Effect of High-Titer Convalescent Plasma on Progression to Severe Respiratory Failure or Death in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36246, TSUNAMI, NCT04716556, Nov 2021
RCT 487 patients in Italy, showing no significant difference in outcomes with convalescent plasma.
|
risk of death, 23.4% lower, RR 0.77, p = 0.47, treatment 14 of 231 (6.1%), control 19 of 240 (7.9%), NNT 54.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 3.9% higher, RR 1.04, p = 1.00, treatment 25 of 231 (10.8%), control 25 of 240 (10.4%), mechanical ventilation or death.
|
|
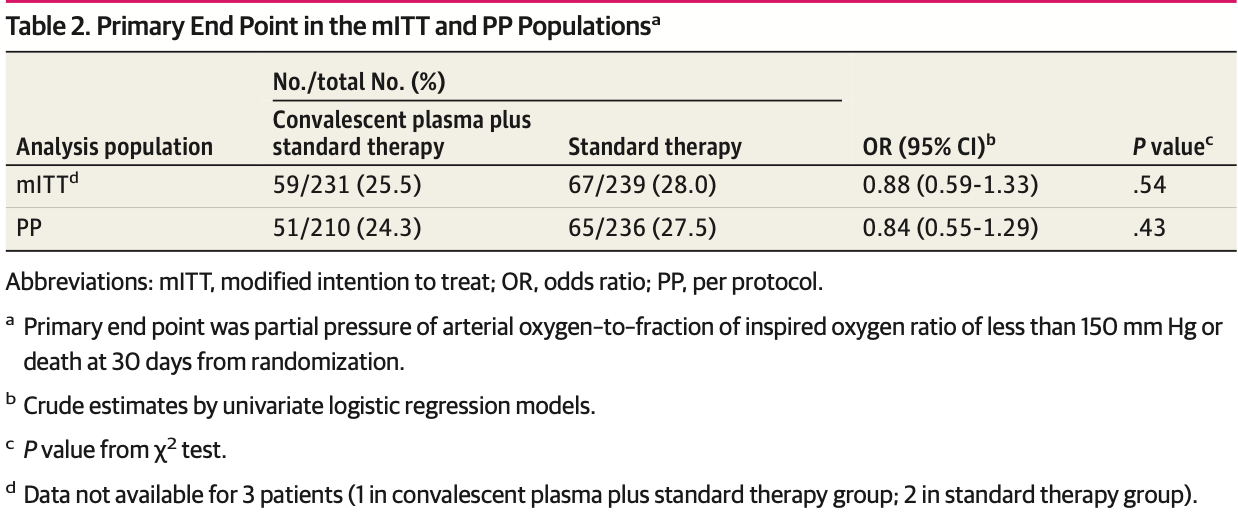
risk of progression, 12.0% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.54, treatment 59 of 231 (25.5%), control 67 of 239 (28.0%), NNT 40, PaO2/FiO2 <150 mm Hg or death, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Menichetti et al., 29 Nov 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Italy, peer-reviewed, 110 authors, study period 15 July, 2020 - 8 December, 2020, average treatment delay 7.0 days, trial NCT04716556 (history) (TSUNAMI).
Effect of High-Titer Convalescent Plasma on Progression to Severe Respiratory Failure or Death in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36246
IMPORTANCE Convalescent plasma (CP) has been generally unsuccessful in preventing worsening of respiratory failure or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. OBJECTIVE To evaluate the efficacy of CP plus standard therapy (ST) vs ST alone in preventing worsening respiratory failure or death in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS This prospective, open-label, randomized clinical trial enrolled (1:1 ratio) hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia to receive CP plus ST or ST alone between July 15 and December 8, 2020, at 27 clinical sites in Italy. Hospitalized adults with COVID-19 pneumonia and a partial pressure of oxygen-to-fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO 2 /FiO 2 ) ratio between 350 and 200 mm Hg were eligible. INTERVENTIONS Patients in the experimental group received intravenous high-titer CP (Ն1:160, by microneutralization test) plus ST. The volume of infused CP was 200 mL given from 1 to a maximum of 3 infusions. Patients in the control group received ST, represented by remdesivir, glucocorticoids, and low-molecular weight heparin, according to the Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco recommendations.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary outcome was a composite of worsening respiratory failure (PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio <150 mm Hg) or death within 30 days from randomization.
