A cohort study of COVID-19 infection in pediatric oncology patients plus the utility and safety of remdesivir treatment
et al., Acta Oncologica, doi:10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079, Jan 2023
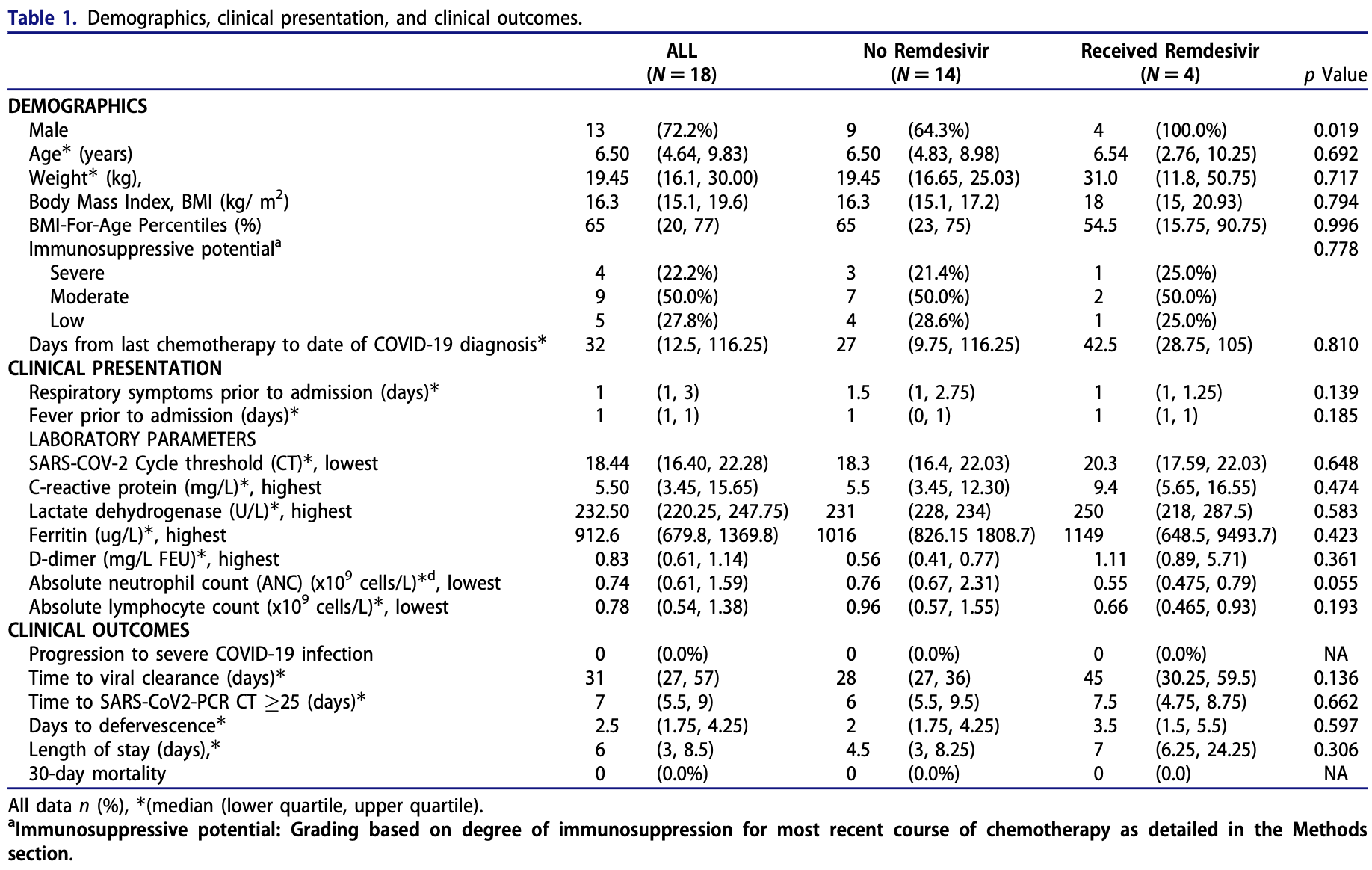
Retrospective 18 immunocompromised pediatric COVID-19 patients in Singapore, showing slower viral clearance with remdesivir, without statistical significance.
