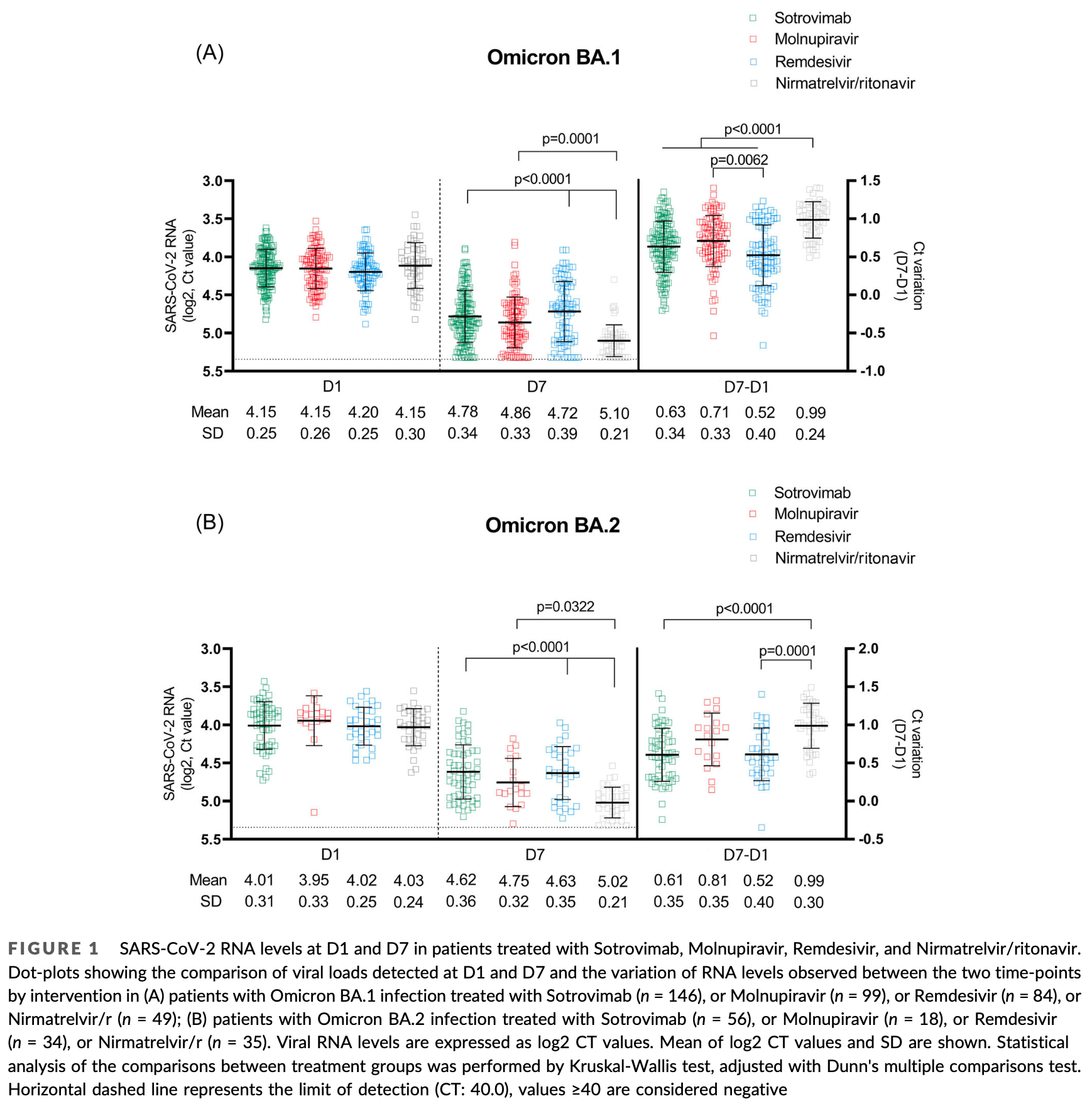
Viral load decrease in SARS‐CoV‐2 BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron sublineages infection after treatment with monoclonal antibodies and direct antiviral agents
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28186, Oct 2022
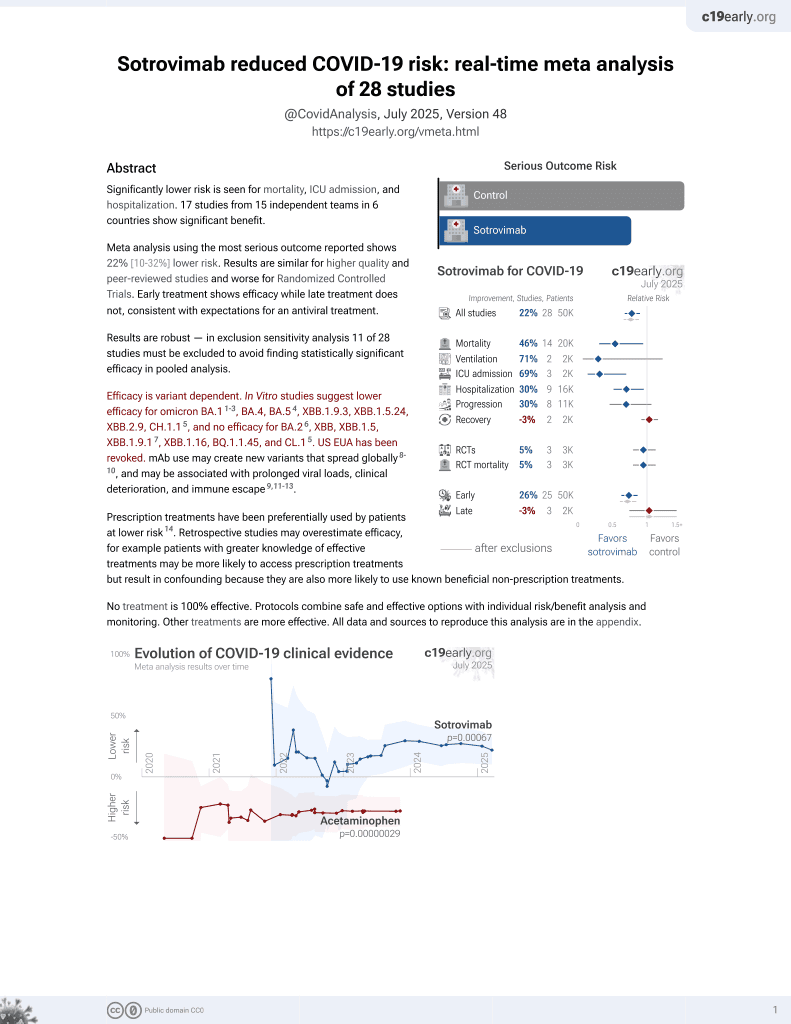
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Observational study of 521 outpatients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 showing paxlovid had stronger viral load reduction against Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 variants compared to sotrovimab, molnupiravir, and remdesivir, with the exception of comparable activity to molnupiravir against BA.2. There was no control group.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Mazzotta et al., 7 Oct 2022, Italy, peer-reviewed, median age 66.0, 25 authors.
Contact: valentina.mazzotta@inmi.it.