RESULTS Of the 487 randomized patients (241 to CP plus ST; 246 to ST alone), 312 (64.1%) were men; the median (IQR) age was 64 (54.0-74.0) years. The modified intention-to-treat population included 473 patients. The primary end point occurred in 59 of 231 patients (25.5%) treated with CP and ST and in 67 of 239 patients (28.0%) who received ST (odds ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.59-1.33; P = .54). Adverse events occurred more frequently in the CP group (12 of 241 [5.0%]) compared with the control group (4 of 246 [1.6%]; P = .04).
CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE In patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 pneumonia, hightiter anti-SARS-CoV-2 CP did not reduce the progression to severe respiratory failure or death within 30 days. (continued) Key Points Question Is convalescent plasma useful in preventing worsening respiratory failure or death in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia? Findings In this randomized clinical trial of 487 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and a partial pressure of arterial oxygen-to-fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO 2 /FiO 2 ) ratio between 350 and 200 mm Hg at enrollment, the rate of the primary clinical end point (need for mechanical ventilation, defined as PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio <150 mm Hg, or death) was not significantly different between the convalescent plasma group and the control group. Meaning In this trial, convalescent plasma did not reduce the progression to severe respiratory failure or death within 30 days.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Menichetti reported serving as the principal investigator for an AstraZenecasponsored trial and a Toscana Life Science-sponsored trial evaluating monoclonal antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 (for which no personal fees were received), and receiving speaker honoraria or advisory board or support for meetings from Angelini, Menarini, Correvio, MSD, Pfizer, Astellas, Gilead, BMS, Janssen, ViiV, BioMerieux, Biotest, Becton-Dickinson, Pfizer, Shionogi, Roche, GSK, Advanz Pharma, and ThermoFisher in the last 3 years outside the submitted work. Dr Bartoloni reported receiving study grants from MSD, ViiV Healthcare, and Nordic Pharma and receiving fees for presentations at local congress or expert meetings from Pfizer and MSD in the last 3 years outside the submitted work; Dr Puoti reported receiving personal fees and nonfinancial support from Abbvie, grants and nonfinancial support from Gilead Science, and personal fees from Merck and Theratechnologies outside the submitted work. Dr Marchetti reported receiving grants for lectures, advisory board, or conferences by Gilead, ViiV, and Janssen in the last 3 years outside the submitted work. Dr d'Arminio Monforte reported receiving grants for lectures, advisory board, or conferences by Gilead, ViiV, MSD, Angelini, and Janssen in the last 3 years outside the submitted work; Dr Bonfanti reported receiving personal fees from Viiv, Gilead, Jannsen Pharmaceuticals, Merck, and Pfizer outside the submitted work. Dr..
