Oral MIB‐626 (β Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) Safely Raises Blood Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Levels in Hospitalized Patients With COVID‐19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Randomized Controlled Trial
et al., FASEB BioAdvances, doi:10.1096/fba.2025-00014, NCT05038488, Jun 2025
RCT 42 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and acute kidney injury (AKI) showing no clinical benefit with MIB-626 (β-nicotinamide mononucleotide) treatment. The study found that 1.0g of MIB-626 twice daily safely and significantly raised blood NAD+ levels, but this did not result in any significant difference in the primary endpoint (serum creatinine). Furthermore, there were no significant differences in secondary endpoints, including other markers of AKI (cystatin C, NGAL, KIM-1), inflammation (CRP, IL-6, TNFa), or overall clinical disease severity.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
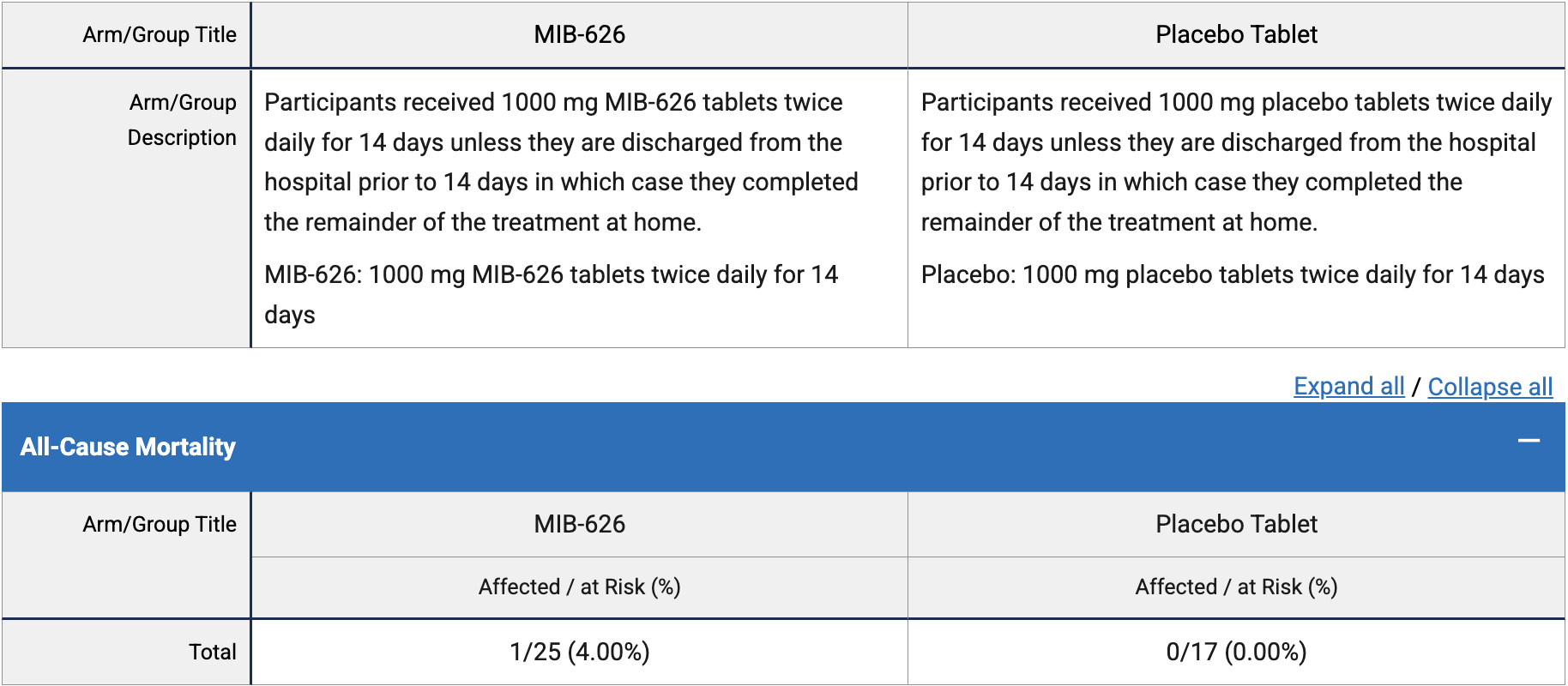
risk of death, 156.0% higher, RR 2.56, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 25 (4.0%), control 0 of 14 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 42.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 18.2% lower, RR 0.82, p = 0.71, treatment mean 1.1 (±1.72) n=19, control mean 0.9 (±1.33) n=15, relative WHO 8-point scale improvement, day 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 50.0% higher, RR 1.50, p = 0.80, treatment mean 0.4 (±2.47) n=14, control mean 0.6 (±1.55) n=14, relative mSOFA improvement, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pencina et al., 18 Jun 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 68.4, 16 authors, trial NCT05038488 (history).