Viral load decrease in SARS‐CoV‐2 BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron sublineages infection after treatment with monoclonal antibodies and direct antiviral agents
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.28186
The efficacy on the Omicron variant of the approved early coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) therapies, especially monoclonal antibodies, has been challenged by in vitro neutralization data, while data on in vivo antiviral activity are lacking. We assessed potential decrease from Day 1 to Day 7 viral load (VL) in nasopharyngeal swabs of outpatients receiving Sotrovimab, Molnupiravir, Remdesivir, or Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for mild-to-moderate COVID-19 due to sublineages BA.1 or BA.2, and average treatment effect by weighted marginal linear regression models. A total of 521 patients (378 BA.1 [73%], 143 [27%] BA.2) received treatments (Sotrovimab 202, Molnupiravir 117, Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 84, and Remdesivir 118): median age 66 years, 90% vaccinated, median time from symptoms onset 3 days. Day 1 mean VL was 4.12 log2 (4.16 for BA.1 and 4.01 for BA.2). The adjusted analysis showed that Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir significantly reduced VL compared to all the other drugs, except versus Molnupiravir in BA.2. Molnupiravir was superior to Remdesivir in both BA.1 and BA.2, and to Sotrovimab in BA.2. Sotrovimab had better activity than
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST A. A. declares consultancy fees from Gilead Sciences, Merck, GSK, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, and research institutional grants from Gilead Sciences and the Italian Medicine Agency (AIFA). E. N. declares consultancy fees from Gilead Sciences, Eli-lilly, Roche and Sobi. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT Anonymized participant data will be made available upon reasonable requests directed to the corresponding author. Proposals will be reviewed and approved by investigator, and collaborators on the basis of scientific merit. After approval of a proposal, data can be shared through a secure online platform after signing a data access agreement.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section at the end of this article.
References
Arbel, Sagy, Hoshen, Oral Nirmatrelvir and Severe Covid-19 Outcomes During the Omicron Surge, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1705061/v1
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Bruel, Hadjadj, Maes, Serum neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages BA.1 and BA.2 in patients receiving monoclonal antibodies, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01792-5
Cameroni, Bowen, Rosen, Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2
Cao, Song, Wang, Characterizations of enhanced infectivity and antibody evasion of, Omicron BA, doi:10.1101/2022.07.18.500332
Cao, Wang, Jian, Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03796-6
Covariants, Overview of variants/mutations
Dejnirattisai, Huo, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-B.1.1.529 leads to widespread escape from neutralizing antibody responses, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, BLAZE-1 investigators. bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2102685
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Gottlieb, Vaca, Paredes, GS-US-540-9012 (PINETREE) investigators. early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116846
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Early treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107934
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, EPIC-HR investigators. oral nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4
Iketani, Liu, Guo, Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4
Islam, Hasan, Rahman, Islam, Comparative evaluation of authorized drugs for treating Covid-19 patients, health. Sci Rep, doi:10.1002/hsr2.671
Meschi, Colavita, Bordi, Performance evaluation of Abbott ARCHITECT SARS-CoV-2 IgG immunoassay in comparison with indirect immunofluorescence and virus microneutralization test, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104539
Meschi, Matusali, Colavita, Predicting the protective humoral response to a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine, Clin Chem Lab Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2021-0700
Mohapatra, Tiwari, Sarangi, Islam, Chakraborty et al., Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant of SARS-CoV-2: concerns, challenges, and recent updates, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27633
Nyberg, Ferguson, Nash, Comparative analysis of the risks of hospitalisation and death associated with SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and delta (B.1.617.2) variants in england: a cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7
Perchetti, Pepper, Shrestha, Performance characteristics of the abbott alinity m SARS-CoV-2 assay, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104869
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z
Sberna, Fabeni, Berno, Rapid and qualitative identification of SARS-CoV-2 mutations associated with variants of concern using a multiplex RT-PCR assay coupled with melting analysis, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.032
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against Covid-19 omicron variant, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2119407
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2201933
Vanderweele, Surrogate measures and consistent surrogates, Biometrics, doi:10.1111/biom.12071
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial investigators. REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
Wu, He, Geng, Sufficient conditions for concluding surrogacy based on observed data, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.4273