References
Acquisition, Menichetti, Popoli, Puopolo, Alegiani et al., Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content
Administrative, Tiseo, Socio, Pallotto, Fabiani et al., None
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate COVID-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3939
Alegria, Sud, Steinberg, Gai, Siddiqui, Reporting of participant race, sex, and socioeconomic status in randomized clinical trials in general medical journals, 2015 vs 2019, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11516&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.36246
Alqahtani, Abdulrahman, Almadani, Randomized controlled trial of convalescent plasma therapy against standard therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 disease, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-89444-5
Amanat, White, Miorin, An in vitro microneutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2 Serology and drug screening, Curr Protoc Microbiol, doi:10.1002/cpmc.108
Avendaño-Solà, Ramos-Martinez, Muñez-Rubio, Convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.26.20182444
Bajpai, Kumar, Maheshwari, Efficacy of convalescent plasma therapy compared to fresh frozen plasma in severely ill COVID-19 patients: a pilot randomized controlled trial. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.25.20219337
Balcells, Rojas, Corre, Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: a randomized phase II clinical trial, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003415
Bellan, Patti, Hayden, Fatality rate and predictors of mortality in an Italian cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77698-4
Gharbharan, Jordans, Geurtsvankessel, Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23469-2
Harris, Taylor, Thielke, Payne, Gonzalez et al., Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J Biomed Inform, doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Horby, Estcourt, Peto, Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
Hubbard, Backholer, Wiltshire, Cardigan, Ariëns, Effects of riboflavin and amotosalen photoactivation systems for pathogen inactivation of fresh-frozen plasma on fibrin clot structure, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.13261
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031893
Korley, Durkalski-Mauldin, Yeatts, Early convalescent plasma for highrisk outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med. Published online, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103784
Körper, Weiss, Zickler, Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in severe COVID-19 patients, J Clin Invest. Published online, doi:10.1172/JCI152264
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2020.10044&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.36246
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Fundación INFANT-COVID-19 Group. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033700
Medical, World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jama.2013.281053&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.36246
Menichetti, Puopolo, Alegiani, Tiseo, Toschi et al., data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis
Nazionale, Ai Responsibili delle Strutture di Coordinamento per la Attività Trasfusionali delle Regioni e Province Autonome
O'donnell, Grinsztejn, Cummings, A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI150646
Ray, Paul, Bandopadhyay, Clinical and immunological benefits of convalescent plasmatherapy in severe COVID-19: insights from a single center open label randomised control trial. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.11.25.20237883
Rome, Bocchino, Md, National Institute for Infectious Diseases
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 Severe Pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
Wang, Lagakos, Ware, Hunter, Drazen, Statistics in medicine-reporting of subgroup analyses in clinical trials, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsr077003
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36246",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.36246",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Menichetti",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Drug Research and Evaluation, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Popoli",
"given": "Patrizia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Puopolo",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Drug Research and Evaluation, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Spila Alegiani",
"given": "Stefania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Tiseo",
"given": "Giusy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Unit, Florence Department of Medicine, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bartoloni",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, “Santa Maria della Misericordia” Hospital, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "De Socio",
"given": "Giuseppe Vittorio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Hospital of Lucca, Lucca, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Luchi",
"given": "Sauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Ospedale S. Maria Annunziata, Firenze, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Blanc",
"given": "Pierluigi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Milano-Bicocca School of Medicine, Milan, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Azienda socio sanitaria territorial (ASST) Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Puoti",
"given": "Massimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Coordination and Support Service (CoRi), Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Toschi",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Drug Research and Evaluation, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Massari",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Center for Drug Research and Evaluation, Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Palmisano",
"given": "Lucia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Italian National Blood Centre, Rome, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Marano",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unit of Infectious Diseases, Carlo Poma Hospital, Mantova, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Chiamenti",
"given": "Margherita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Unità Sanitaria Locale (USL)–Umbria 1, Ospedale Città di Castello, Città di Castello, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Martinelli",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Unità Sanitaria Locale (USL)–Umbria 1, Ospedale Città di Castello, Città di Castello, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Franchi",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Unit, San Giuseppe Hospital, Azienda USL Toscana Centro, Empoli, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pallotto",
"given": "Carlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
},
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Unit, San Giuseppe Hospital, Azienda USL Toscana Centro, Empoli, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Suardi",
"given": "Lorenzo Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro Regionale Sangue, Servizio Immunotrasfusionale, Azienda Ospedaliera di Perugia, Perugia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Luciani Pasqua",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Azienda socio sanitaria territorial (ASST) Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Merli",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Ospedale Unico della Versilia, Lido di Camaiore, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fabiani",
"given": "Plinio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Ospedale Unico della Versilia, Lido di Camaiore, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bertolucci",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Unit, Florence Department of Medicine, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Borchi",
