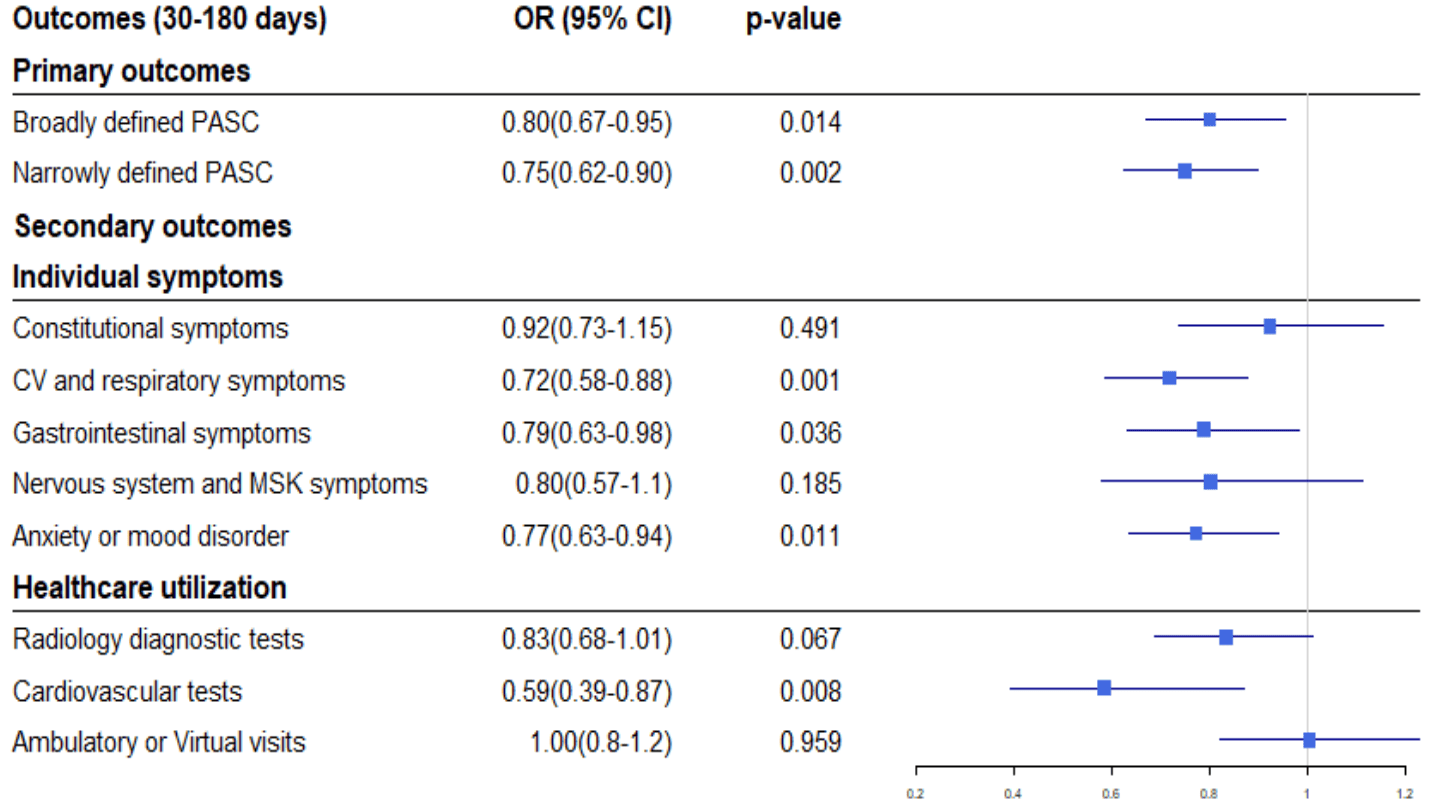
Incidence of Symptoms Associated with Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Non-Hospitalized Vaccinated Patients Receiving Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196, Apr 2023
TriNetX retrospective 1,004 paxlovid patients and matched controls, showing lower risk of PASC with treatment.
Confounding by treatment propensity. This study analyzes a population
where only a fraction of eligible patients received the treatment. Patients
receiving treatment may be more likely to follow other recommendations, more
likely to receive additional care, and more likely to use additional
treatments that are not tracked in the data (e.g., nasal/oral hygiene1,2, vitamin D3, etc.) — either because the physician
recommending paxlovid also recommended them, or
because the patient seeking out paxlovid is more
likely to be familiar with the efficacy of additional treatments and more
likely to take the time to use them.
Malden et al. confirm significant bias in the use of paxlovid, showing that treated
patients are more likely to be from affluent neighborhoods, be more health-conscious, and
have better access to care. Campion et al. also show that female patients were more
likely to receive paxlovid, and studies show that female patients are significantly more
likely to be health-conscious, for example being more likely to take additional
non-prescription treatments.
Therefore, these kind of studies may
overestimate efficacy.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid6-13. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID14. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid15. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid16. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury17 and liver injury18,19. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound20-22.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments23.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of long COVID, 20.0% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.01, treatment 1,004, control 1,004, broadly defined, 30-180 days, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 25.0% lower, RR 0.75, p = 0.01, treatment 1,004, control 1,004, narrowly defined, 30-180 days, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 29.0% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.01, treatment 1,004, control 1,004, broadly defined, 90-180 days, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 26.0% lower, RR 0.74, p = 0.01, treatment 1,004, control 1,004, narrowly defined, 90-180 days, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
4.