Contact: sbhasin@bwh.harvard.edu.
MIB-626 is an oral formulation of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a small molecule NAD+ precursor that may restore host NAD+ levels depleted during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Oral MIB ‐626 (β Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) Safely Raises Blood Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Levels in Hospitalized Patients With COVID ‐19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Randomized Controlled Trial
FASEB BioAdvances, doi:10.1096/fba.2025-00014
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD + ) plays an important role in the innate immune response and is depleted during SARS-CoV-2 infection due to increased turnover. It is unknown whether treatment with NAD + precursors can safely raise NAD + levels in patients with COVID-19. To determine whether MIB-626 (β-nicotinamide mononucleotide), an NAD + precursor, can safely increase blood NAD + levels and attenuate acute kidney injury (AKI) and inflammation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, 42 adults, ≥ 18 years, hospitalized with COVID-19 and AKI, were randomized in a 3:2 ratio to MIB-626 1.0-g or placebo tablets twice daily for 14 days. Circulating NAD + and its metabolites, markers of AKI, inflammation, and disease severity, were assessed. MIB-626 treatment significantly but gradually raised blood NAD + levels to a peak between 5 to 14 days (16.0 ± 6.9, 25.5 ± 12.6, and 42.6 ± 25.6 μg/mL at baseline, days 5 and 14) and raised plasma concentrations of NAD + metabolites 1-methylnicotinamide, N-methyl, 2-pyridone, 4-carboxamide rapidly to a peak by day 3. Changes in serum creatinine, cystatin-C, and serum markers of AKI did not differ significantly between groups. Serum CRP, IL-6, and TNFα and indices of disease severity also did not differ between groups. MIB-626 treatment of patients with COVID-19 and AKI safely and substantially raised blood NAD + and plasma concentrations of NAD + metabolites. Markers of AKI, inflammation, and disease severity did not differ between groups, likely due to the slow rise in NAD + levels. Future studies should assess whether a rapid increase in NAD + by parenteral administration can attenuate disease severity and AKI.
Author Contributions S.B., K.M.P., D.J.L., and S.S.W. designed the trial; S.B. obtained the funding for the trial; D.E.L., R.J.V., T.S.M., E.V., D.F., T.J., N.K.L., S.L., S.K., Y.M.-B., and S.K. performed research; K.M.P., T.S.M., T.J., and Y.V.S. analyzed the data; K.M.P. and S.B. wrote the first version of the paper; T.S.M. and T.J. developed the case report forms and the secure database; all other co-authors reviewed the paper and provided critical feedback.
Conflicts of Interest The authors have disclosed their other interests below, but none poses
Supporting Information Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section.