"given": "Beatrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Unit, Florence Department of Medicine, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Modica",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Hospital of Lucca, Lucca, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Moneta",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Unit, Department of Health Sciences, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo University Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Marchetti",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases Unit, Department of Health Sciences, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo University Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "d’Arminio Monforte",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Ospedale di Foligno, Foligno, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Stoppini",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Ospedale di Foligno, Foligno, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ferracchiato",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Azienda Ospedaliera di Lecco, Lecco, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Piconi",
"given": "Stefania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Ospedale San Jacopo, Pistoia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fabbri",
"given": "Claudio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cell Therapy and Transfusion Medicine, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Beccastrini",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cell Therapy and Transfusion Medicine, Careggi University Hospital, Florence, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Saccardi",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria, Ospedali Riuniti di Ancona, Ancona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Giacometti",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Ospedale S. Maria Annunziata, Firenze, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Esperti",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Ospedale S. Maria Annunziata, Firenze, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pierotti",
"given": "Piera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Arezzo Hospital, Arezzo, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bernini",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Arezzo Hospital, Arezzo, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bianco",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, “Santa Maria della Misericordia” Hospital, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Benedetti",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinic of Infectious Diseases, “Santa Maria della Misericordia” Hospital, University of Perugia, Perugia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Lanzi",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, ASST Monza, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Bonfanti",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Azienda USL–Istituto di Ricovero e Cura a Carattere Scientifico (IRCCS) di Reggio Emilia, Reggio Emilia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Massari",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, Livorno Hospital, Livorno, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Sani",
"given": "Spartaco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Bari University Hospital, Bari, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Saracino",
"given": "Annalisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Diseases, IRCCS Ospedale San Raffaele, Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Castagna",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Foggia, Foggia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Trabace",
"given": "Luigia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "North-Western Tuscany Blood Bank, Pisa University Hospital, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Lanza",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "North-Western Tuscany Blood Bank, Pisa University Hospital, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Focosi",
"given": "Daniele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Transfusion Medicine and Transplant Biology, Pisa University Hospital, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Mazzoni",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Virology, University Hospital of Pisa, Retrovirus Center, Department of Translational Research, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pistello",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Unit, Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Pisana, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Falcone",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Palazzolo",
"given": "Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Casari",
"given": "Salvatore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Occhionero",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Grazzini",
"given": "Tiziana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Silvestri",
"given": "Dina Leonarda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Iorio",
"given": "Mariacarla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Tosti",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Francisci",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Becattini",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Pirro",
"given": "Matteo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Marchesi",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Bastianelli",
"given": "Sabrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Pierucci",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Busti",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Mencacci",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Bozza",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Camilloni",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Annoni",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Bellotto",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Cioppi",
"given": "Adriano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Querci",
"given": "Giorgia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Ciusa",
"given": "Giacomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Tassara",
"given": "Michela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Danise",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Chigiotti",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Morelli",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Meini",
"given": "Micaela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Galfo",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Ferranti",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Tagliaferri",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Iapoce",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Barbieri",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Forniti",
"given": "Arianna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Caroselli",
"given": "Claudio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Verdenelli",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Monzani",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Mazzetti",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Moscato",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Barchiesi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Andreotti",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Baldanti",
"given": "Fausto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Binelli",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Capobianchi",
"given": "Maria R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Da Cas",
"given": "Roberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Di Sevo",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Fazi",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Gasparrini",
"given": "Cinzia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Ippoliti",
"given": "Ilaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Mancino",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Menniti Ippolito",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Paoloni",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Ruggeri",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Rughini",
"given": "Arianna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Salvi",
"given": "Emanuela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Sargentini",
"given": "Valeria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Trotta",
"given": "Maria P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the TSUNAMI Study group"
}
],
"family": "Vignetti",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "TSUNAMI Study group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Netw Open",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-29T16:33:18Z",