Malden et al., Predictors of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir receipt among COVID-19 patients in a large US health system, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-57633-7.
5.
Campion et al., Disparities in the Use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1809.
6.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
7.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
8.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
9.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
10.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
11.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
12.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
13.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
14.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
15.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
16.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
17.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
18.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
19.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
20.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
21.
Shah et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious shedding and rebound among adults with and without oral antiviral use: two case-ascertained prospective household studies, The Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.lanmic.2025.101227.
Patel et al., 6 Apr 2023, retrospective, USA, preprint, mean age 57.2, 17 authors, study period 1 December, 2021 - 17 April, 2022.
Contact: sarju.ganatra@lahey.org.
Incidence of Symptoms Associated with Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Non-Hospitalized Vaccinated Patients Receiving Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir
doi:10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196
Assessment of Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir (NMV-r) in preventing post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), based on broad and narrow definitions in non-hospitalized, vaccinated patients between 30-180 days and 90-180 days.
References
Al-Aly, Bowe, Xie, Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Med
Antonelli, Pujol, Spector, Ourselin, Steves, Risk of long COVID associated with delta versus omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2, Lancet
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients, N Engl J Med
Cdc, Long COVID or Post-COVID Conditions
Elfein, Number of coronavirus (COVID-19) cases, recoveries, and deaths worldwide
Fad, FDA Authorizes New Monoclonal Antibody for Treatment of COVID-19 that Retains Activity Against Omicron Variant
Ganatra, Dani, Ahmad, Oral Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir in Nonhospitalized Vaccinated Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clinical Infectious Diseases
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe Covid-19 in Outpatients, N Engl J Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Organization, Post COVID-19 condition (Long COVID
Rando, Bennett, Byrd, Challenges in defining Long COVID: Striking differences across literature, Electronic Health Records, and patient-reported information, medRxiv
Recover, Explore Research
Rio, Collins, Malani, Long-term Health Consequences of COVID-19, JAMA
Swank, Senussi, Manickas-Hill, Persistent circulating SARS-CoV-2 spike is associated with post-acute COVID-19 sequelae, Clin Infect Dis
Trinetx, The global health research network
University, Paxlovid for Treatment of Long Covid
Uo, COVID-OUT: Early Outpatient Treatment for SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19
Xie, Choi, Al-Aly, Nirmatrelvir and the Risk of Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19, medRxiv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The role of Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir (NMV-r) in preventing post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) is unknown. The objective of this study is to assess the effect of NMV-r in non-hospitalized, vaccinated patients on the occurrence of PASC. Methods: We performed a comparative retrospective cohort study utilizing data from the TriNetX research network, including vaccinated patients ≥18 years old who subsequently developed Covid-19 between December 2021-April 2022. Cohorts were based on NMV-r administration within five days of diagnosis. Based on previously validated broad and narrow definitions, the main outcome was the presence of symptoms associated with PASC. Outcomes were assessed between 30-180 days and 90-180 days after the index Covid-19 infection. Results 1,004 patients remained in each cohort after propensity-score matching. PASC (broad definition) occurred in 425 patients (42%) in the NMV-r cohort, vs. 480 patients (48%) in the control cohort (OR 0.8 CI 0.67-0.96; p=0.01) from 30-180 days and in 273 patients (27%) in the NMV-r cohort, as compared to 347 patients (35%) in the control cohort (OR 0.707, CI 0.59-0.86; p<0.001) from 90-180 days. Narrowly defined PASC was reported in 337 (34%) patients in the NMV-r and 404 (40%) in the control cohort between 30-180 days (OR=0.75, CI 0.62-0.9, p=0.002) and in 221 (22%) in the NMV-r cohort as compared to in 278 (28%) patients in the control cohort (OR=0.7, CI 0.63-0.9, p=0.003) between 90 -180 days. Conclusions NMV-r treatment in non-hospitalized vaccinated patients with Covid-19 was associated with a reduction in the development of symptoms commonly observed with PASC and healthcare utilization.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
6
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "PATEL",
"given": "RUSHIN",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3434-6136",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dani",
"given": "Sourbha S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7262-6905",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Khadke",
"given": "Sumanth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6828-6154",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Javaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Jui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Neev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wener",
"given": "Kenneth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4654-4217",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "McQuillen",
"given": "Daniel P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faust",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maley",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Smita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9156-9424",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mullington",
"given": "Janet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3226-2737",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wachter",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mosenthal",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8434-174X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sax",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0296-6864",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ganatra",
"given": "Sarju",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-07T04:30:14Z",
"timestamp": 1680841814000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-07T04:30:14Z",
"timestamp": 1680841814000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-08T05:03:11Z",
"timestamp": 1680930191368
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
6
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
6
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2023.04.05.23288196"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Incidence of Symptoms Associated with Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Non-Hospitalized Vaccinated Patients Receiving Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir ",
"type": "posted-content"
}