaheri-Tehrani S, Kieliszek M, et al (2021) COVID-19 and selenium deficiency: a systematic review. Biol Trace Elem Res 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02997-4"
},
{
"key": "3124_CR24",
"unstructured": "Heavy metal content of a medicinal moss tea for hypertension - PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22236074/. Accessed 11 Jan 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3124_CR25",
"unstructured": "Yadav D, Birdi A, Tomo S, et al (2021) Association of vitamin D status with COVID-19 infection and mortality in the Asia Pacific region: a cross-sectional study. Indian J Clin Biochem IJCB 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-020-00950-1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12291-021-00961-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3124_CR26",
"unstructured": "Dharmalingam K, Birdi A, Tomo S, et al (2021) Trace elements as immunoregulators in SARS-CoV-2 and other viral infections. Indian J Clin Biochem IJCB 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-021-00961-6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02377-4",
"author": "M Taheri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2475",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "3124_CR27",
"unstructured": "Taheri M, Bahrami A, Habibi P, Nouri F (2021) A review on the serum electrolytes and trace elements role in the pathophysiology of COVID-19. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:2475–2481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02377-4",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"author": "M-Y Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Poverty",
"key": "3124_CR28",
"unstructured": "Li M-Y, Li L, Zhang Y, Wang X-S (2020) Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues. Infect Dis Poverty 9:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"author": "D Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis",
"key": "3124_CR29",
"unstructured": "Jothimani D, Kailasam E, Danielraj S et al (2020) COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis 100:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111467",
"author": "F Arrieta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "3124_CR30",
"unstructured": "Arrieta F, Martinez-Vaello V, Bengoa N et al (2021) Serum zinc and copper in people with COVID-19 and zinc supplementation in parenteral nutrition. Nutrition 91–92:111467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111467",
"volume": "91–92",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02496-y",
"author": "AT Anuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3608",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "3124_CR31",
"unstructured": "Anuk AT, Polat N, Akdas S et al (2021) The relation between trace element status (zinc, copper, magnesium) and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infection during pregnancy. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:3608–3617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02496-y",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"author": "PM Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1228",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol",
"key": "3124_CR32",
"unstructured": "Carlucci PM, Ahuja T, Petrilli C et al (2020) Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J Med Microbiol 69:1228–1234. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2050312121991246",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3124_CR33",
"unstructured": "Muhammad Y, Kani YA, Iliya S, et al (2021) Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: a cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria. SAGE Open Med 9:2050312121991246. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050312121991246"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110670",
"author": "H-L Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Environ Res",
"key": "3124_CR34",
"unstructured": "Zeng H-L, Zhang B, Wang X et al (2021) Urinary trace elements in association with disease severity and outcome in patients with COVID-19. Environ Res 194:110670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110670",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-017-1039-6",
"author": "X Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "3124_CR35",
"unstructured": "Chen X, Li Y, Zhang T et al (2018) Association of serum trace elements with schizophrenia and effects of antipsychotic treatment. Biol Trace Elem Res 181:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1039-6",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.03015-14",
"author": "MDL Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1684",
"journal-title": "Infect Immun",
"key": "3124_CR36",
"unstructured": "Johnson MDL, Kehl-Fie TE, Klein R et al (2015) Role of copper efflux in pneumococcal pathogenesis and resistance to macrophage-mediated immune clearance. Infect Immun 83:1684–1694. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.03015-14",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.022",
"author": "S Fooladi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "3124_CR37",
"unstructured": "Fooladi S, Matin S, Mahmoodpoor A (2020) Copper as a potential adjunct therapy for critically ill COVID-19 patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN 40:90–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.022",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13061898",
"author": "J Hackler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1898",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "3124_CR38",
"unstructured": "Hackler J, Heller RA, Sun Q et al (2021) Relation of serum copper status to survival in COVID-19. Nutrients 13:1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061898",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00644-1",
"author": "JT Laine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1149",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "3124_CR39",
"unstructured": "Laine JT, Tuomainen T-P, Salonen JT, Virtanen JK (2020) Serum copper-to-zinc-ratio and risk of incident infection in men: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Eur J Epidemiol 35:1149–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-020-00644-1",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.002",
"author": "JA Maier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Semin Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "3124_CR40",
"unstructured": "Maier JA, Castiglioni S, Locatelli L et al (2021) Magnesium and inflammation: advances and perspectives. Semin Cell Dev Biol 115:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.002",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/mrh.2020.0465",
"author": "S Iotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Magnes Res",
"key": "3124_CR41",
"unstructured": "Iotti S, Wolf F, Mazur A, Maier JA (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic: is there a role for magnesium? Hypotheses and perspectives. Magnes Res 33:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1684/mrh.2020.0465",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202002346RR",
"author": "H-L Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol",
"key": "3124_CR42",
"unstructured": "Zeng H-L, Yang Q, Yuan P et al (2021) Associations of essential and toxic metals/metalloids in whole blood with both disease severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 35:e21392. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202002346RR",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008",
"author": "Y Yasui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis",
"key": "3124_CR43",
"unstructured": "Yasui Y, Yasui H, Suzuki K et al (2020) Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment - relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis IJID Off Publ Int Soc Infect Dis 100:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"author": "RA Heller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "3124_CR44",
"unstructured": "Heller RA, Sun Q, Hackler J et al (2021) Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker. Redox Biol 38:101764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Biol Trace Elem Res"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Biochemistry (medical)",
"Inorganic Chemistry",
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"General Medicine",
"Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Comparative Analysis of Serum Zinc, Copper and Magnesium Level and Their Relations in Association with Severity and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Patients"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}