Gérard, Zhou, Wu, Kamo, Choi, Kim show increased risk of acute kidney injury, Leo, Briciu, Muntean, Petrov show increased risk of liver injury, and Negru, Cheng, Mohammed, Kwok show increased risk of cardiac disorders with remdesivir.
|
recovery time, 75.0% higher, relative time 1.75, p = 0.60, treatment 4, control 14, defervescence.
|
|
hospitalization time, 55.6% higher, relative time 1.56, p = 0.31, treatment 4, control 14.
|
|
time to viral-, 60.7% higher, relative time 1.61, p = 0.14, treatment 4, control 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Gérard et al., Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2145.
2.
Zhou et al., Acute Kidney Injury and Drugs Prescribed for COVID-19 in Diabetes Patients: A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.833679.
3.
Wu et al., Acute Kidney Injury Associated With Remdesivir: A Comprehensive Pharmacovigilance Analysis of COVID-19 Reports in FAERS, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.692828.
4.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
5.
Choi et al., Comparative effectiveness of combination therapy with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir and remdesivir versus monotherapy with remdesivir or nirmatrelvir–ritonavir in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a target trial emulation study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00353-0.
6.
Kim et al., Investigating the Safety Profile of Fast‐Track COVID‐19 Drugs Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database: A Comparative Observational Study, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, doi:10.1002/pds.70043.
7.
Leo et al., Hepatocellular liver injury in hospitalized patients affected by COVID-19: Presence of different risk factors at different time points, Digestive and Liver Disease, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2021.12.014.
8.
Briciu et al., Evolving Clinical Manifestations and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Comparative Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Waves in a Romanian Hospital Setting, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens12121453.
9.
Muntean et al., Effects of COVID-19 on the Liver and Mortality in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia Caused by Delta and Non-Delta Variants: An Analysis in a Single Centre, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph17010003.
10.
Petrov et al., The Effect of Potentially Hepatotoxic Medicinal Products on Alanine Transaminase Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Case–Control Study, Safety and Risk of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.30895/2312-7821-2025-458.
11.
Negru et al., Comparative Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Approved and Repurposed Antivirals for COVID-19: Insights from EudraVigilance Data, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines13061387.
12.
Cheng et al., Cardiovascular Safety of COVID-19 Treatments: A Disproportionality Analysis of Adverse Event Reports from the WHO VigiBase, Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01225-z.
Ong et al., 20 Jan 2023, retrospective, Singapore, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, average treatment delay 3.5 days.
Contact: rina.ong.yl@kkh.com.sg, yung.chee.fu@singhealth.com.sg.
Abstract: Acta Oncologica
ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ionc20
A cohort study of COVID-19 infection in pediatric
oncology patients plus the utility and safety of
remdesivir treatment
Rina Yue Ling Ong, Valerie Xue Fen Seah, Chia Yin Chong, Koh Cheng Thoon,
Natalie Woon Hui Tan, Jiahui Li, Karen Donceras Nadua, Shui Yen Soh,
Michaela Su-Fern Seng, Thi Ngoc Anh Pham, Chee Fu Yung & Kai-Qian Kam
To cite this article: Rina Yue Ling Ong, Valerie Xue Fen Seah, Chia Yin Chong, Koh Cheng
Thoon, Natalie Woon Hui Tan, Jiahui Li, Karen Donceras Nadua, Shui Yen Soh, Michaela Su-Fern
Seng, Thi Ngoc Anh Pham, Chee Fu Yung & Kai-Qian Kam (2023) A cohort study of COVID-19
infection in pediatric oncology patients plus the utility and safety of remdesivir treatment, Acta
Oncologica, 62:1, 53-57, DOI: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079
To link to this article: https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079
Published online: 20 Jan 2023.