"timestamp": 1638203598000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T19:53:14Z",
"timestamp": 1642535594000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-27T02:25:28Z",
"timestamp": 1672107928765
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 31,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2786680/menichetti_2021_oi_211022_1642100496.70738.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2136246",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"article-title": "Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi211022r1",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate COVID-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial).",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3939",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "zoi211022r2",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"article-title": "A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 Severe Pneumonia.",
"author": "Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi211022r3",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2049",
"issue": "10289",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi211022r4",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23469-2",
"article-title": "Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Gharbharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3189",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "zoi211022r5",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-89444-5",
"article-title": "Randomized controlled trial of convalescent plasma therapy against standard therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 disease.",
"author": "AlQahtani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9927",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "zoi211022r6",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003415",
"article-title": "Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: a randomized phase II clinical trial.",
"author": "Balcells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "zoi211022r7",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103784",
"article-title": "Early convalescent plasma for high-risk outpatients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Korley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi211022r8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI152264",
"article-title": "Results of the CAPSID randomized trial for high-dose convalescent plasma in severe COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Körper",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "zoi211022r9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from COVID-19.",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1015",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi211022r13",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI150646",
"article-title": "A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19.",
"author": "O’Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "zoi211022r14",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"article-title": "Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 in older adults.",
"author": "Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "610",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi211022r15",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"article-title": "Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support.",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "zoi211022r16",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"article-title": "World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects.",
"author": "World Medical Association",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2191",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "zoi211022r17",
"volume": "310",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11516",
"article-title": "Reporting of participant race, sex, and socioeconomic status in randomized clinical trials in general medical journals, 2015 vs 2019.",
"author": "Alegria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi211022r18",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpmc.108",
"article-title": "An in vitro microneutralization assay for SARS-CoV-2 Serology and drug screening.",
"author": "Amanat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Protoc Microbiol",
"key": "zoi211022r20",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.13261",
"article-title": "Effects of riboflavin and amotosalen photoactivation systems for pathogen inactivation of fresh-frozen plasma on fibrin clot structure.",
"author": "Hubbard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "zoi211022r21",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsr077003",
"article-title": "Statistics in medicine—reporting of subgroup analyses in clinical trials.",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2189",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi211022r23",
"volume": "357",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77698-4",
"article-title": "Fatality rate and predictors of mortality in an Italian cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Bellan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20731",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "zoi211022r24",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.02257-20",
"article-title": "Comparative performance of five commercially available serologic assays to detect antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and identify individuals with high neutralizing titers.",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e02257",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "zoi211022r25",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028",
"article-title": "Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients.",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1888",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "zoi211022r26",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m4072",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma is ineffective for COVID-19.",
"author": "Pathak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m4072",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "zoi211022r27",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.25.20219337",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "zoi211022r10",
"unstructured": "Bajpai? M, Kumar? S, Maheshwari? A, . Efficacy of convalescent plasma therapy compared to fresh frozen plasma in severely ill COVID-19 patients: a pilot randomized controlled trial.? medRxiv. Preprint published online October 27, 2020. doi:10.1101/2020.10.25.20219337"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.26.20182444",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "zoi211022r11",
"unstructured": "Avendaño-Solà? C, Ramos-Martinez? A, Muñez-Rubio? E, . Convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial.? medRxiv. Preprint published online September 29, 2020. doi:10.1101/2020.08.26.20182444"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.25.20237883",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "zoi211022r12",
"unstructured": "Ray? Y, Paul? SR, Bandopadhyay? P, . Clinical and immunological benefits of convalescent plasmatherapy in severe COVID-19: insights from a single center open label randomised control trial.? medRxiv. Preprint published online November 29, 2020. doi:10.1101/2020.11.25.20237883"
},
{
"key": "zoi211022r19",
"unstructured": "Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA). Trattamenti utilizzabili nei pazienti COVID-19 nel setting ospedaliero. Accessed May 7, 2021. https://www.aifa.gov.it/documents/20142/1269602/SOC_ospedaliera_09.12.2020.pdf"
},
{
"key": "zoi211022r22",
"unstructured": "Centro Nazionale Sangue. Ai Responsibili delle Strutture di Coordinamento per la Attività Trasfusionali delle Regioni e Province Autonome. Accessed October 28, 2021. https://www.avis.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Prot.-n.-1296.CNS_.2020_Donazione-di-plasma-da-convalescente-COVID-19.pdf"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2786680"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Effect of High-Titer Convalescent Plasma on Progression to Severe Respiratory Failure or Death in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}