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28186",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.28186",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:label/><jats:p>The efficacy on the Omicron variant of the approved early coronavirus disease‐2019 (COVID‐19) therapies, especially monoclonal antibodies, has been challenged by in vitro neutralization data, while data on in vivo antiviral activity are lacking. We assessed potential decrease from Day 1 to Day 7 viral load (VL) in nasopharyngeal swabs of outpatients receiving Sotrovimab, Molnupiravir, Remdesivir, or Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir for mild‐to‐moderate COVID‐19 due to sublineages BA.1 or BA.2, and average treatment effect by weighted marginal linear regression models. A total of 521 patients (378 BA.1 [73%], 143 [27%] BA.2) received treatments (Sotrovimab 202, Molnupiravir 117, Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir 84, and Remdesivir 118): median age 66 years, 90% vaccinated, median time from symptoms onset 3 days. Day 1 mean VL was 4.12 log2 (4.16 for BA.1 and 4.01 for BA.2). The adjusted analysis showed that Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir significantly reduced VL compared to all the other drugs, except versus Molnupiravir in BA.2. Molnupiravir was superior to Remdesivir in both BA.1 and BA.2, and to Sotrovimab in BA.2. Sotrovimab had better activity than Remdesivir only against BA.1. Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir showed the greatest antiviral activity against Omicron variant, comparable to Molnupiravir only in the BA.2 subgroup. VL decrease could be a valuable surrogate of drug activity in the context of the high prevalence of vaccinated people and low probability of hospital admission.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.28186"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-07-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-09-26"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-10-07"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0240-7504",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
},
{
"name": "PhD course in Microbiology, Immunology, Infectious Diseases, and Transplants (MIMIT) University of Rome Tor Vergata Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mazzotta",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Clinical Research, Epidemiology, Modelling and Evaluation (CREME), UCL London UK"
}
],
"family": "Cozzi Lepri",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Colavita",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Rosati",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Lalle",
"given": "Eleonora",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Epidemiology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Cimaglia",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Paulicelli",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Mastrorosa",
"given": "Ilaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Vita",
"given": "Serena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fabeni",
"given": "Lavinia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6944-0686",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vergori",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Maffongelli",
"given": "Gaetano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Carletti",
"given": "Fabrizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Lanini",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Caraffa",
"given": "Emanuela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Milozzi",
"given": "Eugenia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Libertone",
"given": "Raffaella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7342-0263",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Epidemiology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Piselli",
"given": "Pierluca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Scientific Direction, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Girardi",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Garbuglia",
"given": "AnnaRosa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "General Direction, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Vaia",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Virology, National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Maggi",
"given": "Fabrizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Nicastri",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical and Research Infectious Diseases Department National Institute for Infectious Diseases Lazzaro Spallanzani IRCCS Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Antinori",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "INMI COVID‐19 Outpatient Treatment Study Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-03T06:53:05Z",
"timestamp": 1664779985000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-02T13:12:59Z",
"timestamp": 1719925979000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000780",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100000780",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "European Commission"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100003196",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Ministero della Salute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T02:15:41Z",
"timestamp": 1740104141007,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 18,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1665100800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.28186",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/jmv.28186",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.28186",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1",
"unstructured": "CoVariants. Overview of variants/mutations. April 4 2022.https://covariants.org/per-variant"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04389-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01792-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00462-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative evaluation of authorized drugs for treating Covid‐19 patients. health",
"author": "Islam T",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27633",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.0202",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104869",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104539",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2021-0700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/biom.12071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.4273",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1705061/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1",
"unstructured": "ArbelR SagyYW HoshenM et al. Oral Nirmatrelvir and Severe Covid‐19 Outcomes During the Omicron Surge. Research Square. [Preprint posted June 1 2022]. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1705061/v1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.07.18.500332",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1",
"unstructured": "CaoY SongW WangL et al. Characterizations of enhanced infectivity and antibody evasion of Omicron BA.2.75. 2022. bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2022.07.18.500332"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2022.06.23.22276509",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.28186"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Viral load decrease in SARS‐CoV‐2 BA.1 and BA.2 Omicron sublineages infection after treatment with monoclonal antibodies and direct antiviral agents",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "95"
}