References
Airhart, Shireman, Risler, An Open-Label, Non-Randomized Study of the Pharmacokinetics of the Nutritional Supplement Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Its Effects on Blood NAD+ Levels in Healthy Volunteers, PLoS One
Al-Shabany, Moody, Foey, Billington, Intracellular NAD+ Levels Are Associated With LPS-Induced TNF-Alpha Release in Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages, Bioscience Reports
Altay, Arif, Li, Combined Metabolic Activators Accelerates Recovery in Mild-To-Moderate COVID-19, Advanced Science
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Covid-19 in Critically Ill Patients in the Seattle Region -Case Series, New England Journal of Medicine
Conze, Brenner, Kruger, Safety and Metabolism of Long-Term Administration of NIAGEN (Nicotinamide Riboside Chloride) in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Healthy Overweight Adults, Scientific Reports
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Epidemiology, Clinical Course, and Outcomes of Critically Ill Adults With COVID-19 in New York City: A Prospective Cohort Study, Lancet
Dellinger, Holmes, Hu-Seliger, Nicotinamide Riboside and Pterostilbene Reduces Markers of Hepatic Inflammation in NAFLD: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.32778
Dellinger, Santos, Morris, Repeat Dose NRPT (Nicotinamide Riboside and Pterostilbene) Increases NAD(+) Levels in Humans Safely and Sustainably: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study, NPJ Aging and Mechanisms of Disease
Dollerup, Christensen, Svart, A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Nicotinamide Riboside in Obese Men: Safety, Insulin-Sensitivity, and Lipid-Mobilizing Effects, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Heer, Sanderson, Voth, Coronavirus Infection and PARP Expression Dysregulate the NAD Metabolome: An Actionable Component of Innate Immunity, Journal of Biological Chemistry
Izadpanah, Mudd, Garcia, SARS-CoV-2 Infection Dysregulates NAD Metabolism, Frontiers in Immunology
Kauppinen, Gan, Swanson, Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1-Induced NAD(+) Depletion Promotes Nuclear Factor-kappaB Transcriptional Activity by Preventing p65 De-Acetylation, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
Kimura, Ichikawa, Sugawara, Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is Safely Metabolized and Significantly Reduces Blood Triglyceride Levels in Healthy Individuals, Cureus
Kramer, Prinz, Fichtner, Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Liu, Zhou, Yang, The Cytokine Storm of Severe Influenza and Development of Immunomodulatory Therapy, Cellular & Molecular Immunology
Martens, Denman, Mazzo, Chronic Nicotinamide Riboside Supplementation Is Well-Tolerated and Elevates NAD(+) in Healthy Middle-Aged and Older Adults, Nature Communications
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: A Storm Is Raging, Journal of Clinical Investigation
Pencina, Lavu, Santos, MIB-626, an Oral Formulation of a Microcrystalline Unique Polymorph of Beta-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, Increases Circulating Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and Its Metabolome in Middle-Aged and Older Adults, Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences
Pencina, Valderrabano, Wipper, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Augmentation in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Physiologic Study, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism
Poyan Mehr, Tran, Ralto, De Novo NAD(+) Biosynthetic Impairment in Acute Kidney Injury in Humans, Nature Medicine
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Raines, Ganatra, Nissaisorakarn, Niacinamide May be Associated With Improved Outcomes in COVID-19-Related Acute Kidney Injury: An Observational Study, Kidney
Ramos, Fernandez-Sesma, Modulating the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus: Potential Therapeutic Use of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Frontiers in Immunology
Shankar-Hari, Vale, Association Between Administration of IL-6 Antagonists and Mortality Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis, Journal of the American Medical Association
Shen, Kim, Oh, NAD(+) Augmentation Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis Through Regulation of Inflammasome Signalling, Scientific Reports
Trammell, Schmidt, Weidemann, Nicotinamide Riboside Is Uniquely and Orally Bioavailable in Mice and Humans, Nature Communications
Uscu, Guidance for Clinical Investigators, Sponsors, and IRBs-Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs)-Determining Whether Human Research Studies Can Be Conducted Without an IND
Valderrábano, Wipper, Pencina, Dysregulated Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Metabolome in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19, Aging Cell
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Yoshino, Yoshino, Kayser, Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Increases Muscle Insulin Sensitivity in Prediabetic Women, Science
Zheng, Schultz, Sinclair, NAD(+) in COVID-19 and Viral Infections, Trends in Immunology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fba.2025-00014",
"ISSN": [
"2573-9832",
"2573-9832"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fba.2025-00014",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n ) plays an important role in the innate immune response and is depleted during SARS‐CoV‐2 infection due to increased turnover. It is unknown whether treatment with NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n precursors can safely raise NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n levels in patients with COVID‐19. To determine whether MIB‐626 (\n <jats:italic>β‐</jats:italic>\n nicotinamide mononucleotide), an NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n precursor, can safely increase blood NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n levels and attenuate acute kidney injury (AKI) and inflammation in hospitalized patients with COVID‐19, 42 adults, ≥ 18 years, hospitalized with COVID‐19 and AKI, were randomized in a 3:2 ratio to MIB‐626 1.0‐g or placebo tablets twice daily for 14 days. Circulating NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n and its metabolites, markers of AKI, inflammation, and disease severity, were assessed. MIB‐626 treatment significantly but gradually raised blood NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n levels to a peak between 5 to 14 days (16.0 ± 6.9, 25.5 ± 12.6, and 42.6 ± 25.6 μg/mL at baseline, days 5 and 14) and raised plasma concentrations of NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n metabolites 1‐methylnicotinamide, N‐methyl, 2‐pyridone, 4‐carboxamide rapidly to a peak by day 3. Changes in serum creatinine, cystatin‐C, and serum markers of AKI did not differ significantly between groups. Serum CRP, IL‐6, and TNFα and indices of disease severity also did not differ between groups. MIB‐626 treatment of patients with COVID‐19 and AKI safely and substantially raised blood NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n and plasma concentrations of NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n metabolites. Markers of AKI, inflammation, and disease severity did not differ between groups, likely due to the slow rise in NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n levels. Future studies should assess whether a rapid increase in NAD\n <jats:sup>+</jats:sup>\n by parenteral administration can attenuate disease severity and AKI.