Early Convalescent Plasma for High-Risk Outpatients with Covid-19
et al., NEJM, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103784, C3PO, NCT04355767, Aug 2021
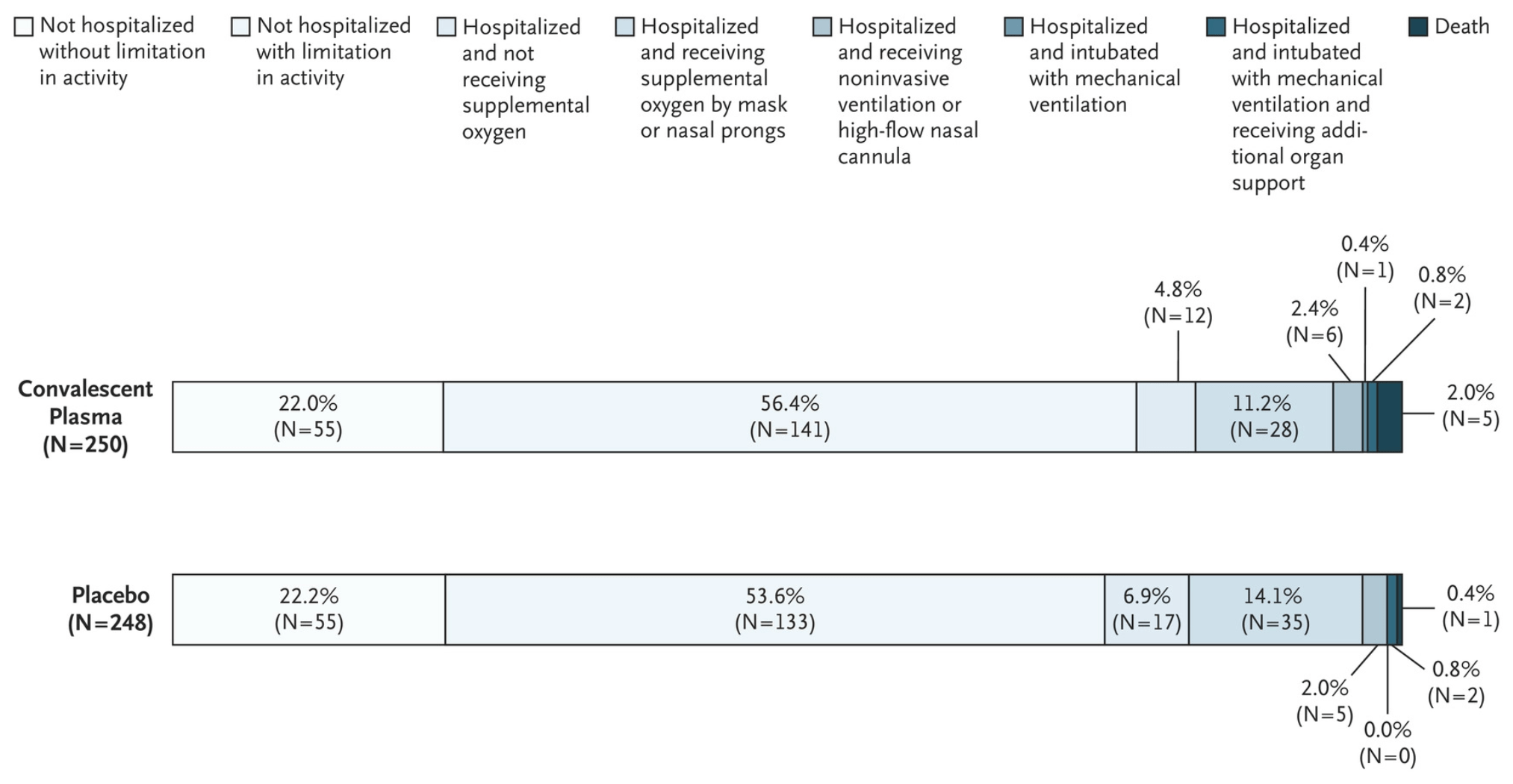
RCT 511 emergency department patients, 257 assigned to convalescent plasma, showing no significant difference in outcomes.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 396.0% higher, RR 4.96, p = 0.22, treatment 5 of 250 (2.0%), control 1 of 248 (0.4%).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 10.0% lower, RR 0.90, p = 0.59, treatment 51 of 257 (19.8%), control 56 of 254 (22.0%), NNT 45.
|
|
risk of progression, 6.0% lower, RR 0.94, p = 0.70, treatment 77 of 257 (30.0%), control 81 of 254 (31.9%), NNT 52.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Korley et al., 18 Aug 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 28 authors, study period August 2020 - February 2021, average treatment delay 3.7 days, trial NCT04355767 (history) (C3PO).
Early Convalescent Plasma for High-Risk Outpatients with Covid-19
New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2103784
BACKGROUND Early administration of convalescent plasma obtained from blood donors who have recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) may prevent disease progression in acutely ill, high-risk patients with Covid-19.
