An Independent Analysis of a Retrospective Cohort of 30,423 Covid-19 Patients Treated at IHU-Mediterranean in Marseille, France: Part 1, Efficacy of early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin
et al., Archives of Microbiology & Immunology, doi:10.26502/ami.936500153, Feb 2024
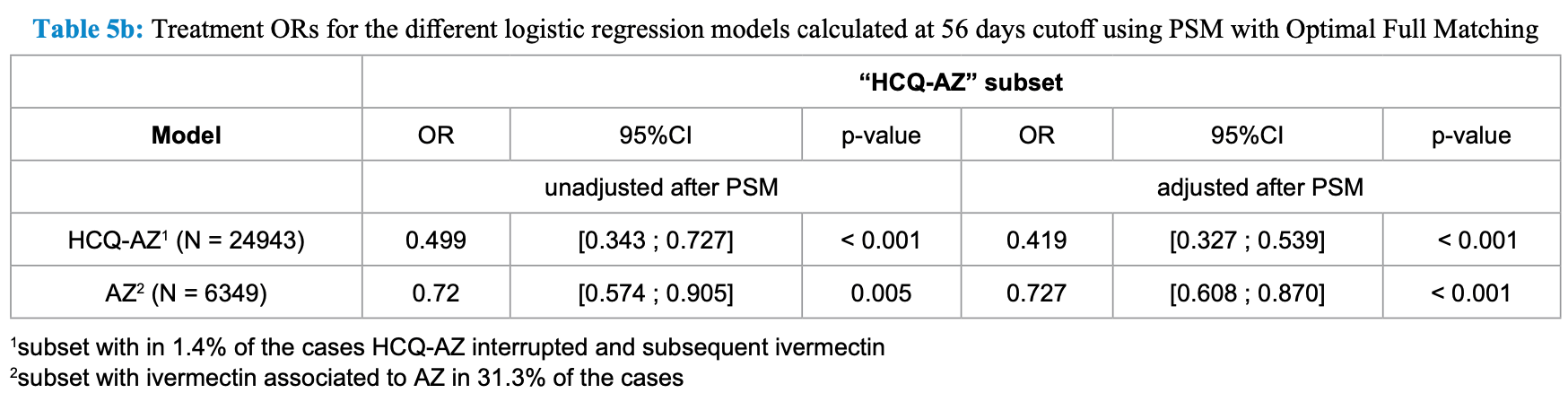
Independent analysis of the IHU-Mediterranean data1 with 30,423 COVID-19 patients showing significantly lower risk of ICU admission or death with early treatment of hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin (HCQ-AZ), and with azithromycin, both compared to no treatment.
|
risk of death/ICU, 27.3% lower, OR 0.73, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lounnas et al., 29 Feb 2024, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period March 2020 - December 2021.
An Independent Analysis of a Retrospective Cohort of 30,423 Covid-19 Patients Treated at IHU-Mediterranean in Marseille, France: Part 1, Efficacy of early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin
Archives of Microbiology & Immunology, doi:10.26502/ami.936500153
A cohort of 30, patients treated between March 2020 and December 2021 at the IHU-Méditerranée Infection in Marseille (France) was retrospectively analyzed in terms of treatment attempted and disease worsening factors to quantify efficacy with respect to the composite endpoint of transfer to intensive care unit or death, within a couple of months (56 days) from admission. Within limitations of the data and of the models, after adjustment for sampling biases, multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to determine unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios (ORs) for the subset of patients having received the combined treatment hydroxychloroquine plus azithromycin (HCQ-AZ) or no specific treatment (i.e. no HCQ, no AZ and no ivermectin (IVM)) (24,943 patients). An efficacy of 58% in reducing the risk of ICU transfer and death was measured (HCQ-AZ unadjusted OR = 0.499; 95%CI = [0.343; 0.727], p < 0.001) (HCQ-AZ adjusted OR = 0.419; 95%CI = [0.327; 0.539], p < 0.001). AZ without HCQ but associated with ivermectin in 31.3% of the cases was significantly active as well with respect to no specific treatment, with a measured efficacy of 27% (unadjusted OR = 0.720, 95% CI = [0.574; 0.905] p = 0.005 and adjusted OR = 0.727, 95%CI = [0.608; 0.870] p < 0.001). Interactions between HCQ-AZ and the model covariates were systematically explored. No interaction between HCQ-AZ treatment and vaccination was detected. Statistically significant favorable interactions were detected between HCQ-AZ treatment and male sex, age categories ≥ 50 years, the UK variant and when the variant was not determined, obesity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cancer, immunodeficiency, confirming the high efficacy of this early treatment. No statistically significant unfavorable interaction of HCQ-AZ with any covariate was detected. Limitations of the models and their implications for the results are discussed extensively.