\n </jats:p>\n <jats:p>\n <jats:bold>Trial Registration:</jats:bold>\n <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" xlink:href=\"http://clinicaltrials.gov\">ClinicalTrials.gov</jats:ext-link>\n Identifier: NCT05038488\n </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1096/fba.2025-00014"
],
"article-number": "e70011",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2025-01-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-03-31"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-06-18"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Pencina",
"given": "Karol M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Renal Medicine Brigham and Women's Hospital Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Leaf",
"given": "David E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Valderrabano",
"given": "Rodrigo J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology Boston Medical Center and Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Waikar",
"given": "Sushrut S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family and Community Medicine University of Alabama Birmingham Alabama USA"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Tapan S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Shang",
"given": "Yili Valentine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Latham",
"given": "Nancy K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Family and Community Medicine University of Alabama Birmingham Alabama USA"
}
],
"family": "John",
"given": "Tejossy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston Texas USA"
}
],
"family": "Volpi",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tulane University School of Medicine New Orleans Louisiana USA"
}
],
"family": "Fusco",
"given": "Dahlene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Memish‐Beleva",
"given": "Yusnie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Renal Medicine Brigham and Women's Hospital Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Krishnamurthy",
"given": "Shobana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metro International Biotech Worcester Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Lavu",
"given": "Siva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metro International Biotech Worcester Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Karmi",
"given": "Salma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Metro International Biotech Worcester Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"family": "Livingston",
"given": "David J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3982-6200",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Program in Men's Health: Aging and Metabolism Boston Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bhasin",
"given": "Shalender",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "FASEB BioAdvances",
"container-title-short": "FASEB BioAdvances",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-19T00:45:49Z",
"timestamp": 1750293949000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-28T15:37:59Z",
"timestamp": 1761665879000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-28T15:46:16Z",
"timestamp": 1761666376303,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1750204800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1096/fba.2025-00014",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1096",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1",
"unstructured": "350(c)(1)(B). USCU “Guidance for Clinical Investigators Sponsors and IRBs—Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs)—Determining Whether Human Research Studies Can Be Conducted Without an IND September 2013 (Final Guidance)”."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137647",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(20)30628‐0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cmi.2015.74",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2015.00361",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00510-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11330",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of COVID‐19",
"author": "Kramer A.",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2022.02.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA120.015138",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.14326",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms12948",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgad027",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glac049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-03421-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0186459",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20150247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-46120-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.32778",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41514-017-0016-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/nqy132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe9985",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-03418-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.04.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1158455",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-018-0138-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34067/KID.0006452020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is Safely Metabolized and Significantly Reduces Blood Triglyceride Levels in Healthy Individuals",
"author": "Kimura S.",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202101222",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1096/fba.2025-00014"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Oral\n <scp>MIB</scp>\n ‐626 (β Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) Safely Raises Blood Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Levels in Hospitalized Patients With\n <scp>COVID</scp>\n ‐19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Randomized Controlled Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "7"
}