Submit your article to this journal
Article views: 470
View related articles
View Crossmark data
Full Terms & Conditions of access and use can be found at
https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=ionc20
ACTA ONCOLOGICA
2023, VOL. 62, NO. 1, 53–57
https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
A cohort study of COVID-19 infection in pediatric oncology patients plus the
utility and safety of remdesivir treatment
Rina Yue Ling Onga , Valerie Xue Fen Seaha , Chia Yin Chongb,c,d,e , Koh Cheng Thoonb,c,d,e ,
Natalie Woon Hui Tanb,c,d,e , Jiahui Lib,c,d,e, Karen Donceras Naduab,c,d,e , Shui Yen Sohc,d,e,f ,
Michaela Su-Fern Sengc,d,e,f , Thi Ngoc Anh Phamg, Chee Fu Yungb,d,e
and Kai-Qian Kamb,c,d,e
a
Department of Pharmacy, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore; bInfectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics,
KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore; cYong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore,
Singapore; dDuke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore; eLee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang
Technological University, Singapore, Singapore; fHaematology/Oncology Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s
Hospital, Singapore, Singapore; gNursing Clinical Services, Division of Nursing, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
ARTICLE HISTORY Received 22 November 2022; Accepted 11 January 2023
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/0284186x.2023.2169079",
"ISSN": [
"0284-186X",
"1651-226X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=ionc20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=ionc20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-11-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-01-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-01-20"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1599-619X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ong",
"given": "Rina Yue Ling",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7775-6987",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacy, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Seah",
"given": "Valerie Xue Fen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3919-3324",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chong",
"given": "Chia Yin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2844-010X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thoon",
"given": "Koh Cheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7380-5008",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Natalie Woon Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jiahui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1313-7458",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nadua",
"given": "Karen Donceras",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4237-8904",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Haematology/Oncology Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Soh",
"given": "Shui Yen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6245-2446",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Haematology/Oncology Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Seng",
"given": "Michaela Su-Fern",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nursing Clinical Services, Division of Nursing, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Pham",
"given": "Thi Ngoc Anh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9605-7690",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yung",
"given": "Chee Fu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2402-7262",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Service, Department of Pediatrics, KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Duke-National University of Singapore Medical School, Singapore, Singapore"
},
{
"name": "Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kam",
"given": "Kai-Qian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Oncologica",
"container-title-short": "Acta Oncologica",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-20T09:42:30Z",
"timestamp": 1674207750000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-03T05:09:15Z",
"timestamp": 1680498555000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"AM/COV001/2020"
],
"name": "Singhealth Duke-NUS Academic Medicine COVID-19 Rapid Response Research Grant"
},
{
"award": [
"AM/COV001/2020"
],
"name": "Singhealth Duke-NUS Academic Medicine COVID-19 Rapid Response Research Grant"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-04T04:44:53Z",
"timestamp": 1680583493450
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "53-57",
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15270",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000003043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30177-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2031670",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0006"
},
{
"key": "CIT0007",
"unstructured": "National Institute of Health (NIH). NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines: Clinical Spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. 2022. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.28843",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa638",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00454-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/pore.2022.1610261",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4084/MJHID.2022.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01181-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clml.2021.07.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.28432",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.28514",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.28392",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.28710",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10082002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac253",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers14194720",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S378347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pbc.29277",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab397",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab217",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.3988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S095026882100008X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000002814",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0028"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsb2104756",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0029"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-047803",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-020-03876-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0031"
},
{
"key": "CIT0032",
"unstructured": "U.S. National Library of Medicine. Study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of remdesivir (GS-5734TM) in participants from birth to <18 years of age with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) (CARAVAN). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04431453. 2020. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04431453"
},
{
"key": "CIT0033",
"unstructured": "Ahmed A, Rojo P, Agwu A, et al. Remdesivir treatment for COVID-19 in hospitalized children: CARAVAN interim results. In Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) 2022 Annual Meeting; 2022. Denver, CO. Abstract 744."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0000000000003214",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0034"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jpids/piab029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0035"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-03940-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0036"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12121384",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0037"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/0284186X.2023.2169079"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Radiology, Nuclear Medicine and imaging",
"Oncology",
"Hematology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A cohort study of COVID-19 infection in pediatric oncology patients plus the utility and safety of remdesivir treatment",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01",
"volume": "62"
}