References
Aa, Chloroquine analogues in drug discovery: new directions of uses, mechanisms of actions and toxic manifestations from malaria to multifarious diseases, J Antimicrob Chemother
Ader, Peiffer-Smadja, Poissy, An openlabel randomized, controlled trial of the effect of lopinavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir plus IFN-β-1a and hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: final results, Clin Microbiol Infect
Andreania, Bideaua, Duflota, In vitro testing of combined hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin on SARSCoV-2 shows synergistic effect, Microb Pathog
Anglemyer, Horvath, Bero, Healthcare outcomes assessed with observational study designs compared with those assessed in randomized trials, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Benson, Hartz, A Comparison of Observational Studies and Randomized, Controlled Trials, N Engl J Med
Borba, De, Val, Sampaio, Chloroquine diphosphate in two different dosages as adjunctive therapy of hospitalized patients with severe respiratory syndrome in the context of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection: Preliminary safety results of a randomized, double-blinded, phase IIb clinical trial (CloroCovid-19 Study)
Brooks, CloroCovid-19 trial of high-dose chloroquine halted early due to toxicity, deaths, Reuters Biotechnology
Brouqui, Million, Parola, Outcomes after early treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: An analysis of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients, New Microbes New Infect
Brouqui, Raoult, Construction, quality control and regulatory aspect of a database of 30,423 COVID-19 patients cared for at the IHU Méditerranée infection France, Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid19, New England Journal of Medicine
Chen, Liu, Li, A pilot study of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of patients with moderate COVID-19, Journal of Zhejiang University (Medical Sciences)
Cone, Padilla, Potts, Delirium in the elderly resulting from azithromycin therapy, Surg Neurol
Crowle, May, Inhibition of Tubercle Bacilli in Cultured Human Macrophages by Chloroquine Used Alone and in Combination with Streptomycin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, and Two Metabolites of Vitamin D3, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Deaton, Cartwright, Understanding and misunderstanding randomized controlled trials, Social Science & Medicine
Derendorf, Excessive lysosomal ion-trapping of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Derwand, Scholz, Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?, Medical Hypotheses
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients -early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: a retrospective case series study, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Zelenko, Statistical analysis methods applied to early outpatient COVID-19 treatment case series data, COVID
Greifer, Estimating Effects After Matching, Github
Ho, Imai, King, Matching as Nonparametric Preprocessing for Reducing Model Dependence in Parametric Causal Inference, Political Analysis
Lacout, Perronne, Lounnas, Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, The New England Journal of Medicine
Lagier, Million, Gautret, An Independent Analysis of a Retrospective Cohort of 30,423 Covid-19 Patients Treated at IHU-Mediterranean in Marseille, France: Part 1, Efficacy of early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin, Archives of Microbiology and Immunology
Liu, Cao, Xu, Wang, Zhang, Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro, Cell Discov
Lounnas, Azalbert, Oxford-Recovery: are the data hiding the deaths?, France Soir
Lounnas, Azalbert, Perronne, In reply to the Discovery trial report evaluating the potential benefit of hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir and ritonavir with and without interferon β-1a in hospitalized Covid-19 patients, Archives of Microbiology & Immunology
Lounnas, Lacout, Azalbert, Perronne, Revisiting a Meta-analysis Shows that Hydroxychloroquine with Azithromycin may be Efficient in Covid-19 patients, Archives of Microbiology & Immunology
Lounnas, Lacout, Azalbert, Perronne, Shunt due to Hydroxychloroquine Sub-lethal Dosage Resulted in Excess Transfer to Mechanical Ventilation and Death in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, Archives of Microbiology & Immunology
Mccullough, Alexander, Armstrong, Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Medical, World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects, JAMA
Million, Cortaredona, Delorme, Early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin: A 'Real-World' Monocentric Retrospective Cohort Study of 30,423 COVID-19 Patients, MedRXiv Withdrawn
Million, Lagier, Gautret, Early treatment of COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective analysis of 1061 cases in Marseille, France, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Million, Lagier, Tissot-Dupont, Early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin in 10,429 COVID-19 Outpatients: A Monocentric Retrospective Cohort Study, Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Million, Monocentric retrospective cohort of 30,423 COVID-19 patients, DRYAD
Neugebauer, Mvd, Why prefer double robust estimators in causal inference?, J Stat Plan Inference
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for highrisk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Early Ambulatory Multidrug Therapy Reduces Hospitalization and Death in High-Risk Patients with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), International Journal of Innovative Research in Medical Science
Sbidian, Josse, Lemaitre, Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin and in-hospital mortality or discharge in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 infection: a cohort study of 4,642 in-patients in France, MedRXiv Posted
Stuart, Matching methods for causal inference: A review and a look forward, Stat Sci
Stuart, Moving towards best practice when using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) using the propensity score to estimate causal treatment effects in observational studies, Stat Med
Sävje, Higgins, Sekhon, Generalized Full Matching
Sävje, Higgins, Sekhon, Generalized Full Matching, Political Analysis
Thomas, Furin at the cutting edge: from protein traffic to embryogenesis and disease, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Vincent, Bergeron, Benjannet, Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread, Virol J
Yao, Ye, Zhang, In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clinical Infectious Diseases
Zhao, Luo, Su, Zhang, Propensity score matching with R: conventional methods and new features, Ann Transl Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.26502/ami.936500153",
"ISSN": [
"2572-9365"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.26502/ami.936500153",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lounnas",
"given": "Valere",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gkioulekas",
"given": "Eleftherios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rendell",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacout",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azalbert",
"given": "Xavier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perronne",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Archives of Microbiology & Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Arch Microbiol Immunology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-16T07:07:27Z",
"timestamp": 1713251247000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-16T07:07:28Z",
"timestamp": 1713251248000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-17T00:47:21Z",
"timestamp": 1713314841504
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "01",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "01",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
}
},
"member": "11040",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.26502",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024
]
]
},
"publisher": "Fortune Journals",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.fortunejournals.com/articles/an-independent-analysis-of-a-retrospective-cohort-of-30423-covid19-patients-treated-at-ihumediterranean-in-marseille-france-part-1.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "An Independent Analysis of a Retrospective Cohort of 30,423 Covid-19 Patients Treated at IHU-Mediterranean in Marseille, France: Part 1, Efficacy of early Treatment with Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "08"
}
lounnas2