METHODS In this randomized, multicenter, single-blind trial, we assigned patients who were being treated in an emergency department for Covid-19 symptoms to receive either one unit of convalescent plasma with a high titer of antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or placebo. All the patients were either 50 years of age or older or had one or more risk factors for disease progression. In addition, all the patients presented to the emergency department within 7 days after symptom onset and were in stable condition for outpatient management. The primary outcome was disease progression within 15 days after randomization, which was a composite of hospital admission for any reason, seeking emergency or urgent care, or death without hospitalization. Secondary outcomes included the worst severity of illness on an 8-category ordinal scale, hospital-free days within 30 days after randomization, and death from any cause.
RESULTS A total of 511 patients were enrolled in the trial (257 in the convalescent-plasma group and 254 in the placebo group). The median age of the patients was 54 years; the median symptom duration was 4 days. In the donor plasma samples, the median titer of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies was 1:641. Disease progression occurred in 77 patients (30.0%) in the convalescent-plasma group and in 81 patients (31.9%) in the placebo group (risk difference, 1.9 percentage points; 95% credible interval, −6.0 to 9.8; posterior probability of superiority of convalescent plasma, 0.68). Five patients in the plasma group and 1 patient in the placebo group died. Outcomes regarding worst illness severity and hospital-free days were similar in the two groups.
CONCLUSIONS The administration of Covid-19 convalescent plasma to high-risk outpatients within 1 week after the onset of symptoms of Covid-19 did not prevent disease progression. (SIREN-C3PO ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04355767.
Appendix The authors' full names and academic degrees are as follows: Frederick K. Korley Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights reserved. n engl j med nejm.org
References
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ
Germanio, Simmons, Kelly, SARS-CoV-2 antibody persistence in COVID-19 convalescent plasma donors, doi:10.1101/2021.03.24.21254260v1
Janiaud, Axfors, Schmitt, Association of convalescent plasma treatment with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Ko, Danielson, Town, Risk factors for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated hospitalization: COVID-19-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Clin Infect Dis
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med
Long, Liu, Deng, Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19, Nat Med
Peng, Rhind, Beckett, Convalescent plasma for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and quantitative analysis, JMIR Public Health Surveill
Ripoll, Van Helmond, Senefeld, Convalescent plasma for infectious diseases: historical framework and use in COVID-19, Clin Microbiol Newsl
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2103784",
"ISSN": [
"0028-4793",
"1533-4406"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2103784",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1056/NEJMoa2103784"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Korley",
"given": "Frederick K.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Durkalski-Mauldin",
"given": "Valerie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Yeatts",
"given": "Sharon D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Schulman",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Davenport",
"given": "Robertson D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Dumont",
"given": "Larry J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "El Kassar",
"given": "Nahed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "Lydia D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9739-3968",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hah",
"given": "Jennifer M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Jaiswal",
"given": "Siddartha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Kaplan",
"given": "Alesia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Lowell",
"given": "Ezekiel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "McDyer",
"given": "John F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Triulzi",
"given": "Darrell J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Van Huysen",
"given": "Carol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Stevenson",
"given": "Valerie L.W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Yadav",
"given": "Kabir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Christopher W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Kea",
"given": "Bory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Burnett",
"given": "Aaron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Joshua C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Greineder",
"given": "Colin F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Haas",
"given": "Nathan L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Beiser",
"given": "David G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Silbergleit",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Barsan",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "From the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (F.K.K., R.D.D., C.V.H., V.L.W.S., C.F.G., N.L.H., R.S., W.B.), Spectrum Health, Grand Rapids (J.C.R.), and Michigan State University, East Lansing (J.C.R.) — all in Michigan; the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston (V.D.-M., S.D.Y., L.D.F., E.L.); Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA (K.S., J.M.H., S.J., J.Q.); Vitalant Research Institute, Scottsdale, AZ (L.J.D.); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD (N.E.K.); the University of..."
}
],
"family": "Callaway",
"given": "Clifton W.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "N Engl J Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-18T21:01:03Z",
"timestamp": 1629320463000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-17T23:03:58Z",
"timestamp": 1637190238000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000065",
"award": [
"U24NS100655",
"U24NS100659"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000050",
"award": [
"1OT2HL156812-01"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100012399",
"award": [
"75A50120C00094"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T19:49:32Z",
"timestamp": 1712692172404
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 167,
"issue": "21",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "21",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nejmgroup.org/legal/terms-of-use.htm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1637193600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2103784",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "150",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1951-1960",
"prefix": "10.1056",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Massachusetts Medical Society",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinmicnews.2021.02.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0897-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/25500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.2747",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "r12"
}
],
"reference-count": 11,
"references-count": 11,
"relation": {
"has-review": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.3410/f.740663052.793590544",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2103784"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early Convalescent Plasma for High-Risk Outpatients with Covid-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "385"
}